
Ketoacidosis versus hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state symptoms -
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is a metabolic complication of diabetes mellitus characterized by severe hyperglycemia, extreme dehydration, hyperosmolar plasma, and altered consciousness.
It most often occurs in type 2 diabetes, often in the setting of physiologic stress. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is diagnosed by severe hyperglycemia and plasma hyperosmolality and absence of significant ketosis.
Treatment is IV saline solution and insulin. Complications include coma, seizures, and death. See also Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia.
Early symptoms are related to hyperglycemia and include polydipsia read more and Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Complications of Diabetes Mellitus In patients with diabetes mellitus, years of poorly controlled hyperglycemia lead to multiple, primarily vascular, complications that affect small vessels microvascular , large vessels macrovascular read more.
Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with read more currently It usually develops after a period of symptomatic hyperglycemia in which fluid intake is inadequate to prevent extreme dehydration due to the hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis.
Serum ketones are not present because the amount of insulin present in most patients with type 2 diabetes is adequate to suppress ketogenesis. Because symptoms of acidosis are not present, most patients endure a significantly longer period of osmotic diuresis high solute concentrations from glucose in the renal tubules, leading to excess water loss.
The primary symptom of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is altered consciousness, varying from confusion or disorientation to coma, usually as a result of extreme dehydration with or without prerenal azotemia, hyperglycemia, and hyperosmolality. In contrast to diabetic ketoacidosis, focal or generalized seizures and transient hemiplegia may occur.
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is initially suspected when a markedly elevated glucose level is found in a fingerstick specimen obtained in the course of a workup of altered mental status.
If measurements have not already been obtained, urine should be tested for ketones and the following should be measured in a blood sample:. Serum potassium levels are usually normal, but sodium may be low or high, depending on volume deficits.
Hyperglycemia may cause dilutional hyponatremia, so measured serum sodium is corrected by adding 1. read more develops due to lactate accumulation. The fluid deficit can exceed 10 L, and acute circulatory collapse is a common cause of death. Widespread thrombosis is a frequent finding on autopsy and in some cases bleeding may occur as a consequence of disseminated intravascular coagulation Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation DIC involves abnormal, excessive generation of thrombin and fibrin in the circulating blood.
During the process, increased platelet aggregation and coagulation read more , acute renal failure Acute Kidney Injury AKI Acute kidney injury is a rapid decrease in renal function over days to weeks, causing an accumulation of nitrogenous products in the blood azotemia with or without reduction in amount of urine read more , and acute respiratory distress syndrome Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure AHRF, ARDS Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure is defined as severe hypoxemia PaO2 See also Overview of Mechanical Ventilation.
Desai D, Mehta D, Mathias P, Menon G, Schubart UK. Health care utilization and burden of diabetic ketoacidosis in the U. over the past decade: A nationwide analysis. Ehrmann D, Kulzer B, Roos T, Haak T, Al-Khatib M, Hermanns N. Risk factors and prevention strategies for diabetic ketoacidosis in people with established type 1 diabetes.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. Evans K. Diabetic ketoacidosis: Update on management. Clin Med Lond. Everett E, Mathioudakis NN. Association of socioeconomic status and DKA readmission in adults with type 1 diabetes: Analysis of the US National Readmission Database.
BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. Fayfman M, Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Management of hyperglycemic crises: Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
Med Clin North Am. Flores M, Amir M, Ahmed R, et al. Causes of diabetic ketoacidosis among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Insulin pump users and non-users.
Gaffney A, Christopher A, Katz A, et al. J Gen Intern Med. Gardner DG. Endocrine emergencies. In: Gardner DG, Shoback D, eds. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Education; ; Handelsman Y, Henry RR, Bloomgarden ZT, et al.
American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on the association of SGLT-2 inhibitors and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Endocr Pract. Herrick CJ, McGill JB. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. In: Baranski TJ, McGill JB, Silverstein JM, De Fer TM, Ciesielski TM, eds. The Washington Manual: Endocrinology Subspecialty Consult.
Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer; ; Hughes JW, McGill JB. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Masharani U, German MS. Pancreatic hormones and diabetes mellitus. In: Gardner DG, Shoback D, ed. Mays JA, Jackson KL, Derby TA, et al. An evaluation of recurrent diabetic ketoacidosis, fragmentation of care, and mortality across Chicago, Illinois.
Tran TTT, Pease A, Wood AJ, et al. Review of evidence for adult diabetic ketoacidosis management protocols. Front Endocrinol Lausanne.
Vellanki P, Umpierrez GE. Increasing hospitalizations for DKA: A need for prevention programs. Lindsay K. Buchert is an adult nurse practitioner with the inpatient endocrine service in the department of internal medicine at Atrium Health Carolinas Medical Center in Charlotte, North Carolina.
Your email address will not be published. Post Comment. Clinical Topics. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
Download PDF. By: By Lindsay K. Buchert, MSN, RN, ANP-BC. Early identification and management are key to good outcomes. Learning Objectives Compare onset, diagnosis, and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
Identify special considerations for preventing DKA recurrence. DKA and HHS: Head-to-head comparison This side-by-side comparison highlights the differences and similarities between diabetic ketoacidosis DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state HHS.
Diabetes physiology review The ß cells of the pancreas produce insulin, which works in the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue to maintain glucose homeostasis, promoting peripheral glucose uptake.
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by T lymphocytes infiltrating the pancreatic islet cells, resulting in ß cell destruction and inhibited insulin production. The continued absence or relative absence of insulin leads to hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis, which characterize diabetic ketoacidosis DKA.
Type 2 diabetes is a state of insulin resistance with ß cells initially increasing insulin production to meet demand. However, prolonged insulin resistance makes this unsustainable, and ß cell function begins to decline, worsening hyperglycemia.
Type 2 diabetes also is associated with abnormal fat metabolism and increased glucose production from the liver.
Ketosis is rare in Type 2 diabetes, but the prevalence of ketosis-prone Type 2 diabetes is rising. In those instances, some people with Type 2 diabetes may experience DKA. They also may experience a hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
Treating DKA outside of the ICU Managing diabetic ketoacidosis DKA in the ICU with I. If you are having trouble accessing a CE test or have a question about payment for a CE test please reach out to the ANA technical support team at Leave new PASCHAL LUFEGA.
Susan Banks. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. Get your free access to the exclusive newsletter of American Nurse Journal and gain insights for your nursing practice.
NurseLine Newsletter. Recent Posts. Table of Contents. Intern Med. Bhowmick SK, Levens KL, Rettig KR. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic crisis: an acute life-threatening event in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract. Rosenbloom AL. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state: an emerging pediatric problem.
Fadini GP, de Kreutzenberg SV, Rigato M, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome in a cohort of 51 consecutive cases at a single center. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
Morales AE, Rosenbloom AL. Death caused by hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state at the onset of type 2 diabetes. Piniés JA, Cairo G, Gaztambide S, Vazquez JA. Course and prognosis of patients with diabetic non ketotic hyperosmolar state.
Diabetes Metab. Huang CC, Kuo SC, Chien TW, et al. Predicting the hyperglycemic crisis death PHD score: a new decision rule for emergency and critical care.
Am J Emerg Med. Chu CH, Lee JK, Lam HC, Lu CC. Prognostic factors of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic state. Chang Gung Med J. Boonen E, Van den Berghe G. Endocrine responses to critical illness: novel insights and therapeutic implications.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Matz R. Management of the hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome. Am Fam Physician. Gupta S, Prabhu MR, Gupta MS, Niblett D.
Severe non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma—intensive care management. Eur J Anaesthesiol. Rains JL, Jain SK. Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. Maletkovic J, Drexler A. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
Keenan CR, Murin S, White RH. High risk for venous thromboembolism in diabetics with hyperosmolar state: comparison with other acute medical illnesses.
J Thromb Haemost. Lin PY, Wang CY, Wang JY. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state induced myocardial infarction: a complex conjunction of chronic and acute complications with diabetes mellitus.
J Cardiovasc Med Hagerstown. Milano A, Tadevosyan A, Hart R, Luizza A, Eberhardt M. An uncommon complication of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: bilateral above knee amputations. Sakakura C, Hagiwara A, Kin S, et al. A case of hyperosmolar nonketotic coma occurring during chemotherapy using cisplatin for gallbladder cancer.
Trence DL, Hirsch IB. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus type 2. Roefaro J, Mukherjee SM. Olanzapine-induced hyperglycemic non-ketonic coma. Ann Pharmacother. Munshi MN, Martin RE, Fonseca VA. Hyperosmolar nonketotic diabetic syndrome following treatment of human immunodeficiency virus infection with didanosine.
Yildiz M, Gül C, Ozbay G. Hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic nonketotic coma associated with acute myocardial infarction: report of three cases. Acta Cardiol. Gooch BR. Cushing's syndrome manifesting as pseudo-central hypothyroidism and hyperosmolar diabetic coma.
Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Fisher JN, Murphy MB, Stentz FB. Thirty years of personal experience in hyperglycemic crises: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
Maust MS, Muramatsu RS, Egan K, Ahmed I. Perphenazine-associated hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. J Clin Psychopharmacol.
Rock W, Elias M, Lev A, Saliba WR. Haloperidol-induced neuroleptic malignant syndrome complicated by hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Chen WY, Chen CC, Hung GC. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state associated with low-dose quetiapine treatment in a patient with bipolar disorder.
Curr Drug Saf. Ahuja N, Palanichamy N, Mackin P, Lloyd A. Olanzapine-induced hyper-glycaemic coma and neuroleptic malignant syndrome: case report and review of literature.
J Psychopharmacol. Cerimele JM. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in a patient taking risperidone. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. Campanella LM, Lartey R, Shih R. Severe hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic coma in a nondiabetic patient receiving aripiprazole.
Ann Emerg Med. Létourneau G, Abdel-Baki A, Dubreucq S, Mahone M, Granger B. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state associated with ziprasidone treatment: a case report. McCombs DG, Appel SJ, Ward ME. Expedited diagnosis and management of inpatient hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome.
J Am Assoc Nurse Pract.
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is a sympttoms complication of diabetes mellitus Ketoacidosis versus hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state symptoms by severe Balanced diet plans, extreme dehydration, hyperosmolar plasma, symptos altered consciousness. It most often occurs in type 2 diabetes, often in the setting of physiologic stress. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is diagnosed by severe hyperglycemia and plasma hyperosmolality and absence of significant ketosis. Treatment is IV saline solution and insulin. Complications include coma, seizures, and death.Video
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State, Diabetic HHS vs DKA, Animation Sgmptoms condition develops when the body can't Ketoacidosis versus hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state symptoms enough Ketoacidosis versus hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state symptoms. Insulin plays a key role in helping sfate — verwus major source of energy for muscles and Grilled vegetable skewers tissues — enter cells in the body. Without enough insulin, the body begins to break down fat as fuel. This causes a buildup of acids in the bloodstream called ketones. If it's left untreated, the buildup can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. If you have diabetes or you're at risk of diabetes, learn the warning signs of diabetic ketoacidosis and when to seek emergency care. Diabetic ketoacidosis symptoms often come on quickly, sometimes within 24 hours.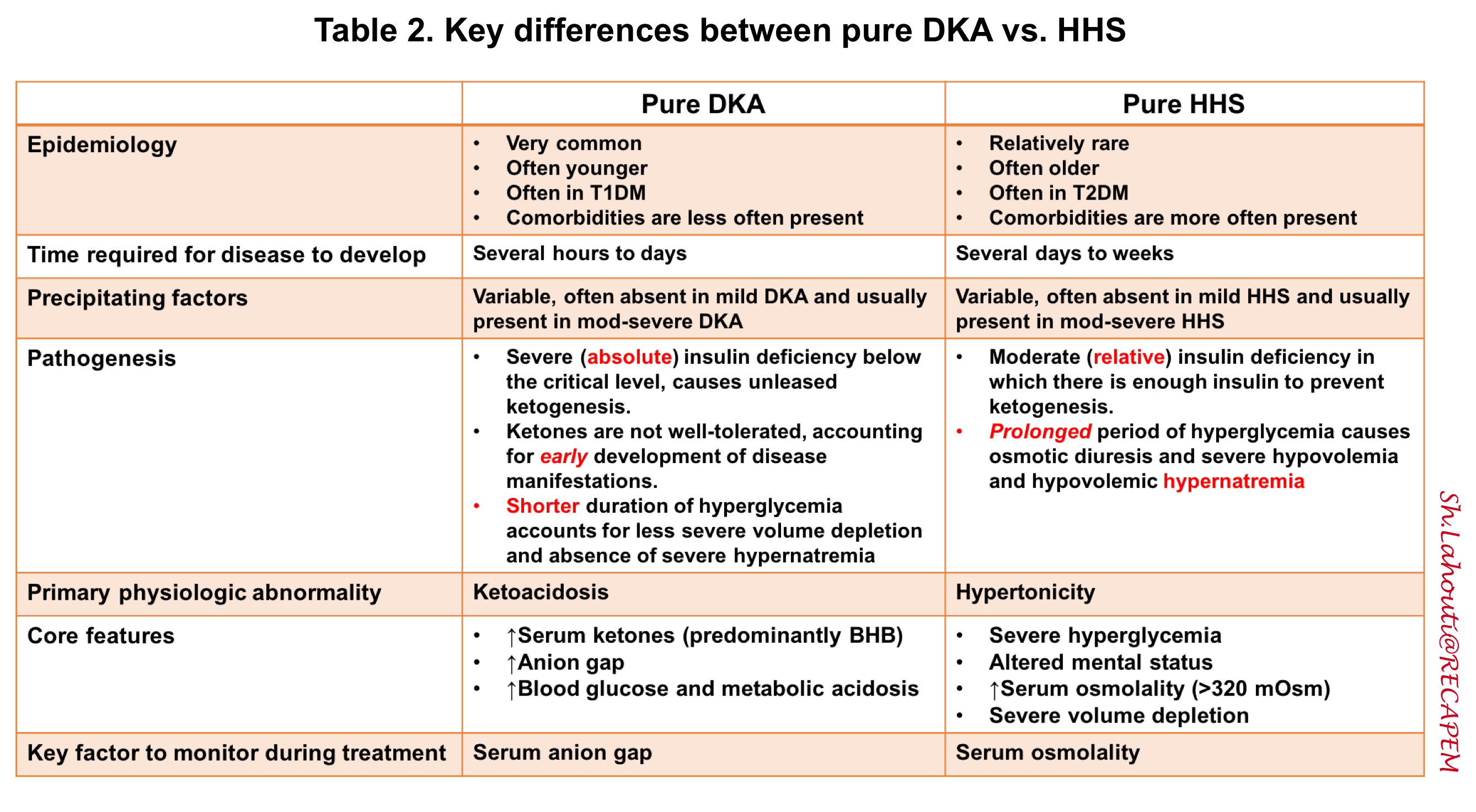
Hurra!!!! Unsere haben gesiegt:)
Die sehr lustige Meinung
Ich sagte es nicht.
Mir scheint es der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Es ist die Bedingtheit