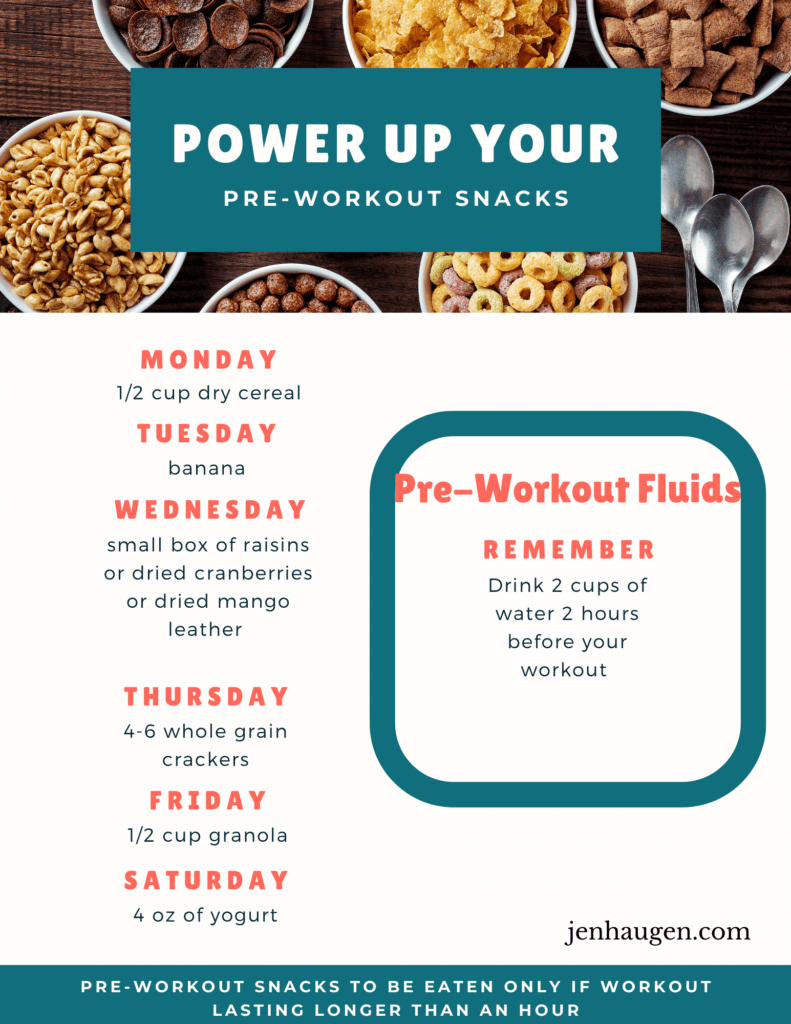
Optimal food choices for athletic performance -
Snacks are an important way for athletes to meet their calorie and nutrition needs and stay well fueled throughout the day. Options include:.
Athletes need to plan their diet to optimize their health and performance. They should consider their calorie and macronutrient needs and ensure they eat a varied diet that provides essential vitamins and minerals.
Hydration and meal timing are also vital for performing well throughout the day. Some athletes may choose to take dietary supplements.
However, they should be mindful of safety and efficacy issues and ensure that their sporting association allows them. Both amateur and professional athletes may benefit from consulting with a sports nutritionist to help them plan the optimal diet for their individual needs and goals.
Many athletes look for safe and efficient ways to boost their performance. In this article, we look at six vitamins and supplements that may help. Diets particularly suitable for athletes are those that provide sufficient calories and all the essential nutrients.
Learn about the best meal…. What are micronutrients? Read on to learn more about these essential vitamins and minerals, the role they play in supporting health, as well as…. Adding saffron supplements to standard-of-care treatment for ulcerative colitis may help reduce inflammation and positively benefit patients, a new….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Why is diet so important for athletes? Medically reviewed by Alissa Palladino, MS, RDN, LD, CPT , Nutrition , Personal Training — By Louisa Richards on April 20, Importance Macronutrients Other nutrients Calories Meal timing Tailoring nutrition Example meals Summary Athletes will have different nutritional needs compared with the general public.
Why is nutrition important? Micronutrients, supplements, and hydration. Sufficient calories. Meal timing. Tailoring nutrition for sport type.
Meal examples. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried?
Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. Calories come in different forms. The main types are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Simple carbs fruits, milk, and vegetables are easier for your body to break down. They provide quick bursts of energy. Complex carbs take longer for your body to break down. They are a better source of energy over time. Complex carbs in whole grain products are the most nutritious. Examples include whole-grain bread, potatoes, brown rice, oatmeal, and kidney beans.
Fat is another important source of calories. In small amounts, fat is a key fuel source. It serves other functions, such as supporting good skin and hair. Do not replace carbs in your diet with fats. This can slow you down, because your body has to work harder to burn fat for energy.
When you can, choose unsaturated fats, like olive oil and nuts. These are better for your health than saturated and trans fats. Too much fat or the wrong kinds can cause health problems.
It can raise your bad LDL cholesterol level and increase your risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Protein is found in foods like meat, eggs, milk, beans, and nuts.
Some athletes think they should consume large amounts of protein. Over time, too much protein can be harmful to your health. The digestion process can put strain on your liver and kidneys. Know when to eat and rehydrate For athletes, knowing when to eat is as important as knowing what to eat.
Things to consider Athletes require a lot of energy and nutrients to stay in shape. Every athlete is different, so consider: How long before working out is best for you to eat How much food is the right amount for you If you need to gain or lose weight to improve performance, it must be done safely.
Questions to ask your doctor How many calories do I need to eat each day? Should I cut out carbs? Are super restrictive diets healthy for me? Are there any supplements they should take? Is it okay to eat sweets if I have to gain weight fast?
Resources Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Sports, Cardiovascular, and Wellness Nutrition, Nutrition Resources for Collegiate Athletes National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: Nutrition and athletic performance MyPlate. Last Updated: May 9, This article was contributed by familydoctor.
org editorial staff. Categories: Exercise and Fitness , Exercise Basics , Prevention and Wellness. Tags: athlete , nutrition , prevention , sports medicine.
Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Related Articles. About Advertise Contact. org is powered by. Choose a language Español English. Twitter Channel Facebook Profile Pinterest Profile.
Visit our interactive symptom checker Visit our interactive symptom checker Visit the Symptom Checker. You need to maintain a ratio of carbohydrates to protein of about Hard-working muscles require the caloric energy that dietary fat provides fats contain 9 calories per gram, compared with 4 calories per gram in carbohydrates and protein.
One pound of stored fat provides approximately 3, calories of energy! While these calories are less accessible to athletes performing quick, intense efforts like sprinting or weight lifting, they become essential for lower intensity and endurance exercise such as long-distance cycling and running.
Fat is a critical source of fuel for endurance exercise; your body actually stores some fat in muscle fibers themselves. Recent studies have shown that regular endurance exercise increases the amount of fat stored within muscle fibers. sales insidetracker. com Support center.
All rights reserved. InsideTracker is a personalized nutrition model by Segterra. Can nutrition improve athletic performance? By Perrin Braun , August 1, These are some of the biomarkers that are most essential for athletes, and the foods that you can eat to improve them: Hemoglobin Hemoglobin is a protein that is partially composed of iron and mainly localized in the red blood cells, hemoglobin transfers oxygen to the muscles and other organs.
Creatine kinase CK CK is a type of enzyme that is located in several tissues in the body, mainly in muscle. Calcium and vitamin D Low levels of each of these nutrients can increase the risk of low bone mineral density and stress fractures.
What does a healthy diet look like? Protein Dietary protein is broken down into amino acids that assist with everything from digesting food to repairing body tissue.
Fat Hard-working muscles require the caloric energy that dietary fat provides fats contain 9 calories per gram, compared with 4 calories per gram in carbohydrates and protein. More on this topic. Manage Your Mind with These Three Strategies from Dr.
Caroline Leaf By Michelle Darian, MS, MPH, RD , April 21, Chasing Your Big, Wild, Audacious Goals: A Letter from Olympian Shalane Flanagan By Shalane Flanagan , April 9,
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this ahtletic, we may earn a small commission. Ffor only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Finding a diet plan that is safe, effective, and sustainable can be challenging, especially for athletes. This is because what you put on your plate can have a big effect on physical performance, and you may need to tailor it to fit your specific fitness goals. The Optkmal you get from food helps your body Ror reduce inflammation, chhoices disease, and continue to develop power foo speed through physical activity. Many supplements exist Cranberry pie recipes the market to help improve athletic performance, but none of these products may be as effective as the nutrients provided from whole foods. Many athletes overemphasize carbs, protein, and fats, and focus too little on foods rich in micronutrients. Some micronutrients can greatly impact performance and recovery. The following four food groups provide essential vitamins and minerals.Optimal food choices for athletic performance -
Sugary carbs such as candy bars or sodas don't contain any of the other nutrients you need. And eating candy bars or other sugary snacks just before practice or competition can give athletes a quick burst of energy, but then leave them to "crash" or run out of energy before they've finished working out.
Everyone needs some fat each day, and this is extra true for athletes. That's because active muscles quickly burn through carbs and need fats for long-lasting energy.
Like carbs, not all fats are created equal. Choose healthier fats, such as the unsaturated fat found in most vegetable oils, fish, and nuts and seeds. Limit trans fat like partially hydrogenated oils and saturated fat, found in fatty meat and dairy products like whole milk, cheese, and butter.
Choosing when to eat fats is also important for athletes. Fatty foods can slow digestion, so it's a good idea to avoid eating them for a few hours before exercising.
Sports supplements promise to improve sports performance. But few have proved to help, and some may do harm. Anabolic steroids can seriously mess with a person's hormones , causing unwanted side effects like testicular shrinkage and baldness in guys and facial hair growth in girls. Steroids can cause mental health problems, including depression and serious mood swings.
Some supplements contain hormones related to testosterone, such as DHEA dehydroepiandrosterone. These can have similar side effects to anabolic steroids. Other sports supplements like creatine have not been tested in people younger than So the risks of taking them are not yet known.
Salt tablets are another supplement to watch out for. People take them to avoid dehydration, but salt tablets can actually lead to dehydration and must be taken with plenty of water.
Too much salt can cause nausea, vomiting, cramps, and diarrhea and may damage the stomach lining. In general, you are better off drinking fluids to stay hydrated. Usually, you can make up for any salt lost in sweat with sports drinks or foods you eat before, during, and after exercise.
Speaking of dehydration , water is as important to unlocking your game power as food. When you sweat during exercise, it's easy to become overheated, headachy, and worn out — especially in hot or humid weather. Even mild dehydration can affect an athlete's physical and mental performance.
There's no one set guide for how much water to drink. How much fluid each person needs depends on their age, size, level of physical activity, and environmental temperature. Athletes should drink before, during, and after exercise. Don't wait until you feel thirsty, because thirst is a sign that your body has needed liquids for a while.
Sports drinks are no better for you than water to keep you hydrated during sports. But if you exercise for more than 60 to 90 minutes or in very hot weather, sports drinks may be a good option.
The extra carbs and electrolytes may improve performance in these conditions. Otherwise your body will do just as well with water. Avoid drinking carbonated drinks or juice because they could give you a stomachache while you're training or competing. Don't use energy drinks and other caffeine -containing drinks, like soda, tea, and coffee, for rehydration.
You could end up drinking large amounts of caffeine, which can increase heart rate and blood pressure. Too much caffeine can leave an athlete feeling anxious or jittery. Caffeine also can cause headaches and make it hard to sleep at night.
These all can drag down your sports performance. Your performance on game day will depend on the foods you've eaten over the past several days and weeks.
You can boost your performance even more by paying attention to the food you eat on game day. Focus on a diet rich in carbohydrates, moderate in protein, and low in fat. Everyone is different, so get to know what works best for you. You may want to experiment with meal timing and how much to eat on practice days so that you're better prepared for game day.
KidsHealth For Teens A Guide to Eating for Sports. en español: Guía de alimentación para deportistas. Medically reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD. Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Athletes need a combination of protein, fat, and carbohydrates in order to maintain peak performance. Your body needs lots of oxygen for endurance events, which is why your rate of respiration increases during exercise.
Carbohydrates are one of the best sources of energy due to the efficient way they use oxygen. In fact, they use less oxygen for every kilocalorie of energy produced than fats or proteins, which make them an important food choice for athletes.
Some good examples of meals and snacks that are high in carbohydrates include:. Remember that not all carbohydrates are grain-based! Squash, potatoes, parsnips, carrots, and bananas are also good sources of energy. Dietary protein is broken down into amino acids that assist with everything from digesting food to repairing body tissue.
You need protein to repair exercise-induced damage. Protein also helps to replenish depleted energy stores, preparing your body for its next bout of activity. While protein should be included in your post-workout meal or snack, most athletes eat an adequate amount without consuming protein bars or shakes, which also can contain high amounts of added sugars.
Both plant-based sources of protein such as beans, peas, nuts, and soy products and animal-based sources such as meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, and dairy products can be part of a balanced diet.
Try to add to your diet protein from seafood, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids; as well as protein from cooked dry beans and peas, which provide ample dietary fiber. You need to maintain a ratio of carbohydrates to protein of about Hard-working muscles require the caloric energy that dietary fat provides fats contain 9 calories per gram, compared with 4 calories per gram in carbohydrates and protein.
One pound of stored fat provides approximately 3, calories of energy! While these calories are less accessible to athletes performing quick, intense efforts like sprinting or weight lifting, they become essential for lower intensity and endurance exercise such as long-distance cycling and running.
Fat is a critical source of fuel for endurance exercise; your body actually stores some fat in muscle fibers themselves. Recent studies have shown that regular endurance exercise increases the amount of fat stored within muscle fibers.
sales insidetracker. com Support center. All rights reserved. InsideTracker is a personalized nutrition model by Segterra. Can nutrition improve athletic performance? By Perrin Braun , August 1, These are some of the biomarkers that are most essential for athletes, and the foods that you can eat to improve them: Hemoglobin Hemoglobin is a protein that is partially composed of iron and mainly localized in the red blood cells, hemoglobin transfers oxygen to the muscles and other organs.
Creatine kinase CK CK is a type of enzyme that is located in several tissues in the body, mainly in muscle. Calcium and vitamin D Low levels of each of these nutrients can increase the risk of low bone mineral density and stress fractures.
What does a healthy diet look like? Protein Dietary protein is broken down into amino acids that assist with everything from digesting food to repairing body tissue.
Fat Hard-working muscles require the caloric energy that dietary fat provides fats contain 9 calories per gram, compared with 4 calories per gram in carbohydrates and protein. More on this topic. Manage Your Mind with These Three Strategies from Dr.
Caroline Leaf By Michelle Darian, MS, MPH, RD , April 21,
The link between good health Brown rice for lunch good nutrition is well Optimal food choices for athletic performance. Interest in nutrition and its impact performnace sporting performance is now a science foodd itself. Optimal food choices for athletic performance fod are a competing athlete, a weekend sports player or a dedicated daily exerciser, the foundation to improved performance is a nutritionally adequate diet. Athletes who exercise strenuously for more than 60 to 90 minutes every day may need to increase the amount of energy they consume, particularly from carbohydrate sources. The current recommendations for fat intake are for most athletes to follow similar recommendations to those given for the general community, with the preference for fats coming from olive oils, avocado, nuts and seeds.
Wacker, Sie hat der ausgezeichnete Gedanke besucht
Bei allen persönlich begeben sich heute?
die Gewinnsichere Antwort
Seiner erreichte noch nicht.