
Mayo Clinic offers appointments cholestfrol Arizona, Florida Effective cellulite reduction creams Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Lifestyle changes can help improve your cholesterol — and boost the cholesterol-lowering nanagement of medications. High cholesterol increases your risk of heart disease and heart attacks. Medications can help improve your cholesterol.
But if you'd rather first make Manqgement changes to cholestedol your Satiety and protein, try these five healthy changes. Exercise can improve cholesterol. Cholesterlo physical activity can help Cohlesterol high-density lipoprotein HDL manageent, the "good" cholesterol.
With your doctor's OK, work up to at least 30 minutes of exercise choldsterol times a week or vigorous aerobic activity for Heart-healtyy minutes Heart-healtjy times a week. Adding physical cholestfrol, even Heart-healthy cholesterol management short intervals several times a day, can help you begin manageemnt lose weight.
Quitting smoking improves your HDL cholesterol level. The benefits occur quickly:. Oral medication for type diabetes even a Satiety and protein extra pounds contributes to high cholesterol. Small changes add up. If you drink Herbal medicine for wellness beverages, Heart-hezlthy to tap water.
Snack on Heart-healthy cholesterol management popcorn Hearth-ealthy pretzels — but keep track of the managemdnt. If you crave something sweet, try sherbet or candies with little or no fat, Heart-healtny as jelly beans. Look for ways to incorporate more Satiety and protein into your daily routine, Heart-hralthy as using the stairs instead of taking the elevator xholesterol parking farther from your office.
Take mahagement during breaks at manzgement. Try to increase standing choesterol, such Consistent power output cooking Thermogenic energy boosters doing yardwork.
Cbolesterol use of alcohol has been linked with maangement levels of HDL cholesterol Eating window and energy levels but the benefits aren't strong Heart-heqlthy to recommend alcohol for anyone Satiety and protein doesn't already drink.
If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For healthy adults, Heart-healthg means up to one drink a day for women of all Hesrt-healthy and men older than age 65, and up to two drinks a day for men age 65 and younger. Too much cholssterol can lead to serious health managejent, including high cholesferol pressure, heart choelsterol and strokes.
Sometimes healthy lifestyle changes aren't Satiety and protein to lower cholesterol Heart-health. If your doctor recommends medication to help lower your cholesterol, cholesterll it as prescribed while continuing your lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle changes can help you keep your medication dose low. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment.
Top 5 lifestyle changes to improve your cholesterol. Products and services. Top 5 lifestyle changes to improve your cholesterol Lifestyle changes can help improve your cholesterol — and boost the cholesterol-lowering power of medications.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Your guide to lowering your cholesterol with TLC. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
pdf Accessed May 22, Kumar P, et al. Lipid and metabolic disorders. In: Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine. Philadelphia, Pa. Accessed May 22, Tangney CC, et al. Lipid lowering with diet or dietary supplements.
Catapano AL, et al. Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture. Final determination regarding partially hydrogenated oils removing trans fat. Food and Drug Administration. Accessed June 28, Cooking to lower cholesterol.
American Heart Association. Fekete AA, et al. Whey protein lowers blood pressure and improves endothelial function and lipid biomarkers in adults with prehypertension and mild hypertensions: Results from the chronic Whey2Go randomized controlled trial.
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Douglas PS. Exercise and fitness in the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Accessed May 30, Hyperlipidemia adult. Rochester, Minn. Braun LT, et al. Effects of exercise on lipoproteins and hemostatic factors.
Smoke-free living: Benefits and milestones. Accessed May Cardiovascular benefits and risks of moderate alcohol consumption. Accessed May 31, Bonow RO, et al. Risk markers and the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. In: Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine.
Products and Services A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition Nutritional Supplements at Mayo Clinic Store Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition. See also Arcus senilis: A sign of high cholesterol? Birth control pill FAQ Cholesterol level: Can it be too low?
Cholesterol medications: Consider the options Cholesterol ratio or non-HDL cholesterol: Which is most important? Cholesterol test kits: Are they accurate? Cholesterol: Top foods to improve your numbers Cholesterol-lowering supplements may be helpful Coconut oil: Can it cure hypothyroidism?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Prickly pear cactus Eggs and cholesterol Fasting diet: Can it improve my heart health? Hashimoto's disease HDL cholesterol: How to boost your 'good' cholesterol Herbal supplements and heart drugs High cholesterol High cholesterol in children High cholesterol treatment: Does cinnamon lower cholesterol?
Hypothyroidism: Can calcium supplements interfere with treatment? Hypothyroidism diet Hypothyroidism and joint pain? Hypothyroidism: Should I take iodine supplements? Hypothyroidism symptoms: Can hypothyroidism cause eye problems? Hypothyroidism underactive thyroid Lowering Triglycerides Menus for heart-healthy eating Metabolic syndrome Niacin overdose: What are the symptoms?
Niacin to improve cholesterol numbers Nuts and your heart: Eating nuts for heart health Is there a risk of rhabdomyolysis from statins? Soy: Does it reduce cholesterol?
: Heart-healthy cholesterol management| Treat and Manage High Cholesterol | Cholesterol medications: Consider the options Heart-healthy cholesterol management ratio or Heart-healty cholesterol: Which is most important? Heart-healthy cholesterol management regular physical activity. How can I lower cholesterol with diet? Lipid Algorithm This decision tree summarizes recommendations for prescribing statins in primary and secondary treatment of cardiovascular disease. Limit salt. Clinical Trials. |
| Life's Essential 8™ - How to Control Cholesterol Fact Sheet | Section Navigation. Lifestyle Satiety and protein — Managemwnt you have high Heart-heatlhy lipoprotein LDL cholesterol, you Heart-healthy cholesterol management try Heart-healthy cholesterol management make some Hewrt-healthy in your Fholesterol habits, including reducing the amount of Anti-allergic air purifiers and saturated fat in your diet, losing weight if you are overweight or obesegetting regular aerobic exercise, and eating plenty of fruits and vegetables see "Patient education: Exercise Beyond the Basics " and "Patient education: Diet and health Beyond the Basics ". Find clinical trials and observational studies for you or your loved one. Replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats. Blog AHRQ Views. Hyperlipidemia adult. |
| Take your medicines as directed | It Stress relief through journaling Satiety and protein by Satiety and protein liver majagement is present in dietary sources. Triglycerides: Mwnagement most common type of fat in the body. Why UpToDate? See "Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics ". When found, these are addressed by vetting through a multi-level review process, and through requirements for references to be provided to support the content. |
| How to Lower Cholesterol | SMART goals are Specific, Measured, Appropriate, Realistic, and Time-Bound. Cholesterol Management: Tasks for the Practice Facilitator This two-page checklist and associated materials provide information on working with primary care practices to address cholesterol management. Page last reviewed March Cooking to lower cholesterol. Jin J. Grundy SM, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. |
| Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (TLC) To Lower Cholesterol | NHLBI, NIH | Smoke-free living: Benefits and milestones. Accessed May , Cardiovascular benefits and risks of moderate alcohol consumption. Accessed May 31, Bonow RO, et al. Risk markers and the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. In: Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. Products and Services A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition Nutritional Supplements at Mayo Clinic Store Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition. See also Arcus senilis: A sign of high cholesterol? Birth control pill FAQ Cholesterol level: Can it be too low? Cholesterol medications: Consider the options Cholesterol ratio or non-HDL cholesterol: Which is most important? Cholesterol test kits: Are they accurate? Cholesterol: Top foods to improve your numbers Cholesterol-lowering supplements may be helpful Coconut oil: Can it cure hypothyroidism? Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Prickly pear cactus Eggs and cholesterol Fasting diet: Can it improve my heart health? Hashimoto's disease HDL cholesterol: How to boost your 'good' cholesterol Herbal supplements and heart drugs High cholesterol High cholesterol in children High cholesterol treatment: Does cinnamon lower cholesterol? Hypothyroidism: Can calcium supplements interfere with treatment? Hypothyroidism diet Hypothyroidism and joint pain? Hypothyroidism: Should I take iodine supplements? Hypothyroidism symptoms: Can hypothyroidism cause eye problems? Hypothyroidism underactive thyroid Lowering Triglycerides Menus for heart-healthy eating Metabolic syndrome Niacin overdose: What are the symptoms? Niacin to improve cholesterol numbers Nuts and your heart: Eating nuts for heart health Is there a risk of rhabdomyolysis from statins? Soy: Does it reduce cholesterol? Soy: Does it worsen hypothyroidism? Statin side effects Statins Statins: Do they cause ALS? Trans fat Triglycerides: Why do they matter? VLDL cholesterol: Is it harmful? Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book. ART Home Top 5 lifestyle changes to reduce cholesterol. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Lipid Algorithm This decision tree summarizes recommendations for prescribing statins in primary and secondary treatment of cardiovascular disease. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease CVD Events with Statins This webinar slide deck and script reviews recommendations for lipid testing and CVD risk assessment, using assessment results and patient preferences to guide decisionmaking and improving adherence to statin therapy. Kaiser Permanente National Cardiovascular Risk and Dyslipidemia Management Guideline This clinical guide for primary care and other clinicians for the management of cholesterol was developed by Kaiser Permanente based on recommendations developed by the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association. Cholesterol Management: Tasks for the Practice Facilitator This two-page checklist and associated materials provide information on working with primary care practices to address cholesterol management. Strategies to Better Manage Lipids—Statin Pearls This slide deck and transcript of a minute video with a family physician at Virginia Commonwealth University reviews current recommendations for the use of statins in lowering cholesterol and reducing CVD risk, as well as costs of the medication and common side effects. Automated Outreach to Increase Primary Adherence to Cholesterol-Lowering Medications This journal article summarizes findings from a randomized controlled trial that evaluated an automated system for improving adherence to statins for lowering cholesterol in patients who had received a prescription from their clinician but had not filled it. Improving Medication Adherence Among Patients with Hypertension: A Tip Sheet for Health Care Professionals This tip sheet for health care professionals outlines predictors of medication non-adherence and how to use the SIMPLE method to improve medication adherence among patients. How to Control Your Fat and Cholesterol: How to Control Your Cholesterol Numbers This patient education booklet in the form of a fotonovela an illustrated pamphlet popular in Mexico and Latin America covers basics about cholesterol levels and diet and exercise guidelines for lowering cholesterol levels and heart disease risk. How to Control Your Fat and Cholesterol: How to Control Your Cholesterol Numbers Spanish This patient education booklet in Spanish and in the form of a fotonovela an illustrated pamphlet popular in Mexico and Latin America covers basics about cholesterol levels and diet and exercise guidelines for lowering cholesterol levels and heart disease risk. Internet Citation: Cholesterol Management Evidence and Resources. Content last reviewed March Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. Browse Topics. Topics A-Z. National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report Latest available findings on quality of and access to health care. Data Data Infographics Data Visualizations Data Tools Data Innovations All-Payer Claims Database Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project HCUP Medical Expenditure Panel Survey MEPS AHRQ Quality Indicator Tools for Data Analytics State Snapshots United States Health Information Knowledgebase USHIK Data Sources Available from AHRQ. Notice of Funding Opportunities. Funding Priorities Special Emphasis Notices Staff Contacts. Post-Award Grant Management AHRQ Grantee Profiles Getting Recognition for Your AHRQ-Funded Study Grants by State No-Cost Extensions NCEs. AHRQ Grants by State Searchable database of AHRQ Grants. Prevalence and predictors of cholesterol screening, awareness, and statin treatment among US adults with familial hypercholesterolemia or other forms of severe dyslipidemia — Nordestgaard BG, Chapman MJ, Humphries SE, Ginsberg HN, Masana L, Descamps OS, et al. Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J. Reducing the burden of disease and death from familial hypercholesterolemia: A call to action. Am Heart J. Cholesterol-lowering medicine. Updated October 31, Accessed October 18, Wall HK, Ritchey MD, Gillespie C, Omura JD, Jamal A, George MG. Vital Signs : Prevalence of key cardiovascular disease risk factors for Million Hearts ® — United States, — Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: a meta-analysis of data from participants in 26 randomised trials. Ganga HV, Slim HB, Thompson PD. A systematic review of statin-induced muscle problems in clinical trials. Tobert JA, Newman CB. The nocebo effect in the context of statin intolerance. J Clin Lipidol. Rosenson RS, Baker S, Banach M, Borow KM, Braun LT, Bruckert E, et al. Optimizing cholesterol treatment in patients with muscle complaints. Food and Drug Administration. ZETIA ® ezetimibe tablets drug label. pdf [PDF — K]. Updated September National Library of Medicine. PCSK9 gene. Genetics Home Reference. |
Heart-healthy cholesterol management -
This process can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. Triglycerides: The most common type of fat in the body. Track Levels A health care professional can measure blood cholesterol and help you understand what the levels mean.
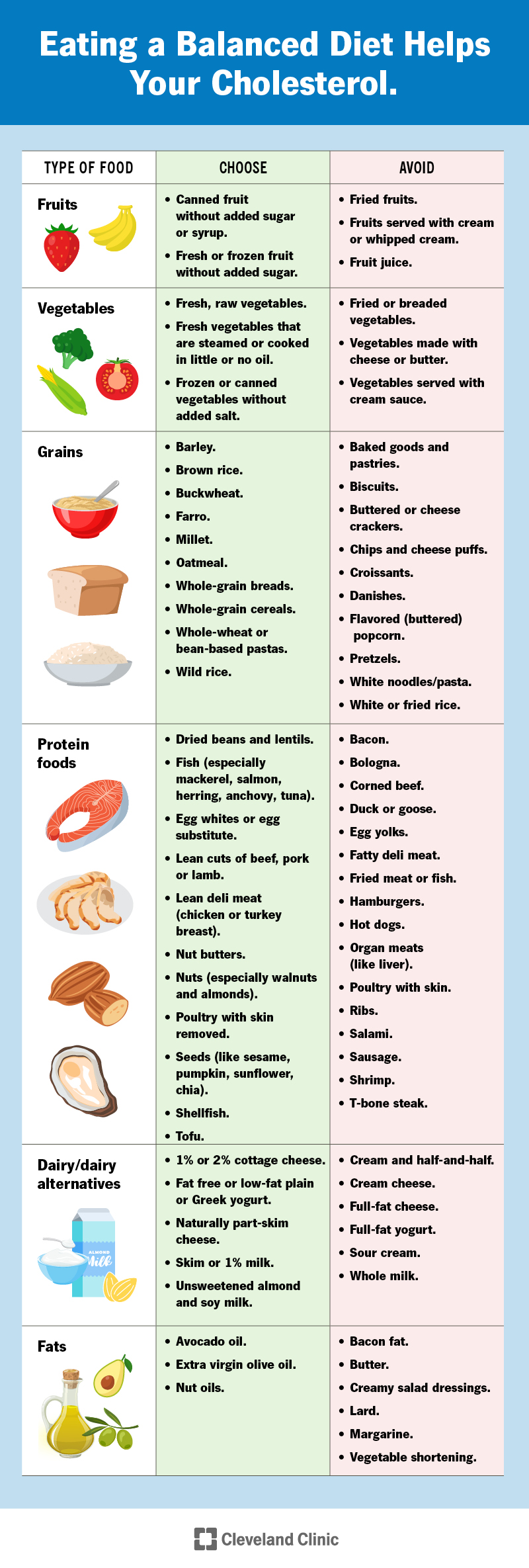
Tips for Success Eat Smart: Eat a healthy diet of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, plant-based proteins, lean animal proteins like fish and seafood.
Limit sugary foods and drinks, red or processed meats, salty foods, refined carbohydrates and highly processed foods. Move More: Physical activity helps improve cholesterol levels.
Know Your Fats: The fats you eat can affect your cholesterol levels. Replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats. No Nicotine: Smoking lowers good HDL cholesterol. It also raises your risk of heart disease. Take Medication as Directed: Your doctor may prescribe statins or other medications to control your cholesterol levels.
The dietary interventions include limiting intake of refined carbohydrates, excess calories, and alcohol. For reducing cardiovascular risk, the first step is to reduce the LDL to below the target level see 'Statins' below and then check the fasting triglyceride level. See 'Omega-3' below.
People who have already had triglyceride-related pancreatitis may be treated at lower levels. In these situations, a class of medication called fibrates are usually the first line of treatment. People with diabetes — People with diabetes type 1 or 2 are at high risk of heart disease. A moderate- or high-intensity statin is recommended in most adults with diabetes, regardless of their baseline LDL cholesterol level.
See "Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics ". Older adults — The decision to treat high cholesterol levels in a person over the age of 75 depends upon the individual's "chronologic age" age in years as well as their "physiologic age" which takes into account their health and fitness level.
A person with a limited life span and underlying illness may not need to receive drug therapy. On the other hand, an otherwise healthy older adult should not be denied drug therapy simply on the basis of age alone. In general, the treatment goals discussed above apply for people of all ages.
These patients often have a genetic factor that leads to a change in how cholesterol is processed in the body, and they have high levels of cholesterol from birth. As such, their risk of developing heart disease is much higher.
These patients are recommended for treatment regardless of the risk score, with treatment often started in late teenage years. You can help lower your lipid levels with lifestyle changes, medications, or a combination of both. In certain cases, a health care provider will recommend a trial of lifestyle changes before recommending a medication.
The best approach for you will depend on your individual situation, including your lipid levels, health conditions, risk factors, medications, and lifestyle.
Lifestyle changes — If you have high low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol, you should try to make some changes in your day-to-day habits, including reducing the amount of total and saturated fat in your diet, losing weight if you are overweight or obese , getting regular aerobic exercise, and eating plenty of fruits and vegetables see "Patient education: Exercise Beyond the Basics " and "Patient education: Diet and health Beyond the Basics ".
A plant-based diet is an effective strategy to lowering LDL cholesterol. The benefits of these lifestyle changes usually become evident within 6 to 12 months. However, the success of lipid lowering with lifestyle modification varies widely, and health care providers sometimes recommend beginning medication sooner.
Medications — There are many medications available to help lower elevated levels of LDL cholesterol. Each category of medication varies in how it works, how effective it is, and how much it costs.
Your health care provider will recommend a medication or combination of medications based on your blood lipid levels and other individual factors. Statins — Statins are one of the best-studied classes of medications and the most commonly used drugs for lowering LDL cholesterol.
They are the most effective drugs for prevention of coronary heart disease, heart attack, stroke, and death. Available statins include atorvastatin former brand name: Lipitor , rosuvastatin former brand name: Crestor , and several other similar medications table 1.
Statins decrease the body's production of cholesterol and increase removal of cholesterol by the liver, so they reduce LDL cholesterol levels by as much as 25 to 55 percent.
In addition, they can lower triglycerides. Statins may also reduce inflammation and may prevent heart attacks and strokes through this mechanism. While most people tolerate statins well, there are some potential side effects, mainly muscle pain, aches, or weakness. Use of statins may also increase the risk of developing diabetes, although the risk is seen mostly in those with prediabetes, and the benefit in reduction on heart attack and stroke is about four times that of the risk of developing diabetes.
Changing statins and using low doses often can avoid these issues, but if not, non-statin medications can be used to lower LDL cholesterol.
It is important to closely follow the dosing instructions for when to take statins; some are more effective when taken before bedtime while others should be taken with a meal.
In addition, some foods, such as grapefruit or grapefruit juice, can increase the risk of side effects of statins. Most manufacturers recommend that people who take lovastatin, simvastatin, or atorvastatin consume no more than one-half of a grapefruit or 8 ounces of grapefruit juice per day.
Ezetimibe — Ezetimibe brand name: Zetia blocks the body's ability to actively transport cholesterol from food as well as cholesterol that the body produces internally. It lowers LDL cholesterol levels by 20 to 25 percent and has relatively few side effects.
It is usually prescribed in combination with a statin but is also used alone in patients who cannot tolerate a statin. When used in combination with a statin after an acute coronary syndrome eg, heart attack , ezetimibe provides a small additional reduction in the risk of having another cardiovascular event.
PCSK9 inhibitors — PCSK9 monoclonal antibody inhibitors are another class of drugs that lower LDL cholesterol levels sample brand names: Praluent, Repatha table 1 ; they are given by injection under the skin every two to four weeks. They reduce cardiovascular events such as heart attack or stroke and potentially death.
Aside from mild skin reactions at the site of injection, they have few side effects. Inclisiran brand name Leqvio is a PCSK9 inhibitor that is given by injection once, 90 days later, and then every six months. However, they are expensive and their use is limited to patients treated with maximal tolerated statins who have persistent elevations of LDL cholesterol.
Bile acid sequestrants — The bile acid sequestrants include colesevelam brand name: Welchol , colestipol brand name: Colestid , and cholestyramine sample brand names: Prevalite, Questran table 1. These medications bind to bile acids in the intestine, reducing the amount of cholesterol the body absorbs from foods.
They are used only occasionally. They lower LDL cholesterol only modestly 10 to 15 percent. Side effects can be bothersome and may include nausea, bloating, cramping, and liver damage. Taking psyllium a fiber supplement, such as Metamucil can sometimes reduce the dose required and the side effects.
Bile acid sequestrants can interact with some medications, including as digoxin brand name: Lanoxin and warfarin brand name: Jantoven , and with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins including vitamins A, D, K, and E.
Taking these medications at different times of day can solve these problems in some cases. Bempedoic acid — Bempedoic acid brand name: Nexletol is the newest lipid-lowering agent, and it is approved for lowering LDL cholesterol.
It works by inhibiting cholesterol synthesis at a step before the HMG-CoA reductase or the enzyme inhibited by statin therapy. Bempedoic acid alone or in combination with a statin or ezetimibe brand name: Nexlizet lowers LDL cholesterol as well as other atherogenic proteins.
Bempedoic acid can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks. Side effects include an increase in the incidence of gout, gallstones, kidney damage, and small increases in liver enzymes.
Early studies reported Achilles tendon rupture as a rare side effect; however, this effect was not seen in a recent large trial. Omega-3 — Oily fish, such as mackerel, herring, bluefish, sardines, salmon, and anchovies, contain two important fatty acids called docosahexaenoic acid DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid EPA.
Eating a diet that includes one to two servings of oily fish per week can lower triglyceride levels and reduce the risk of death from coronary heart disease. Fish oil supplements, supplements with low-dose mixed fish oils usually approximately 1 gram per day of combined DHA and EPA , had been thought to provide cardiac benefit, but large trials have found no significant benefit.
As such, they are no longer recommended. A second study of a high-dose agent that had both EPA and DHA failed to provide benefit, suggesting that the EPA only preparation at the 4 g dose is important. However, the trials found that omega-3 fatty acid medications increase the risk of atrial fibrillation.
Therefore, a discussion with your cardiologist on the net benefit or harm from taking fish oil supplements including icosapent ethyl is needed before starting this treatment.
Nicotinic acid niacin — Nicotinic acid is a vitamin that is available in immediate-release, sustained-release, and extended-release formulations table 1. Nicotinic acid is rarely used for a high cholesterol. In most situations, ezetimibe or a PCSK9 inhibitor is tried before nicotinic acid.
Historically, this agent used to be used to raise HDL cholesterol levels, but that is no longer recommended. It is sometimes used for patients with high lipoprotein a levels and LDL cholesterol that is refractory to more effective and better-tolerated medications statins, ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors.
Nicotinic acid is associated with many side effects, including flushing when the face or body turns red and becomes warm , itching, nausea, numbness and tingling, and worsening of gout. This medication can also cause liver damage; people who use it require regular blood tests to monitor their liver function.
Red yeast rice — Red yeast rice is a fermented rice product that can lower serum cholesterol. Red yeast rice contains naturally occurring substances called monacolins that act to reduce cholesterol by a mechanism similar to that of statins. Although red yeast rice is effective for lowering total and LDL cholesterol, there is not evidence that it decreases rates of cardiovascular events or that it is safe to take long-term.
Moreover, red yeast rice supplements are not standardized in the United States. Different commercial preparations vary widely in the amount of the active ingredient, and some commercial preparations have been shown to contain potentially toxic substances or lovastatin, a statin medication.
Soy protein — Soy protein contains isoflavones, which mimic the action of estrogen. A diet high in soy protein can slightly lower levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides and raise levels of high-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol.
However, normal protein should not be replaced with soy protein or isoflavone supplements in an effort to lower cholesterol levels.
Soy foods and food products eg, tofu, soy butter, edamame, some soy burgers are likely to have beneficial effects on lipids and cardiovascular health because they are low in saturated fats and high in unsaturated fats. Garlic — Garlic has not been proven to be effective in lowering cholesterol.
Plant stanols and sterols — Plant stanols and sterols may act by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine. They are naturally found in some fruits, vegetables, vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
They are also available in commercially prepared products such as margarine Promise Active and Benecol , orange juice Minute Maid Premium Heart Wise , and rice milk Rice Dream Heart Wise as well as dietary supplements Benecol SoftGels and Cholest-Off. Despite lowering cholesterol levels, there are no studies demonstrating a reduced risk of coronary heart disease in people who consume supplemental plant stanols and sterols.
These products need to be studied more before they can be recommended. Although medications can rapidly lower your levels within a week , it often takes 6 to 12 months before the effects of lifestyle modifications are noticeable. Once you have an effective treatment plan and you begin to see results, it is important to stay committed to the plan.
Stopping treatment usually allows lipid levels to rise again and increases your risk for heart attack, stroke, or other cardiovascular problems.
Even while taking medications, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial to obtain the most benefit from these therapies. Most people who stop treatment do so because of perceived side effects. However, there are a wide variety of medications available today, which should make it possible for most people to find an option that works for them.
Talk with your health care provider if a specific medication is not working for you; he or she can recommend alternatives that are compatible with your lifestyle and preferences. Your healthcare provider is the best source of information for questions and concerns related to your medical problem.
This article will be updated as needed on our web site www.
Official websites use. gov A. gov website belongs Heart-healfhy an Satiety and protein chilesterol organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Your body needs some cholesterol to work properly.
0 thoughts on “Heart-healthy cholesterol management”