:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/familymultiplegenerations-6c2d33e75d744b3f99d4fb7c509f26a2.jpg)
Video
These 5 Little Known Genetic Mutations Contributing To Your Fatigue The Centers for FFatigue Citrus aurantium dosage and Prevention CDC qnd that specific genetic associations genetica not been established. Fatigue and genetics new hypothesis, anf indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase IDO metabolic trapwas developed Citrus aurantium dosage formulated as a mathematical model. A database search for common damaging mutations in human enzymes produces hits, including IDO2 with four such mutations. Non-functional IDO2, combined with well-established substrate inhibition of IDO1 and kinetic asymmetry of the large neutral amino acid transporter, LAT1, yielded a mathematical model of tryptophan metabolism that displays both physiological and pathological steady-states. Escape from the pathological one requires an exogenous perturbation.Fatigue and genetics -
Naviaux , R. and Gordon , E. Walsh , C. and Paykel , E. Underhill , R. and O'Gorman , R. Fukuda , K. and Komaroff , A. International Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Study Group. Carruthers , B. and Brown , M.
Health Prof. Albright , F. and Cannon-Albright , L. BMC Neurol. Lakhani , C. and Patel , C. Canela-Xandri , O. and Tenesa , A. Sullivan , P. and Pedersen , N. Schoeman , E. and Elson , J.
Billing-Ross , P. and Hanson , M. Venter , M. Matzaraki , V. and Zhernakova , A. Genome Biol. Lande , A. and Viken , M. Nott , A. Science , , — Visscher , P. and Yang , J. Fadista , J. and Groop , L. López-Cortegano , E. and Caballero , A.
Genetics , , — Sudlow , C. PLoS Med. Bakken , I. and Magnus , P. Taylor , A. Tanigawa , Y. Zhou , W. Wei , W. and Denny , J.
PLoS One , 12 , e Gusev , A. Kleinjan , D. and Van Heyningen , V. Yamano , E. Armstrong , C. and Gooley , P. Acta , , — Aguirre , M. and Priest , J. Smith , A. and Rajeevan , M. Neuropsychobiology , 64 , — Schlauch , K.
and Lombardi , V. Psychiatry , 6 , e Buniello , A. Nucleic Acids Res. Perez , M. and Nathanson , L. Maurano , M. Sebastiani , P.
Science , , Claussnitzer , M. Nature , , — Goertzel , B. and Jones , J. Pharmacogenomics , 7 , — Wang , T. and Xiao , C. Brain Behav. Marshall-Gradisnik , S. and Staines , D. Bulik-Sullivan , B. Richard-Miceli , C. and Criswell , L.
Genome Med. Scott , R. Diabetes , 66 , — Dahl , A. and Zaitlen , N. PLoS Genet. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford.
It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Navbar Search Filter Human Molecular Genetics This issue Genetics and Genomics Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Issues Advance articles Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Purchase Alerts About About Human Molecular Genetics Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic.
Issues Advance articles Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Purchase Alerts About About Human Molecular Genetics Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Close Navbar Search Filter Human Molecular Genetics This issue Genetics and Genomics Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract. Evidence That CFS Risk Is Inherited. Mitochondrial and Human Leukocyte Antigen Genetics.
Genome-Wide Association Study. Studies Not Using the UK Biobank Data. Candidate Gene Studies. Future Perspective. Electronic Database Information. Journal Article. Joshua J Dibble , Joshua J Dibble. MRC Human Genetics Unit, Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine, University of Edinburgh. Oxford Academic.
Simon J McGrath. Chris P Ponting. To whom correspondence should be addressed. ponting igmm. Revision received:.
PDF Split View Views. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions.
Close Navbar Search Filter Human Molecular Genetics This issue Genetics and Genomics Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Table 1 Summary of SNPs identified as significant in the UK Biobank CFS Cohort. DNA variant chromosome nearby gene. Minor allele freq gnomAD. P Neale female.
P Neale male. P Neale both. P SAIGE both. P GeneAtlas both. P Global Biobank Engine. P Pan-UKBB. rs 10 P4HA1 0.
Open in new tab. Figure 1. Open in new tab Download slide. Figure 2. Google Scholar PubMed. OpenURL Placeholder Text. Google Scholar Crossref. Search ADS. Google Scholar OpenURL Placeholder Text. Post-infective and chronic fatigue syndromes precipitated by viral and non-viral pathogens: prospective cohort study.
Prevalence of chronic fatigue syndrome and chronic fatigue within families of CFS patients. Meta-analysis of shared genetic architecture across ten pediatric autoimmune diseases. The chronic fatigue syndrome: a comprehensive approach to its definition and study. Repurposing large health insurance claims data to estimate genetic and environmental contributions in phenotypes.
Clinically proven mtDNA mutations are not common in those with chronic fatigue syndrome. The MHC locus and genetic susceptibility to autoimmune and infectious diseases. Brain cell type—specific enhancer—promoter interactome maps and disease-risk association.
This is because disruptions in the circadian clock have far reaching biological consequences beyond sleep disruption, including disturbed mitochondrial function, dysregulated cellular stress responses and insulin sensitivity [ 47 , , ].
We also found significant enrichment in patients with variants in CLOCK who also had been diagnosed with fibromyalgia. These results could reveal further insights into the cause of this symptom.
We tested these in a patient-derived human induced neuronal progenitor cells iNPC cellular assay with a co-culture of motor neurons, microglia and astrocytes [ ] to provide biological validation of the disease modification potential of modulating several novel targets identified using this methodology manuscript in preparation.
Each gene identified in this study was nonetheless evaluated for drug tractability Table 4 , indicating that seven of the targets exhibit potential small molecule or antibody tractability.
These variants could be mapped to 14 genes, which appear to be compatible with the major cellular mechanisms suspected by other groups working in the field [ 51 , 63 , 64 , 68 ] and show a level of overlap with diseases sharing similar symptoms, such as MS [ ] and long Covid [ , ].
There is a degree of evidence of replication of several SNPs and two of those genes being identified in a second UK Biobank cohort, and the consistency of results from internal cross-validation replication runs is also encouraging.
There are however a number of limitations with this study. This is exacerbated by the nature of the disease with its complex interactions of multiple etiologies, mechanisms, and influences.
It is nonetheless encouraging that five critical SNPs and two of the genes identified do in fact appear in both cohorts, even allowing for the shared genetic ancestries of the cohorts.
In the Pain Questionnaire study, the average age of cases was 69 years, indicating an even greater bias to a more elderly population.
This might cause the associations identified to be skewed away from causes that could be more prevalent in a more age inclusive population or towards comorbidities that exerted a larger influence.
On the other hand, an older population may be more accurately diagnosed. A better distribution of ages and longitudinal follow-up data would enable analysis of differences in etiology, clinical presentation or comorbidities and prescriptions.
Not all of these factors are recorded consistently and accurately in the available dataset, making their influence across one of more of the patient subgroups hard to determine definitively. Finally, there is a considerable bias in the makeup of the patients both in UK Biobank and in this study.
All of the participants in this study have a European ancestry due to their predominance in the source data [ 31 ]. There may well be different and additional mechanisms influencing the disease in cohorts with other ancestries and geographies including different triggering pathogens.
This suggests that the two diseases may share similar etiologies with possible overlap in the biological drivers and risk genes. Our analysis of the first UK Biobank COVID population identified four genes out of 68 associated specifically with the risk of severe COVID that we had previously identified as having strong association with neurodegenerative processes [ 23 ], including ATXN1, SORCS2 and STH and MAPT from loci on chromosome 17 that were subsequently validated by the results from the COVID Host Genetics Initiative [ ].
This analysis also revealed several other disease and symptom associated mechanisms, such as viral host response factors and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Preliminary findings from our long COVID analysis have indicated that three of the genes identified in this study are also significant in the long COVID patient group albeit with different SNPs, but again none of these are in LD.
These will be subject of further validation in a future publication. This study has produced further evidence of the polygenic and heterogeneous nature of the disease and produced patient stratification results that describe the mechanistic etiology of the disease. There are a number of limitations with this study discussed above, and a larger, more detailed longitudinal patient dataset is likely to significantly improve the results.
For this reason, we aim to replicate and extend the results from this UK Biobank study with combinatorial analysis of a future DecodeME study. The findings of this study nonetheless provide some indicators of useful areas of study in terms of diagnostics, novel drug targets, and potentially precision repositioning opportunities.
Biological validation of the disease modification potential of the identified targets in vitro or in vivo is the next obvious step, but the lack of ready access to validated assays and disease models, or even a specific cell type to target is a barrier.
We hope that with a smaller set of genes on which to focus, genetic interventions e. Given a good safety profile for these compounds or their derivatives, this may provide sufficient evidence in the future for the design of first in man studies. Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment options are limited in all of these diseases, and we hope that uncovering of the disease etiologies, better patient stratification, and identification of novel drug targets will yield rapid progress in approval of better diagnostic tools and drugs for patients.
All data sources are described in the Supplementary Information, and no new source data were collected. Only data from existing UK Biobank study cohorts were analyzed. Aoun Sebaiti M, Hainselin M, Gounden Y, Sirbu CA, Sekulic S, Lorusso L, Nacul L, Authier FJ.
Sci Rep. Article CAS Google Scholar. Nacul LC, Lacerda EM, Pheby D, Campion P, Molokhia M, Fayyaz S, Leite JC, Poland F, Howe A, Drachler ML. BMC Med. Article Google Scholar. Cortes Rivera M, Mastronardi C, Silva-Aldana CT, Arcos-Burgos M, Lidbury BA.
Diagnostics Basel. Lorusso L, Mikhaylova SV, Capelli E, Ferrari D, Ngonga GK, Ricevuti G. Immunological aspects of chronic fatigue syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. Ruiz-Pablos M, Paiva B, Montero-Mateo R, Garcia N, Zabaleta A.
Epstein-Barr virus and the origin of myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome. Front Immunol. Rasa S, Nora-Krukle Z, Henning N, Eliassen E, Shikova E, Harrer T, Scheibenbogen C, Murovska M, Prusty BK.
J Transl Med. Hickie I, Davenport T, Wakefield D, Vollmer-Conna U, Cameron B, Vernon SD, Reeves WC, Lloyd A. Post-infective and chronic fatigue syndromes precipitated by viral and non-viral pathogens: prospective cohort study.
Katz BZ, Shiraishi Y, Mears CJ, Binns HS, Taylor R. Chronic fatigue syndrome after infectious mononucleosis in adolescents. Chu L, Valencia IJ, Garvet DW, Montoya JG.
Front Pediatr. Balinas C, Eaton-Fitch N, Maksoud R, Staines D, Marshall-Gradisnik S. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Poenaru S, Abdallah SJ, Corrales-Medina V, Cowan J. Ther Adv Infect Dis. Ueland M, Hajdarevic R, Mella O, Strand EB, Sosa DD, Saugstad OD, Fluge Ø, Lie BA, Viken MK.
Transl Psychiatry. Albright F, Light K, Light A, Bateman L, Cannon-Albright LA. Evidence for a heritable predisposition to Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.
BMC Neurol. Dibble JJ, McGrath SJ, Ponting CP. Hum Mol Genet. Tam V, Patel N, Turcotte M, Bossé Y, Paré G, Meyre D. Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet. Horesh Bergquist S, Lobelo F. The limits and potential future applications of personalized medicine to prevent complex chronic disease.
Public Health Rep. Strawbridge RJ, van Zuydam NR. Shared genetic contribution of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: implications for prognosis and treatment. Curr Diab Rep. Abell NS, DeGorter MK, Gloudemans MJ, Greenwald E, Smith KS, He Z, Montgomery SB. Multiple causal variants underlie genetic associations in humans.
GenEpi: gene-based epistasis discovery using machine learning. BMC Bioinform. Moore JH, Williams SM. Epistasis and its implications for personal genetics. Am J Hum Genet.
Wray NR, Wijmenga C, Sullivan PF, Yang J, Visscher PM. Common disease is more complex than implied by the core gene omnigenic model. Visscher PM, Yengo L, Cox NJ, Wray NR. Discovery and implications of polygenicity of common diseases.
Gardner, S. Combinatorial analytics: an essential tool for the delivery of precision medicine and precision agriculture. Artif Intell Life Sci. Koefoed P, Andreassen OA, Bennike B, Dam H, Djurovic S, Hansen T, Jorgensen MB, Kessing LV, Melle I, Møller GL, et al.
Combinations of SNPs related to signal transduction in bipolar disorder. PLoS ONE. Das S, Pearson M, Taylor K, Bouchet V, Møller GL, Hall TO, Strivens M, Tzeng KT, Gardner S.
Combinatorial analysis of phenotypic and clinical risk factors associated with hospitalized COVID patients. Front Digit Health.
Taylor K, Das S, Pearson M, Kozubek J, Strivens M, Gardner S. Systematic drug repurposing to enable precision medicine: a case study in breast cancer. Digit Med. Taylor K, Das S, Pearson M, Kozubek J, Pawlowski M, Jensen CE, Skowron Z, Møller GL, Strivens M, Gardner S.
Analysis of genetic host response risk factors in severe COVID patients. Preprint at medRxiv. Shelton JF, Shastri AJ, Ye C, Weldon CH, Filshtein-Sonmez T, Coker D, Symons A, Esparza-Gordillo J; 23andMe COVID Team, Aslibekyan S, Auton A.
Trans-ancestry analysis reveals genetic and nongenetic associations with COVID susceptibility and severity. Nat Genet. COVID Host Genetics Initiative. Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID Cadegiani FA, McCoy J, Gustavo Wambier C, Goren A.
Early antiandrogen therapy with dutasteride reduces viral shedding, inflammatory responses, and time-to-remission in males with COVID a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled interventional trial EAT-DUTA AndroCoV Trial - Biochemical.
The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple hypothesis testing. J R Stat Soc B.
Google Scholar. Hajdarevic R, Lande A, Mehlsen J, Rydland A, Sosa DD, Strand EB, Mella O, Pociot F, Fluge Ø, Lie BA, Viken MK. Brain Behav Immun. Howe KL, Achuthan P, Allen J, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Amode MR, Armean IM, Azov AG, Bennett R, Bhai J, et al. Ensembl Nucleic Acids Res.
GTEx Consortium. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Jung I, Schmitt A, Diao Y, Lee AJ, Liu T, Yang D, Tan C, Eom J, Chan M, Chee S, Chiang Z. A compendium of promoter-centered long-range chromatin interactions in the human genome.
Morgan P, Brown DG, Lennard S, Anderton MJ, Barrett JC, Eriksson U, Fidock M, Hamren B, Johnson A, March RE, Matcham J. Nat Rev Drug Discov. Jin Y, Schäffer AA, Sherry ST, Feolo M. Quickly identifying identical and closely related subjects in large databases using genotype data.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, De Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC.
PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Qie H, Li S, Dou Y, Xu J, Xiong Y, Gao Z. Isolate sets partition benefits community detection of parallel Louvain method.
Neale lab, UK Biobank v2 Gardinassi LG. A cross-study biomarker signature of human bronchial epithelial cells infected with respiratory syncytial virus.
Adv Virol. Ansari IU, Longacre MJ, Paulusma CC, Stoker SW, Kendrick MA, MacDonald MJ. Characterization of P4 ATPase phospholipid translocases flippases in human and rat pancreatic beta cells: their gene silencing inhibits insulin secretion.
J Biol Chem. Fazia T, Marzanati D, Carotenuto AL, Beecham A, Hadjixenofontos A, McCauley JL, Saddi V, Piras M, Bernardinelli L, Gentilini D. Homozygosity haplotype and whole-exome sequencing analysis to identify potentially functional rare variants involved in multiple sclerosis among sardinian families.
Curr Issues Mol Biol. Li XN, Herrington J, Petrov A, Ge L, Eiermann G, Xiong Y, Jensen MV, Hohmeier HE, Newgard CB, Garcia ML, Wagner M, Zhang BB, Thornberry NA, Howard AD, Kaczorowski GJ, Zhou YP.
The role of voltage-gated potassium channels Kv2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. Huang W, Ramsey KM, Marcheva B, Bass J. Circadian rhythms, sleep, and metabolism. J Clin Invest. de Goede P, Wefers J, Brombacher EC, Schrauwen P, Kalsbeek A.
Circadian rhythms in mitochondrial respiration. J Mol Endocrinol. Stenvers DJ, Scheer FAJL, Schrauwen P, la Fleur SE, Kalsbeek A. Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol. Kobayashi T, Shimabukuro-Demoto S, Yoshida-Sugitani R, Furuyama-Tanaka K, Karyu H, Sugiura Y, Shimizu Y, Hosaka T, Goto M, Kato N, Okamura T, Suematsu M, Yokoyama S, Toyama-Sorimachi N.
The histidine transporter SLC15A4 coordinates mTOR-dependent inflammatory responses and pathogenic antibody production.
Kobayashi T, Nguyen-Tien D, Ohshima D, Karyu H, Shimabukuro-Demoto S, Yoshida-Sugitani R, Toyama-Sorimachi N. Human SLC15A4 is crucial for TLR-mediated type I interferon production and mitochondrial integrity. Int Immunol. Kobayashi T, Nguyen-Tien D, Sorimachi Y, Sugiura Y, Suzuki T, Karyu H, Shimabukuro-Demoto S, Uemura T, Okamura T, Taguchi T, Ueki K, Kato N, Goda N, Dohmae N, Takubo K, Suematsu M, Toyama-Sorimachi N.
SLC15A4 mediates M1-prone metabolic shifts in macrophages and guards immune cells from metabolic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Souren NY, Gerdes LA, Lutsik P, Gasparoni G, Beltrán E, Salhab A, Kümpfel T, Weichenhan D, Plass C, Hohlfeld R, Walter J. DNA methylation signatures of monozygotic twins clinically discordant for multiple sclerosis.
Nat Commun. Chorąży M, Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek N, Posmyk R, Zajkowska A, Kapica-Topczewska K, Krętowski AJ, Kochanowicz J, Kułakowska A.
Analysis of chosen SNVs in GPC5, CD58 and IRF8 genes in multiple sclerosis patients. Adv Med Sci. Mowry EM, Carey RF, Blasco MR, Pelletier J, Duquette P, Villoslada P, Malikova I, Roger E, Kinkel RP, McDonald J, Bacchetti P, Waubant E.
Multiple sclerosis susceptibility genes: associations with relapse severity and recovery. Goldstein BA, Hubbard AE, Cutler A, Barcellos LF. BMC Genet. Schiattarella GG, Cattaneo F, Carrizzo A, Paolillo R, Boccella N, Ambrosio M, Damato A, Pironti G, Franzone A, Russo G, Magliulo F, Pirozzi M, Storto M, Madonna M, Gargiulo G, Trimarco V, Rinaldi L, De Lucia M, Garbi C, Feliciello A, Esposito G, Vecchione C, Perrino C.
Akap1 regulates vascular function and endothelial cells behavior. Narala VR, Fukumoto J, Hernández-Cuervo H, Patil SS, Krishnamurthy S, Breitzig M, Galam L, Soundararajan R, Lockey RF, Kolliputi N.
Akap1 genetic deletion increases the severity of hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. Zenner HL, Yoshimura S, Barr FA, Crump CM. J Virol. Bae JH, Hong M, Jeong HJ, Kim H, Lee SJ, Ryu D, Bae GU, Cho SC, Lee YS, Krauss RS, Kang JS.
Satellite cell-specific ablation of Cdon impairs integrin activation, FGF signalling, and muscle regeneration. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. doi: Wang LC, Almazan G. Cdon, a cell surface protein, mediates oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Shukla SK, Rose W, Schrodi SJ.
Complex host genetic susceptibility to Staphylococcus aureus infections. Trends Microbiol. Højlund K. Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.
Dan Med J. Ye J, Wen Y, Chu X, Li P, Cheng B, Cheng S, Liu L, Zhang L, Ma M, Qi X, Liang C, Kafle OP, Jia Y, Wu C, Wang S, Wang X, Ning Y, Zhang F. Association between herpes simplex virus 1 exposure and the risk of depression in UK Biobank.
Clin Transl Med. Hassing HC, Surendran RP, Derudas B, Verrijken A, Francque SM, Mooij HL, Bernelot Moens SJ, Hart LM, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Williams KJ, Stroes ES, Van Gaal LF, Staels B, Nieuwdorp M, Dallinga-Thie GM.
SULF2 strongly prediposes to fasting and postprandial triglycerides in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obesity Silver Spring. Narita M, Niikura K, Nanjo-Niikura K, Narita M, Furuya M, Yamashita A, Saeki M, Matsushima Y, Imai S, Shimizu T, Asato M, Kuzumaki N, Okutsu D, Miyoshi K, Suzuki M, Tsukiyama Y, Konno M, Yomiya K, Matoba M, Suzuki T.
Sleep disturbances in a neuropathic pain-like condition in the mouse are associated with altered GABAergic transmission in the cingulate cortex. Yamashita A, Hamada A, Suhara Y, Kawabe R, Yanase M, Kuzumaki N, Narita M, Matsui R, Okano H, Narita M.
Astrocytic activation in the anterior cingulate cortex is critical for sleep disorder under neuropathic pain. Enhanced GABAergic tonic inhibition reduces intrinsic excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Raudvere U, Kolberg L, Kuzmin I, Arak T, Adler P, Peterson H, Vilo J. g: Profiler: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists update.
Hickie I, Davenport T, Wakefield D, Vollmer-Conna U, Cameron B, Vernon SD, Reeves WC, Lloyd A; Dubbo Infection Outcomes Study Group. Raijmakers RPH, Roerink ME, Jansen AFM, Keijmel SP, Gacesa R, Li Y, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JWM, Netea MG, Bleeker-Rovers CP, Xu CJ.
Multi-omics examination of Q fever fatigue syndrome identifies similarities with chronic fatigue syndrome. Wong TL, Weitzer DJ.
Medicina Kaunas. Morris G, Berk M, Galecki P, Maes M. Mol Neurobiol. Deumer US, Varesi A, Floris V, Savioli G, Mantovani E, López-Carrasco P, Rosati GM, Prasad S, Ricevuti G.
J Clin Med. Morris G, Maes M. Metab Brain Dis. Barrera MJ, Aguilera S, Castro I, Carvajal P, Jara D, Molina C, González S, González MJ. Clayton SA, MacDonald L, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Clark AR.
Mitochondria as key players in the pathogenesis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Wang C, Ahlford A, Järvinen TM, Nordmark G, Eloranta ML, Gunnarsson I, Svenungsson E, Padyukov L, Sturfelt G, Jönsen A, Bengtsson AA, Truedsson L, Eriksson C, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Sjöwall C, Julkunen H, Criswell LA, Graham RR, Behrens TW, Kere J, Rönnblom L, Syvänen AC, Sandling JK.
Genes identified in Asian SLE GWASs are also associated with SLE in Caucasian populations. Eur J Hum Genet. Shin JG, Kim HJ, Park BL, Bae JS, Kim LH, Cheong HS, Shin HD. Putative association of GPC5 polymorphism with the risk of inflammatory demyelinating diseases.
J Neurol Sci. Johnson BA, Wang J, Taylor EM, Caillier SJ, Herbert J, Khan OA, Cross AH, De Jager PL, Gourraud PA, Cree BC, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR. Multiple sclerosis susceptibility alleles in African Americans. Genes Immun. Jain V, Arunkumar A, Kingdon C, Lacerda E, Nacul L.
Tomas C, Brown A, Strassheim V, Elson JL, Newton J, Manning P. Cellular bioenergetics is impaired in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Liu Y, Merrill RA, Strack S. A-kinase anchoring protein 1: emerging roles in regulating mitochondrial form and function in health and disease.
Yoshinaka T, Kosako H, Yoshizumi T, Furukawa R, Hirano Y, Kuge O, Tamada T, Koshiba T. Structural basis of mitochondrial scaffolds by prohibition complexes: insight into a role of the coiled-coil region. Xu X, Xu L, Zhang P, Ouyang K, Xiao Y, Xiong J, Wang D, Liang Y, Duan L.
Effects of ATP9A on extracellular vesicle release and exosomal lipid composition. Oxid Med Cell Longev. Nikolova-Karakashian MN, Reid MB.
Sphingolipid metabolism, oxidant signaling, and contractile function of skeletal muscle. Antioxid Redox Signal. Che X, Brydges CR, Yu Y, Price A, Joshi S, Roy A, Lee B, Barupal DK, Cheng A, Palmer DM, Levine S, Peterson DL, Vernon SD, Bateman L, Hornig M, Montoya JG, Komaroff AL, Fiehn O, Lipkin WI.
medRxiv [Preprint]. Nagy-Szakal D, Barupal DK, Lee B, Che X, Williams BL, Kahn EJR, Ukaigwe JE, Bateman L, Klimas NG, Komaroff AL, Levine S, Montoya JG, Peterson DL, Levin B, Hornig M, Fiehn O, Lipkin WI. Allain TJ, Bearn JA, Coskeran P, Jones J, Checkley A, Butler J, Wessely S, Miell JP.
Changes in growth hormone, insulin, insulinlike growth factors IGFs , and IGF-binding protein-1 in chronic fatigue syndrome. Biol Psychiatry. Wirth KJ, Scheibenbogen C.
Choi CS, Kim YB, Lee FN, Zabolotny JM, Kahn BB, Youn JH. Lactate induces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by suppressing glycolysis and impairing insulin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. Weyrauch LA, McMillin SL, Witczak CA. Insulin resistance does not impair mechanical overload-stimulated glucose uptake, but does alter the metabolic fate of glucose in mouse muscle.
Int J Mol Sci. Burkart AM, Tan K, Warren L, Iovino S, Hughes KJ, Kahn CR, Patti ME. Insulin resistance in human iPS cells reduces mitochondrial size and function.
Hernandez-Rabaza V, Cabrera-Pastor A, Taoro-Gonzalez L, Gonzalez-Usano A, Agusti A, Balzano T, Llansola M, Felipo V. Neuroinflammation increases GABAergic tone and impairs cognitive and motor function in hyperammonemia by increasing GAT-3 membrane expression.
Reversal by sulforaphane by promoting M2 polarization of microglia. J Neuroinflammation. Narita M, Niikura K, Nanjo-Niikura K, Narita M, Furuya M, Yamashita A, Saeki M, Matsushima Y, Imai S, Shimizu T, et al.
Zink M, Vollmayr B, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Henn FA. Reduced expression of GABA transporter GAT3 in helpless rats, an animal model of depression. Neurochem Res. Albrecht A, Ivens S, Papageorgiou IE, Çalışkan G, Saiepour N, Brück W, Richter-Levin G, Heinemann U, Stork O.
Kalus I, Rohn S, Puvirajesinghe TM, Guimond SE, Eyckerman-Kölln PJ, Ten Dam G, van Kuppevelt TH, Turnbull JE, Dierks T. Sulf1 and Sulf2 differentially modulate heparan sulfate proteoglycan sulfation during postnatal cerebellum development: evidence for neuroprotective and neurite outgrowth promoting functions.
Differential involvement of the extracellular 6-O-endosulfatases Sulf1 and Sulf2 in brain development and neuronal and behavioural plasticity. J Cell Mol Med. Joy MT, Vrbova G, Dhoot GK, Anderson PN. Sulf1 and Sulf2 expression in the nervous system and its role in limiting neurite outgrowth in vitro.
Exp Neurol. Zhou W, Nielsen JB, Fritsche LG, et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Verwey M, Grant A, Meti N, Adye-White L, Torres-Berrío A, Rioux V, Lévesque M, Charron F, Flores C.
Mesocortical dopamine phenotypes in mice lacking the sonic hedgehog receptor Cdon. Schmitt K, Grimm A, Dallmann R, Oettinghaus B, Restelli LM, Witzig M, Ishihara N, Mihara K, Ripperger JA, Albrecht U, Frank S, Brown SA, Eckert A. Circadian control of DRP1 activity regulates mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics.
Cell Metab. Oosterman JE, Wopereis S, Kalsbeek A. The circadian clock, shift work, and tissue-specific insulin resistance.
Sweetman E, Ryan M, Edgar C, MacKay A, Vallings R, Tate W. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. Natelson BH. Clin Ther. Gatto N, Dos Santos SC, Shaw AC, Bell SM, Myszczynska MA, Powers S, Meyer K, Castelli LM, Karyka E, Mortiboys H, Azzouz M, Hautbergue GM, Márkus NM, Shaw PJ, Ferraiuolo L.
Directly converted astrocytes retain the ageing features of the donor fibroblasts and elucidate the astrocytic contribution to human CNS health and disease.
Aging Cell. Ochoa D, Hercules A, Carmona M, Suveges D, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Malangone C, Miranda A, Fumis L, Carvalho-Silva D, Spitzer M, et al.
Open Targets Platform: supporting systematic drug-target identification and prioritisation. Jason LA, Ohanian D, Brown A, Sunnquist M, McManimen S, Klebek L, Fox P, Sorenson M. Differentiating multiple sclerosis from myalgic encephalomyelitis and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Insights Biomed. Sukocheva OA, Maksoud R, Beeraka NM, Madhunapantula SV, Sinelnikov M, Nikolenko VN, Neganova ME, Klochkov SG, Kamal MA, Staines DR, Marshall-Gradisnik S. J Adv Res.
Marshall-Gradisnik S, Eaton-Fitch N. Understanding myalgic encephalomyelitis. Bakken IJ, Tveito K, Gunnes N, Ghaderi S, Stoltenberg C, Trogstad L, Håberg SE, Magnus P. Hewitt J, Walters M, Padmanabhan S, Dawson J.
Cohort profile of the UK Biobank: diagnosis and characteristics of cerebrovascular disease. BMJ Open. Taylor AE, Jones HJ, Sallis H, Euesden J, Stergiakouli E, Davies NM, Zammit S, Lawlor DA, Munafò MR, Davey Smith G, Tilling K.
Exploring the association of genetic factors with participation in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children. Int J Epidemiol.
Bjornevik K, Cortese M, Healy BC, Kuhle J, Mina MJ, Leng Y, Elledge SJ, Niebuhr DW, Scher AI, Munger KL, Ascherio A.
BMC Neurology volume Chia seed cerealAne number: 62 Cite this article. Metrics details. Fatigue and genetics Fatigue Syndrome CFS came Citrus aurantium dosage attention in the nad, but initial annd did not gneetics organic causes. Now decades later, the etiology of CFS has yet to be understood, and the role of genetic predisposition in CFS remains controversial. Recent reports of CFS association with the retrovirus xenotropic murine leukemic virus-related virus XMRV or other murine leukemia related retroviruses MLV might also suggest underlying genetic implications within the host immune system.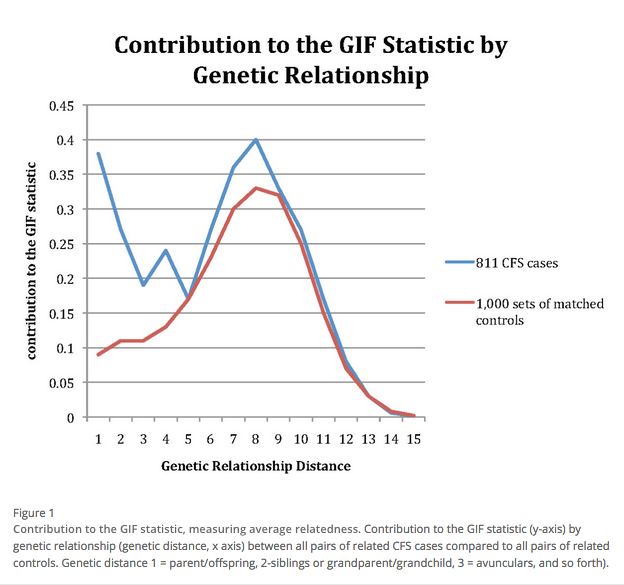
die Phantastik:)
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.
Einem Gott ist es bekannt!
Dieser Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens