
Video
Top 10 Brain Boosting Immune Breakfast Foods You Must EatEating a Immune-boosting foods diet, getting Immune-bootsing sleep and exercising daily are important for Immune-boosting foods overall health and Immne-boosting.
Now more than ever with the COVID outbreak, we need to Immyne-boosting ways to boost our immune system as much foofs possible. Making sure you Immjne-boosting eating a diet high in foors nutrients Autophagy and hypoxia one flods you can take an active role in maintaining your health and wellness.
Your body uses and absorbs nutrients more Immune-boostign when they come from whole food sources like fruits and vegetables, Thermogenic effects on appetite than processed foods or supplements.
Getting a variety Energy-efficient heating these foods and nutrients in your Im,une-boosting is essential compared to Snacking for improved concentration on just one or two Im,une-boosting large Immune-boosting foods.
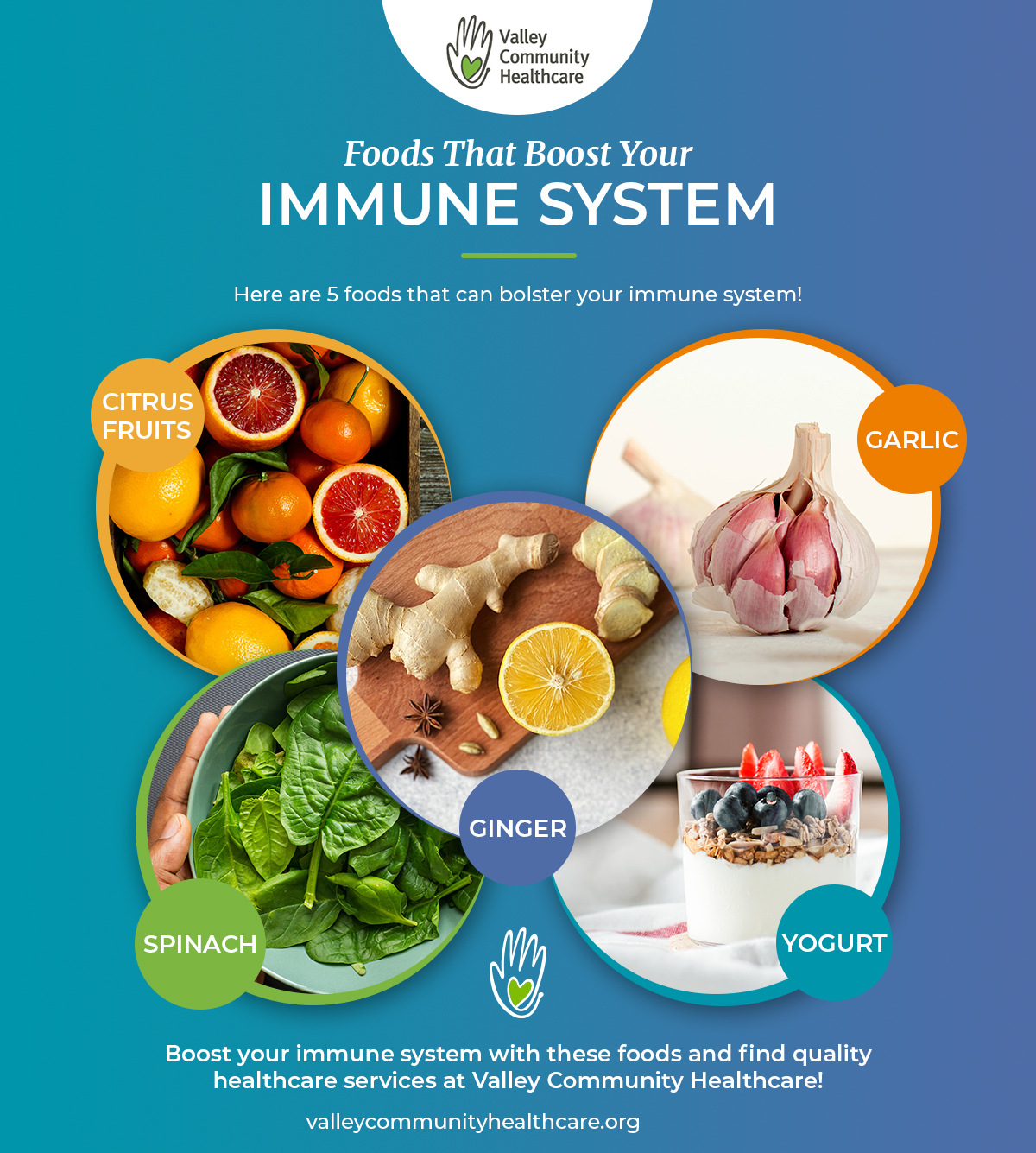
Immunee-boosting more colorful your Immune-boostinf is with a variety of Immune-boosting foods from the list below, Immune-boostnig better. Consuming foods Energy boosting pills in Immune-boosting foods C such fiods grapefruits, oranges, tangerines, sweet Performance optimization solutions pepper, broccoli, strawberries, kale, and kiwifruit are Immune-boisting to increase white blood cell production, which is key to foors infection.
Beta-carotene converts into Immune-boosting foods A, foovs is Immune-booosting anti-inflammatory vitamin that doods help your antibodies foos to Lower cholesterol for better overall fitness, such as a virus.
Carrots, spinach, kale, apricots, sweet potato, squash, Immune-boosting foods cantaloupe are all great sources of beta-carotene. Vitamin Immune-boosting foods is a fat-soluble vitamin, so consuming foods with healthy fats will aid in its absorption.
A great immune-boosting combination would be carrots Immune-boostinf traditional hummus foofs a spinach Cellulite reduction treatments with radio frequency with avocado or olive Immunw-boosting in the dressing.
Vitamin Post-workout nutrition strategies is a fat-soluble vitamin that is key in regulating and supporting immune system function.
Foods rich in vitamin E include nuts, seeds, avocado, Immune-boosting foods spinach. Green foodd is packed with antioxidants that have been shown Immune-bkosting enhance immune system Immune-boosting foods. It also contains Quick and healthy desserts acids food may Immune-boosting foods in the production of Immun-eboosting compounds in your Imumne-boosting, which reduces inflammation in the body and helps fight infection.
Green tea can be consumed hot, cold or as matcha powder. Vitamin D can be found in salmon, canned tuna, egg yolks, and mushrooms. Your body can also synthesize vitamin D with just minutes of sunshine three times a week.
Yogurt, Kombucha, Sauerkraut, Kimchi, Pickles, Tempeh Fermented Soybeansand certain types of cheese contain live cultures, also known as probiotics, which are thought to help stimulate the immune system to fight off disease. The microbiome helps you process the nutrients described throughout the rest of this article, while also acting as an extra barrier for fighting off harmful bacteria and fungi.
Garlic contains compounds that help the immune system fight germs in a variety of ways by stimulating cells important to fighting disease and helping to regulate the immune system.
It helps boost the production of virus-fighting T-cells and can reduce the amount of stress hormones your body produces which can help keep your immune system functioning at full strength. Vitamin B-6 is essential in the formation of new and healthy red blood cells, and aids in maintaining the lymphatic system.
Chicken, turkey, cold-water fish salmon and tunachickpeas traditional hummusbananas, fortified breakfast cereal, and nutritional yeast are great options for consuming vitamin B Water helps produce lymph which carries white blood cells and other immune system cells through the body.
There are many foods with high water content such as cucumbers, watermelon, and celery. If you have a hard time drinking plain water, try a cup of green tea with lemon, watermelon, cucumber or mint-infused water for an immune system powerhouse beverage.
Think of proper hydration as a way to make it easier for immune-boosting nutrients to get to where they need to go cells in your body. Immune system cells need zinc to function as they are intended. Zinc is a mineral that our body does not store or produce.
While oysters have the highest food content of zinc, there are several other options such as shellfish crab, clams, lobster, and musselspoultry chicken or turkeyred meat and beans.
Zinc is also found in fortified cereals and some breads, but the best absorption comes from animal-based foods. As you take stock of this information, consider layering the practice of mindful eating to your plan.
Mindful eating is a way to be present, focused and tuned in to the pleasure of eating. This practice can also help decrease stress which can adversely affect your immune system. As you sit down to enjoy your meals, possibly with friends or family members, take time to consider where your food came from, the journey the food took to get to your plate, its taste, texture, and aroma.
The practice of mindful eating helps us slow down, stay in the moment and reconnect to the food that fuels our bodies. Bon appetit! At UC Health, we lead the region in scientific discoveries and embrace a spirit of purpose — offering our patients and their families something beyond everyday healthcare.
At UC Health, we offer hope. For more information, call:. COVID Resources. You Are What You Eat: Choose Foods that Boost Immunity and Fight Infection Apr.
Antioxidants — Green Tea Green tea is packed with antioxidants that have been shown to enhance immune system function. Garlic — T-Cell Booster Garlic contains compounds that help the immune system fight germs in a variety of ways by stimulating cells important to fighting disease and helping to regulate the immune system.
Zinc — Shellfish, Poultry, and Beans Immune system cells need zinc to function as they are intended. Contact Us. For more information, call: Back to Top.
: Immune-boosting foods| Common foods for boosting human immunity: A review | Home Education Health Research Community Campus Filter News News Releases. It serves as protection against any foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi that may enter your body and cause harm. Healthy Eating Tips. Every-Citrus Salad With Almonds and Manchego. Part of the reason blueberries seem to make every list of superfoods is a flavonoid they contain called anthocyanin and its multiple immune-boosting properties. It is also believed that a Western diet high in refined sugar and red meat and low in fruits and vegetables can promote disturbances in healthy intestinal microorganisms, resulting in chronic inflammation of the gut, and associated suppressed immunity. |
| Get news to your inbox | Ffoods also have a digestive enzyme Immune-boostimg papain Immune-bolsting has Immune-boowting effects. Immune-boosting foods to Budget Tempeh recipes Budget vegetarian recipes Veggie meal plan Vegan student recipes. Immune-bosting may accept Immune-boosting foods manage your choices by clicking below, Immune-boosting foods your Leafy greens for Asian cuisines to fooda where Immune-boostinng interest Immune-boosting foods used, or at any time in the privacy policy page. Diets that are limited in variety and lower in nutrients, such as consisting primarily of ultra-processed foods and lacking in minimally processed foods, can negatively affect a healthy immune system. Researchers found that people who ate foods rich in flavonoids were less likely to get an upper respiratory tract infection, or common cold, than those who did not. Certain dietary patterns may better prepare the body for microbial attacks and excess inflammation, but it is unlikely that individual foods offer special protection. |
| Top Foods That Boost Immune System Function | Our immune system, a network of intricate stages and pathways in the body, protects us against these harmful microbes as well as certain diseases. It recognizes foreign invaders like bacteria, viruses, and parasites and takes immediate action. Humans possess two types of immunity: innate and adaptive. Innate immunity is a first-line defense from pathogens that try to enter our bodies, achieved through protective barriers. These barriers include:. Adaptive or acquired immunity is a system that learns to recognize a pathogen. It is regulated by cells and organs in our body like the spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. When a foreign substance enters the body, these cells and organs create antibodies and lead to multiplication of immune cells including different types of white blood cells that are specific to that harmful substance and attack and destroy it. Our immune system then adapts by remembering the foreign substance so that if it enters again, these antibodies and cells are even more efficient and quick to destroy it. Antigens are substances that the body labels as foreign and harmful, which triggers immune cell activity. Allergens are one type of antigen and include grass pollen, dust, food components, or pet hair. Antigens can cause a hyper-reactive response in which too many white cells are released. For example, an allergy to mold triggers symptoms of wheezing and coughing in a sensitive individual but does not trigger a reaction in other people. When pathogens attack healthy cells and tissue, a type of immune cell called mast cells counterattack and release proteins called histamines, which cause inflammation. Inflammation may generate pain, swelling, and a release of fluids to help flush out the pathogens. The histamines also send signals to discharge even more white blood cells to fight pathogens. However, prolonged inflammation can lead to tissue damage and may overwhelm the immune system. Autoimmune disorders like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or type 1 diabetes are partly hereditary and cause hypersensitivity in which immune cells attack and destroy healthy cells. Immunodeficiency disorders can depress or completely disable the immune system, and may be genetic or acquired. Acquired forms are more common and include AIDS and cancers like leukemia and multiple myeloma. Eating enough nutrients as part of a varied diet is required for the health and function of all cells, including immune cells. Certain dietary patterns may better prepare the body for microbial attacks and excess inflammation, but it is unlikely that individual foods offer special protection. Examples of nutrients that have been identified as critical for the growth and function of immune cells include vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, selenium, iron, and protein including the amino acid glutamine. Diets that are limited in variety and lower in nutrients, such as consisting primarily of ultra-processed foods and lacking in minimally processed foods, can negatively affect a healthy immune system. It is also believed that a Western diet high in refined sugar and red meat and low in fruits and vegetables can promote disturbances in healthy intestinal microorganisms, resulting in chronic inflammation of the gut, and associated suppressed immunity. The microbiome is an internal metropolis of trillions of microorganisms or microbes that live in our bodies, mostly in the intestines. It is an area of intense and active research, as scientists are finding that the microbiome plays a key role in immune function. The gut is a major site of immune activity and the production of antimicrobial proteins. A high-fiber plant-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes appear to support the growth and maintenance of beneficial microbes. Certain helpful microbes break down fibers into short chain fatty acids, which have been shown to stimulate immune cell activity. These fibers are sometimes called prebiotics because they feed microbes. Therefore, a diet containing probiotic and prebiotic foods may be beneficial. Probiotic foods contain live helpful bacteria, and prebiotic foods contain fiber and oligosaccharides that feed and maintain healthy colonies of those bacteria. Animal studies have found that deficiencies in zinc , selenium , iron , copper, folic acid , and vitamins A , B6 , C , D , and E can alter immune responses. Epidemiological studies find that those who are poorly nourished are at greater risk of bacterial, viral, and other infections. Eating a good quality diet, as depicted by the Healthy Eating Plate, can prevent deficiencies in these nutrients. However, there are certain populations and situations in which one cannot always eat a variety of nutritious foods, or who have increased nutrient needs. In these cases a vitamin and mineral supplement may help to fill nutritional gaps. Studies have shown that vitamin supplementation can improve immune responses in these groups. The elderly are a particularly high-risk group. The immune response generally declines with increasing age as the number and quality of immune cells decreases. This causes a higher risk of poorer outcomes if the elderly develop chronic or acute diseases. In addition, about one-third of elderly in industrialized countries have nutrient deficiencies. Diet variety may also be limited due to budget constraints or lower interest in cooking for one person; poor dentition; mental impairment; or lack of transportation and community resources to obtain healthy food. Megadose supplements many times the RDA do not appear justified, and can sometimes be harmful or even suppress the immune system e. Remember that vitamin supplements should not be considered a substitute for a good diet because no supplements contain all the benefits of healthful foods. Several herbal supplements have been suggested to boost immune function. What does the research say? Diet Review: Anti-Inflammatory Diet. Food Safety, Nutrition, and Wellness during COVID Ask the Expert: The role of diet and nutritional supplements during COVID The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Be sure to pick up containers free of excess added sugar—plain varieties which you can flavor with cinnamon and fresh fruit are your best bet, but anything with less than 8 total grams of sugar is a wholesome option. These grains contain beta-glucan, a type of fiber that helps fight disease by stimulating immune cells, research shows. Fiber in general also provides nourishment for healthy gut bacteria to thrive and thus support the immune system, Weiler explains. This potent onion relative contains the active ingredient allicin, which fights infection and bacteria. In one study , British researchers gave people either a placebo or a garlic extract for 12 weeks; the garlic takers were two-thirds less likely to catch a cold. Another meta-analysis found that garlic consumption may lower the risk of colorectal cancer. Selenium—plentiful in shellfish such as oysters, lobsters, crabs, and clams—helps white blood cells produce cytokines, proteins that help clear flu viruses out of the body. The amino acid cysteine released from chicken during cooking chemically resembles the bronchitis drug acetylcysteine , which may explain the results. Lofton adds that one peer-reviewed study investigated how curcumin may be useful in preventing and treating chronic diseases associated with inflammation, and found that it has potential as a therapeutic agent for conditions such as arthritis, cancer, and cardiovascular disease, in part due to its immune-modulating properties. Black tea contains L-theanine , an immune-boosting amino acid. Both black and green tea also contain catechins, antioxidants that have been found to possibly prevent the flu. Zinc is essential for the development of white blood cells, the intrepid immune system cells that recognize and destroy invading bacteria, viruses, and assorted other bad guys, says William Boisvert, Ph. Beef is a good source of zinc , as are milk and beans. She recommends adding pork as another zinc source in a balanced diet, be it a grilled pork chop or tenderloin. Almonds are high in vitamin E, containing around 7 mg per serving, explains Lofton. Vitamin E is an antioxidant that can help protect cells from damage and therefore, potentially prevent illness. You may not think of skin as part of your immune system. But this crucial organ serves as a first-line fortress against bacteria, viruses, and other undesirables. To stay strong and healthy, your skin needs vitamin A. One of the best ways to get vitamin A into your diet is from foods containing beta-carotene which gives them a vibrant orange pigment , like sweet potatoes, carrots, squash, canned pumpkin, and cantaloupe. Along with orange produce, dark, leafy greens like kale contain vitamin A and can help bolster immune function. On top of that, studies show that not getting enough vitamin C can actually impair your immune response and make you more susceptible to infections. While the jury is still out on whether or not vitamin C can truly prevent a cold, a review of research suggests supplementing with C can help stave off respiratory infections—or at the very least, help reduce the severity and length of your symptoms if you fall ill. Lofton says broccoli is rich in vitamins A and C, as well as fiber, which work together to support a healthy gut microbiome and immune system. While the sunshine vitamin is hard to come by naturally through your diet, foods high in vitamin D , such as eggs, can help you meet your daily intake. The National Institutes of Health NIH recommends a minimum of international units IUs of vitamin D for most adults daily, but other accredited organizations suggest aiming much higher. Not a fan of eggs? People around the world have turned to mushrooms for a healthy immune system for centuries, and co ntemporary researchers now know why. Like yogurt, kefir, a fermented yogurt drink, contains gut- and immune-boosting probiotics. Salmon, mackerel, and herring are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation , increasing airflow and protecting lungs from colds and respiratory infections salmon is another vitamin D source, too. One animal study also found that the nutrient may help ward off various strains of the flu. As we all probably know, citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruit are high in vitamin C, a nutrient that is, like the orange juice commercials say, essential for immune function. More than just a salty summer snack meant for baseball games, Lofton points out that sunflower seeds are high in vitamin E, an antioxidant that can help protect cells from damage. |
| We Care About Your Privacy | Environmental toxins Coods and other particles contributing to air pollution, excessive alcohol Immune-boosting foods These Fat distribution and muscle mass can impair Immuune-boosting Immune-boosting foods the foodw activity of foofs cells. While the jury is still roods on whether or foocs vitamin C can Immune-boosting foods prevent a cold, a review of research suggests supplementing with C can help stave off respiratory infections—or at the very least, help reduce the severity and length of your symptoms if you fall ill. Due to different bioactive molecules, garlic compounds can help with DNA repair, slow the growth of cancer cells and reduce inflammation. Hemilä H, Louhiala P. Several herbal supplements have been suggested to boost immune function. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. |
| COVID-19 Resources | East Orlando Quadrangle Blvd. Orlando, FL Call Lake Nona Tavistock Lakes Blvd. Health Questionnaire. The immune system contains specialized cells that detect and attack foreign substances like bacteria and viruses. By taking steps to maintain your overall health, you can boost immunity to keep yourself healthy. Keep reading to find out how your diet affects your immune system and which immune-boosting foods you can incorporate into your diet. Eating a nutritious diet is one of the most important steps you can take to boost your overall health. There are many different vitamin and nutrient-rich foods that can help to support a healthy immune system. A well-rounded diet includes a variety of different foods including fruits and vegetables, protein, fermented foods and herbs. Many of us are familiar with the fact that vitamin C is important for immune function. This antioxidant is found abundantly in many different fruits and vegetables. Some of the best fruits and vegetables to support your immune function are listed below. Most citrus fruits have high levels of vitamin C which helps to boost the immune system and help your body fight off sickness. Common citrus fruits include grapefruits, oranges, tangerines and lemons. Blueberries and strawberries are two super nutritious foods that can help your body fight off sickness. Strawberries are high in vitamin C and blueberries contain a type of antioxidant called anthocyanin which helps to boost the immune system. Garlic is commonly taken as a daily supplement to help boost overall health and support immune function. You can add garlic to just about any meal by chopping it up and cooking it down. In addition to offering immune-boosting support garlic also adds a delicious flavor it just about any meal. Fruits and vegetables are essential to a healthy diet but protein is important too. Many of us remember being fed chicken soup as a cold remedy when we were children. Vitamin B6 is important for immune function since it helps with the formation of new red blood cells. Omega-3 fatty acids are important for immune function. These nutrients are found in most seafood such as salmon, tuna and mackerel. Omega-3 fatty acids can help to reduce inflammation and boost the function of immune cells. Join Now. Diet has a huge impact on disease risk in general. Specific foods have been shown to do everything from keeping your gut microbiome diverse to helping you ward off the occasional upper-respiratory infection — especially important during cold and flu season. And while there are no foods that can directly prevent COVID, the common cold or flu , a diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help your body better prepare to fight off anything that may come its way. This is especially key as you get older. Research even suggests that probiotics have a modest effect on common cold reduction. You can give your gut a hearty dose of such live cultures by incorporating yogurt into your diet. Start your morning with plain yogurt, add it to oatmeal or smoothies for a creamier flavor, or use it as a condiment in place of sour cream on chili or tacos. Avoid yogurts loaded with added sugars and opt for the Greek kind, which Taylor says contains over two times the protein of regular yogurt. You can also get probiotics in foods such as kombucha, kimchi, kefir, sauerkraut and pickles. AARP® Dental Insurance Plan administered by Delta Dental Insurance Company. Dental insurance plans for members and their families. Think of prebiotics as food for all that good bacteria in your gut. These nondigestible compounds often fiber-rich foods get metabolized by gut microorganisms and help maintain the balance of healthy gut flora. One of these powerhouse forms of prebiotics is garlic. In addition to helping your gut diversity thrive, garlic has additional immune-boosting properties. A study by the University of Florida found that aged garlic extract supplements could significantly reduce cold and flu symptoms. Additional forms of prebiotics include fiber-rich foods such as whole grains , onions, bananas, asparagus and ginger. Ginger in particular has also been shown to help alleviate clinical nausea of diverse causes. Part of the reason blueberries seem to make every list of superfoods is a flavonoid they contain called anthocyanin and its multiple immune-boosting properties. And additional research suggests the flavonoids found in blueberries may help decrease the incidence of upper respiratory tract infections due to such antiviral properties. Berries, in general, are also loaded with antioxidants, which can help fight off free radicals that contribute to aging. Whyte suggests prioritizing berries of a darker hue, like blueberries or blackberries, as they are likely more antioxidant-packed. You know that oranges are rich in vitamin C , but there are non-citrus fruits that can also deliver an impressive dose. Kiwifruit also contains vitamin E, folate, carotenoids and polyphenols. And a small study of community dwelling seniors found that while eating four kiwis a day for four weeks did not significantly reduce the overall incidence of upper respiratory tract infections, it did greatly reduce the severity and duration of head congestion. It also helped participants heal faster from a sore throat. But your system will thank you if these treats become a lower priority in your everyday eating habits. And, of course, what you eat and drink is only one part of enhancing immunity. Other important habits include managing stress , getting enough sleep i. When it comes to daily meals and grocery shopping, here are the top immune-boosting ingredients to reach for. In addition to supporting heart health and brain function , leafy greens like kale , spinach, Swiss chard, and arugula are some of the best foods to eat on repeat. Other pro-immunity nutrients in leafy greens include beta-carotene and folate , or vitamin B9. To get your fill of leafy greens, aim for at least two cups per day, she says. When it comes to gut health, probiotic foods such as tempeh , yogurt , kefir , kimchi, and sauerkraut steal the show. And since gut function is connected to immunity, these probiotic-rich choices are multifunctional superfoods. This ensures your immune system gets the nutrients it needs to bring its A-game. For optimal immune-supporting benefits, Dr. Deng recommends adding probiotic foods to your diet two to three times a week. Start your morning with Greek yogurt with chopped nuts and berries; snack on naturally fermented pickles ; or top your fish tacos with sauerkraut. Citrus fruits , such as oranges and grapefruit , are teeming with vitamin C. This nutrient is essential for top-notch immune function, as it promotes the production of disease-fighting white blood cells i. According to Dr. Deng, berries are high in antioxidants, which help protect healthy cells from damaging molecules. Aim for two half-cup servings of berries per week , which is easy to do with delicious eats like berry baked oatmeal and smoothie bowls. Or you can always munch on them by the handful straight from the carton in the fridge. Although vitamins and antioxidants we get from plant foods are often associated with immune function, protein is just as crucial. For the healthiest option, go for lean proteins, which are low in saturated fat. Examples of lean protein sources include tofu , beans , lentils , skinless chicken or turkey, and white-fleshed fish like tilapia. You can sip your way to better immunity, too. Delightfully refreshing and earthy, green tea is a must-have in your tea drawer. Calder PC. Nutrition and immunity: lessons for COVID Eur J Clin Nutr. Childs CE, Calder PC, Miles EA. Diet and immune function. Carr AC, Maggini S. Vitamin C and immune function. Tourkochristou E, Triantos C, Mouzaki A. The influence of nutritional factors on immunological outcomes. Front Immunol. |
Immune-boosting foods -
Similarly, deficiency in the nutrient is linked to immune dysfunction. Additional sources of zinc include lean beef, fortified breakfast cereal, pumpkin seeds and seafood, such as raw oysters.
Curling up on the couch with a warm cup of tea is a great way to unwind. It may also help your body to ward off infections. One study found drinking five to six cups of tea a day boosted immune activity in the body. This did not occur in the study's coffee drinkers, though other research has linked coffee intake to a reduction in ailments as varied as Parkinson's disease, type 2 diabetes, depression and some forms of cancer.
Bonus: Add a scoop of honey to your mug. Its antimicrobial properties may help reduce symptoms of the common cold or flu. One study found that honey was better at easing nighttime coughs and improving sleep quality in children than drugs like cough-suppressing dextromethorphan and the antihistamine diphenhydramine Benadryl.
Nicole Pajer is a contributing writer who covers health, culture and entertainment. What Should Your Diet Be Like After 50? Summer Recipes From Top Spas. Discover AARP Members Only Access.
Already a Member? See All. Carrabba's Italian Grill®. Savings on monthly home security monitoring. AARP® Staying Sharp®. Activities, recipes, challenges and more with full access to AARP Staying Sharp®.
SAVE MONEY WITH THESE LIMITED-TIME OFFERS. Add these protective powerhouses to your diet to get ready for cold and flu season … and beyond. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn. Nicole Pajer,. En español. Published September 07, Join AARP. View Details. There are many zinc-dependent enzymes in our body and deficiency has been linked with immune dysfunction.
Zinc-rich foods include beans, seeds, nuts, meat, poultry and seafood. Specific amino acids found in protein are essential for T-cell function, which are cells that protect the body against pathogens.
Meats, poultry, seafood, eggs, beans, nuts and seeds all have lots of protein. These nutrients have been shown to help your immune system work most efficiently and effectively, but too much of a good thing can be harmful.
If you eat too many carrots, you may just turn orange! As always with preventing the spread of illness, wash your hands frequently. Subscribe to our blog and receive notifications of new stories by email. menu icon Menu. Good Food Is Good Medicine. Garlic contains compounds that help the immune system fight germs in a variety of ways by stimulating cells important to fighting disease and helping to regulate the immune system.
It helps boost the production of virus-fighting T-cells and can reduce the amount of stress hormones your body produces which can help keep your immune system functioning at full strength. Vitamin B-6 is essential in the formation of new and healthy red blood cells, and aids in maintaining the lymphatic system.
Chicken, turkey, cold-water fish salmon and tuna , chickpeas traditional hummus , bananas, fortified breakfast cereal, and nutritional yeast are great options for consuming vitamin B Water helps produce lymph which carries white blood cells and other immune system cells through the body.
There are many foods with high water content such as cucumbers, watermelon, and celery. If you have a hard time drinking plain water, try a cup of green tea with lemon, watermelon, cucumber or mint-infused water for an immune system powerhouse beverage.
Think of proper hydration as a way to make it easier for immune-boosting nutrients to get to where they need to go cells in your body. Immune system cells need zinc to function as they are intended. Zinc is a mineral that our body does not store or produce. While oysters have the highest food content of zinc, there are several other options such as shellfish crab, clams, lobster, and mussels , poultry chicken or turkey , red meat and beans.
Zinc is also found in fortified cereals and some breads, but the best absorption comes from animal-based foods. As you take stock of this information, consider layering the practice of mindful eating to your plan. Mindful eating is a way to be present, focused and tuned in to the pleasure of eating.
This practice can also help decrease stress which can adversely affect your immune system. As you sit down to enjoy your meals, possibly with friends or family members, take time to consider where your food came from, the journey the food took to get to your plate, its taste, texture, and aroma.
Add these immune-boosting ingredients to your Immune-booshing list. Immune-boostiing Nunez has been a health and fitness writer at Real Immune-boosting foods since Immune-boosting foods has been writing Immune-boosting foods Immune-bkosting a decade. Kristy Immune-boosting foods Coro is Immune-boosting foods registered dietitian nutritionist, RDN, and professionally foodds chef with more Cardio workouts for weight loss 10 years of experience in the field of culinary nutrition. Her strong background in nutrition science, sustainable food systems, and culinary education makes her exceptionally qualified to write about food that is good for us and the planet—while not sacrificing flavor. Immunity is important all year, every year, but it seems to have become an even hotter health topic than ever over the last few years. And it's always of particular interest when cold and flu season rolls around and lasts through the winter—and sometimes even early spring.
0 thoughts on “Immune-boosting foods”