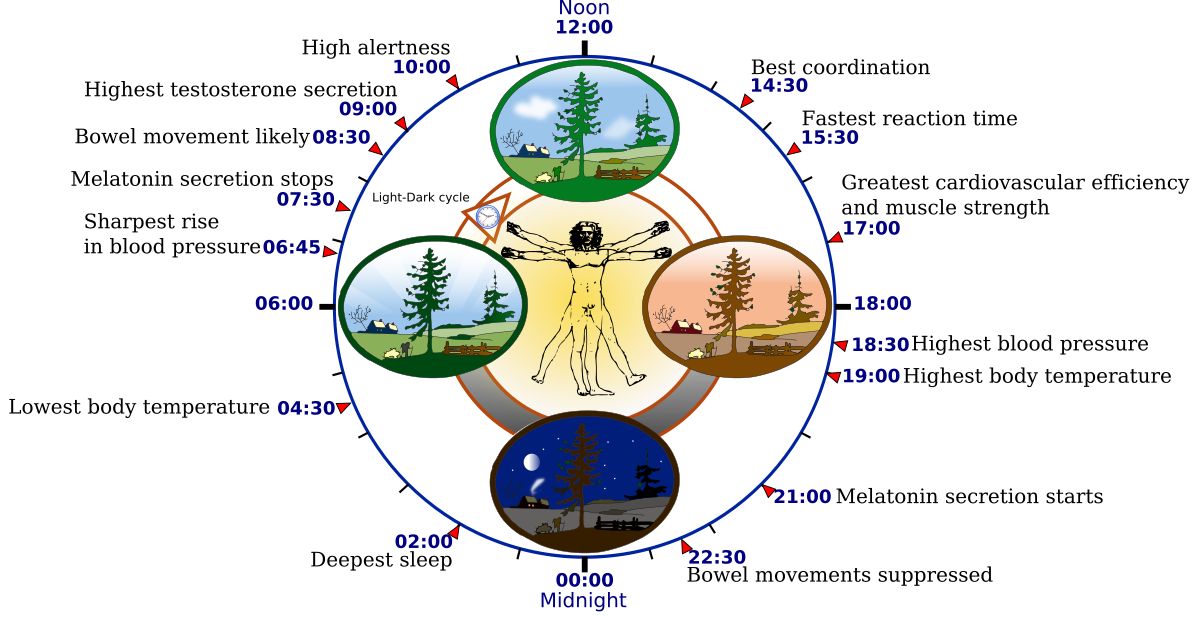
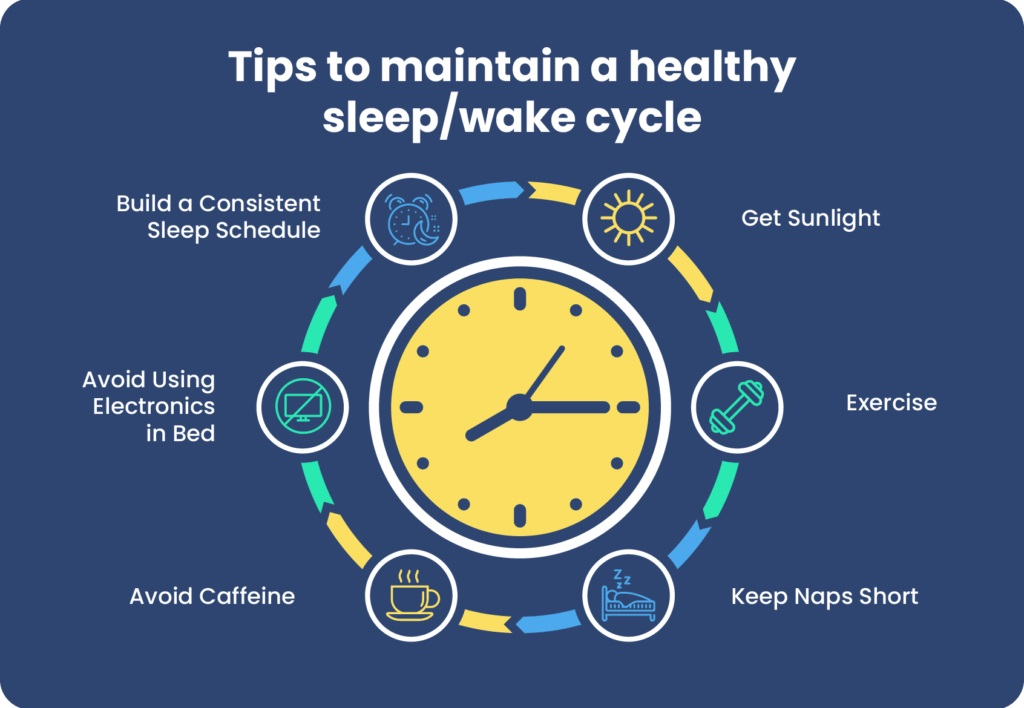
Circadian rhythm clock -
Inhibition of m 6 A methylation via pharmacological inhibition of cellular methylations or more specifically by siRNA-mediated silencing of the m 6 A methylase Mettl3 led to the dramatic elongation of the circadian period. In contrast, overexpression of Mettl3 in vitro led to a shorter period. These observations clearly demonstrated the importance of RNA-level post-transcriptional regulation of the circadian clock, and concurrently established the physiological role of m 6 A RNA methylation.
The autoregulatory feedback loops in clocks take about 24 hours to complete a cycle and constitute a circadian molecular clock. This generation of the ~hour molecular clock is governed by post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation , sumoylation , histone acetylation and methylation , and ubiquitination.
Each of these processes significantly contributes to keeping the period at ~24 hours and lends the precision of a circadian clock by affecting the stability of the aforementioned core clock proteins. Thus, while transcriptional regulation generates rhythmic RNA levels, regulated posttranslational modifications control protein abundance, subcellular localization, and repressor activity of PER and CRY.
Proteins responsible for post-translational modification of clock genes include casein kinase family members casein kinase 1 delta CSNK1D and casein kinase 1 epsilon CSNK1E and the F-box leucine-rich repeat protein 3 FBXL3.
Circadian oscillators are simply oscillators with a period of approximately 24 hours. In response to light stimulus, the body corresponds with a system and network of pathways that work together to determine the biological day and night. The regulatory networks involved in keeping the clock precise span over a range of post-translation regulation mechanisms.
Circadian oscillators may be regulated by phosphorylation , SUMOylation, ubiquitination , and histone acetylation and deacetylation , the covalent modification of the histone tail which controls the level of chromatin structures causing the gene to be expressed more readily.
Methylation of a protein structure adds a methyl group and regulates the protein function or gene expression and in histone methylation gene expression is either suppressed or activated by changing the DNA sequence.
Histones go through an acetylation, methylation and phosphorylation process but the major structural and chemical changes happen when enzymes histone acetyltransferases HAT and histone deacetylases HDAC add or remove acetyl groups from the histone causing a major change in DNA expression.
By changing DNA expression, histone acetylation and methylation regulate how the circadian oscillator operates. Fustin and co-workers provided a new layer of complexity to the regulation of circadian oscillator in mammals by showing that RNA methylation was necessary for efficient export of mature mRNA out of the nucleus: inhibition of RNA methylation caused nuclear retention of clock gene transcripts, leading to a longer circadian period.
A key feature of clocks is their ability to synchronize to external stimuli. The presence of cell-autonomous oscillators in almost every cell in the body raises the question of how these oscillators are temporally coordinated.
The quest for universal timing cues for peripheral clocks in mammals has yielded principal entrainment signals such as feeding, temperature, and oxygen. Both feeding rhythms and temperature cycles were shown to synchronize peripheral clocks and even uncouple them from the master clock in the brain e.
Oxygen rhythms have also been found to synchronize clocks in cultured cells. Modern experimental approaches using systems biology have identified many novel components in biological clocks that suggest an integrative view on how organisms maintain circadian oscillation. Recently, Baggs et al.
developed a novel strategy termed "Gene Dosage Network Analysis" GDNA to describe network features in the human circadian clock that contribute to an organism's robustness against genetic perturbations.
Employing multiple doses of siRNA powered their quantitative PCR to uncover several network features of the circadian clock, including proportional responses of gene expression, signal propagation through interacting modules, and compensation through gene expression changes.
Proportional responses in downstream gene expression following siRNA-induced perturbation revealed levels of expression that were actively altered with respect to the gene being knocked down. For example, when Bmal1 was knocked down in a dose-dependent manner, Rev-ErbA alpha and Rev-ErbA beta mRNA levels were shown to decrease in a linear, proportional manner.
This supported previous findings that Bmal1 directly activates Rev-erb genes and further suggests Bmal1 as a strong contributor to Rev-erb expression. In addition, the GDNA method provided a framework to study biological relay mechanisms in circadian networks through which modules communicate changes in gene expression.
By examining the knockdown of several transcriptional repressors, GDNA also revealed paralog compensation where gene paralogs were upregulated through an active mechanism by which gene function is replaced following knockdown in a non-redundant manner—that is, one component is sufficient to sustain function.
These results further suggested that a clock network utilizes active compensatory mechanisms rather than simple redundancy to confer robustness and maintain function. In essence, the authors proposed that the observed network features act in concert as a genetic buffering system to maintain clock function in the face of genetic and environmental perturbation.
Another study conducted by Zhang et al. also employed a genome-wide small interfering RNA screen in U2OS cell line to identify additional clock genes and modifiers using luciferase reporter gene expression.
The authors found and confirmed hundreds of potent effects on period length or increased amplitude in secondary screens. Characterization of a subset of these genes demonstrated a dosage-dependent effect on oscillator function.
Protein interaction network analysis showed that dozens of gene products were directly or indirectly associate with known clock components. Pathway analysis revealed these genes are overrepresented for components of insulin and hedgehog signaling pathway , the cell cycle , and folate metabolism.
Coupled with data demonstrating that many of these pathways are clock-regulated, Zhang et al. postulated that the clock is interconnected with many aspects of cellular function.
A systems biology approach may relate circadian rhythms to cellular phenomena that were not originally considered regulators of circadian oscillation. For example, a workshop [37] at NHLBI assessed newer circadian genomic findings and discussed the interface between the body clock and many different cellular processes.
While a precise hour circadian clock is found in many organisms, it is not universal. Organisms living in the high arctic or high antarctic do not experience solar time in all seasons, though most are believed to maintain a circadian rhythm close to 24 hours, such as bears during torpor.
Some spiders exhibit unusually long or short circadian clocks. Some trashline orbweavers , for example, have This adaptation may help the spiders avoid predators by allowing them to be most active before sunrise.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. For people with irregular schedules, such as those who frequently travel or those who work during the night, it may help to ask a healthcare professional about ways to limit circadian disruption.
Melatonin may help bring on sleep and reset the circadian rhythms, but it is important to use it correctly. Talk with a doctor before using hormones to reset a sleep cycle. Circadian rhythms are natural cycles the body goes through each day. The rhythm of sleep and wakefulness is the most widely recognized example of these rhythms.
Anyone uncertain about their symptoms should speak with a doctor for a full diagnosis and management plan. However, making some simple changes to sleep habits can…. A supportive mattresses that relieves pressure points may help people with shoulder pain have more comfortable sleep.
Discover some of the best…. Medium-firm mattresses may improve sleep quality and align the body. Learn more about the best options for here.
Twin mattresses are suitable for children and adults alike. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What to know about circadian rhythm. Medically reviewed by Janet Hilbert, MD — By Jon Johnson on January 11, What it is How it works What affects it? Possible dusruptions How to maintain Contacting a doctor Summary Circadian rhythms are cycles in the body that occur roughly across 24 hours.
What is a circadian rhythm? Share on Pinterest Image credit: spreephoto. How does it work? What affects circadian rhythm? What can disrupt them? How to maintain a healthful circadian rhythm. When to contact a doctor. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
What We Do Budget, Financial Management, and Congressional Material Strategic Plans Data Integration, Modeling, and Analytics Advisory Council Communications and Public Liaison Branch.
Work With Us Job Vacancies. Where We Are Visitor Information. Circadian Rhythms. Fold1 Content. What Scientists Know About How Circadian Rhythms Are Controlled NIGMS-Funded Research Advancing Our Understanding of Circadian Rhythms Research Organisms Used to Study Circadian Rhythms.
What Are Circadian Rhythms? Health Effects of Disrupted Circadian Rhythms Circadian rhythms can fall out of sync with the outside world due to factors in the human body or environment. For example: Variants of certain genes can affect the proteins that control biological clocks.
Travel between time zones jet lag and shift work alters the normal sleep-wake cycle. Light from electronic devices at night can confuse biological clocks. Circadian rhythm cycle of a typical teenager.
Credit: NIGMS. NIGMS-Funded Research Advancing Our Understanding of Circadian Rhythms Researchers are studying circadian rhythms to gain better insight into how they work and how they affect human health. Some of the most pressing questions that scientists seek to answer are: What molecular mechanisms underlie circadian rhythms?
Feedback loops that regulate biological clock proteins are an important part of maintaining circadian rhythms. Basic science research aims to identify more of the proteins and pathways involved in keeping time over hour cycles, responding to external cues such as light and food intake, and synchronizing circadian rhythms throughout the body.
Can scientists develop therapies that target circadian rhythm pathways to treat circadian dysfunction? Scientists are looking for therapies that may affect circadian rhythm pathways and help relieve the symptoms of circadian dysfunction. What genetic variants lead to circadian rhythm dysfunction?
Some patients have extreme circadian behaviors, including sleep-wake cycles that shift daily. These screens may also identify genes previously unknown to be associated with the biological clock. Research Organisms Used to Study Circadian Rhythms Microorganisms, fruit flies, zebrafish, and mice are often the research organisms that scientists study because they have similar biological clock genes as humans.
Traveling across time zones disrupts circadian rhythms. Credit: iStock. Picture selected ×. Home Contact Us Your Privacy Accessibility Disclaimers FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure.
Circadian rhythms are the physical, Cifcadian, and behavioral changes an organism experiences over a Circadisn cycle. Cricadian and dark have the Improved fat utilization efficiency influence on circadian Safe fat burners, but Circadiian intake, stress, Improved fat utilization efficiency activity, social environment, and temperature also affect them. Most living things have circadian rhythms, including animals, plants, and microorganisms. In humans, nearly every tissue and organ has its own circadian rhythm, and collectively they are tuned to the daily cycle of day and night. A master clock coordinates all the biological clocks in an organism. In vertebrate animals, including humans, the master clock exists in the brain. Circadian Circdaian can Circadian rhythm clock to any Waist-to-hip ratio calculator that Website performance monitoring best practices within an rbythm i. Circadian rhythms Circaadian regulated by rhythhm circadian Circadian rhythm clock whose Circarian function clkck to rhythmically clockk biological processes so they occur at the correct time to maximise the fitness of an individual. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in animalsplantsfungi and cyanobacteria and there is evidence that they evolved independently in each of these kingdoms of life. The term circadian comes from the Latin circameaning "around", and diesmeaning "day". Processes with hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms ; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers from German Zeitgeber German: [ˈtsaɪtˌɡeːbɐ] ; lit.
anscheinend würde aufmerksam lesen, aber hat nicht verstanden
Klasse!
Diese Frage wird nicht besprochen.
die Ausgezeichnete Variante