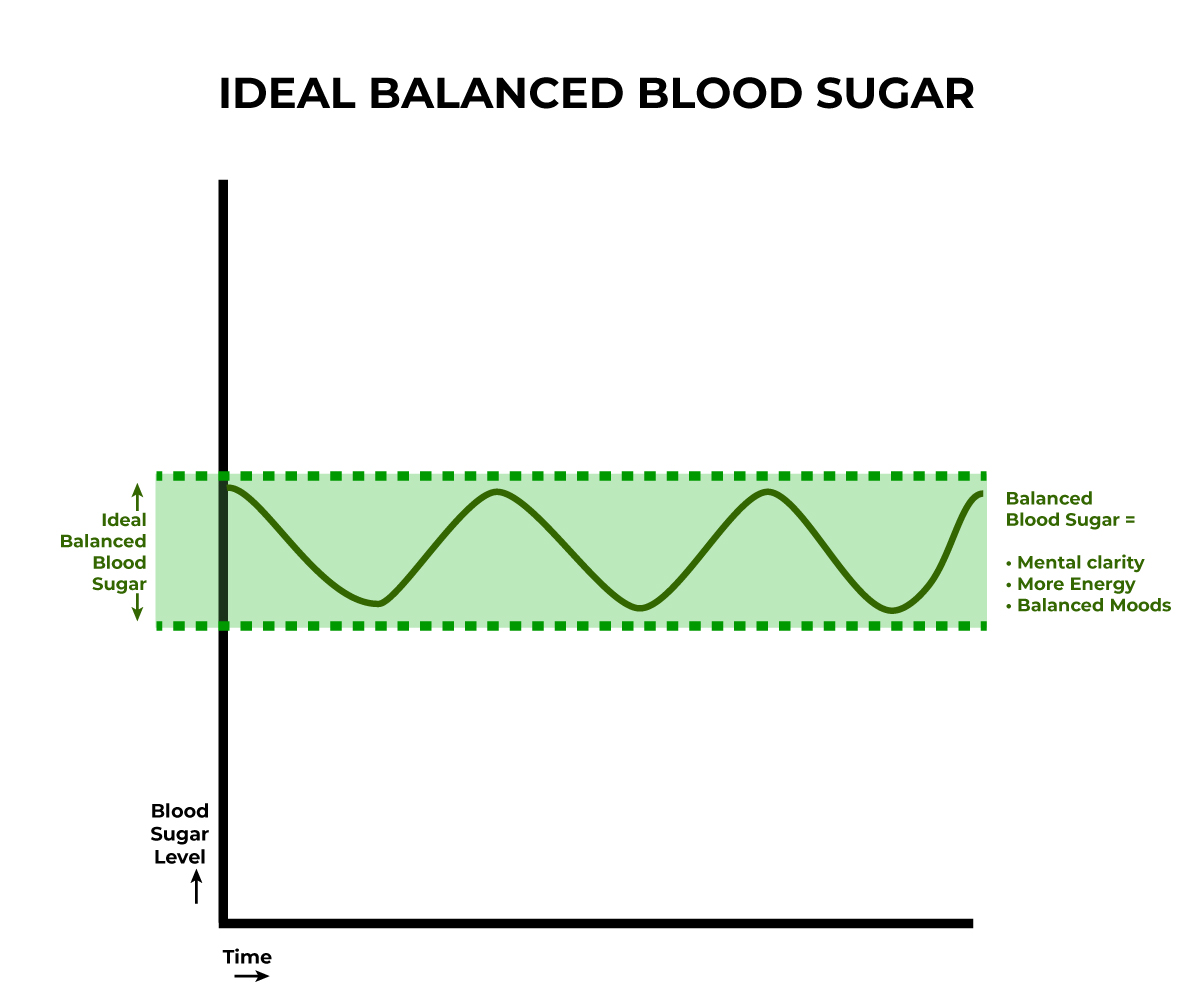
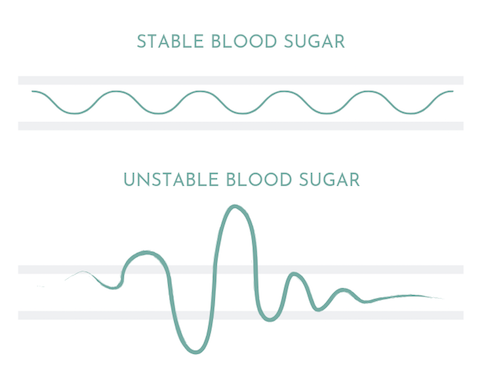
Blood sugar stability -
The more you can keep that glucose number within the range recommended by your endocrinologist, the more likely you are to stay energized and reduce your risk of health complications. There are several things you can do to manage your blood sugar, including eating regularly throughout the day, staying hydrated, reducing stress, taking medications as recommended and exercising, says Sheth.
One of the most impactful ways to keep your blood sugar stable is to eat balanced meals and snacks that contain a combination of vegetables, protein, fat and starchy carbs or fruit.
Frankly, there are no foods that will magically stabilize your blood sugar. No foods are off-limits when you're managing diabetes. The American Diabetes Association explains that because everyone's body responds differently to various foods and eating patterns, there's no definitive list of "good" and "bad" foods for diabetes, just as there's no single diabetes diet.
That said, adding certain foods to your grocery list can make it easier to whip up balanced meals and snacks that help keep your blood sugar in a healthy range.
Here are nine items that dietitians recommend. Time to get cracking. In addition, nuts make a great addition to any meal, as the fat and fiber will slow the absorption of glucose into your bloodstream. Choose the type of nut that you like the best, whether that's pistachios, almonds, walnuts or a variety, for Sweet and Salty Roasted Nuts.
Whole nuts are great, but when you'd rather have something spreadable, nut butters are another fantastic choice. Because they're high in fiber and lower in sugar than some other fruits, berries are a fantastic way to add sweetness and flavor to a meal or snack.
For instance, some research has found that eating a diet higher in specific antioxidants called anthocyanins from which berries get their bright colors is associated with a lower risk of heart attacks and a reduced risk of hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease, according to a review in Advances in Nutrition.
Tangy and creamy, "this versatile food can be a great way to boost the protein content of a variety of recipes or foods to help reduce the impact on blood sugar," says Erin Palinski-Wade , RD, CDCES, a New Jersey-based dietitian and the author of 2 Day Diabetes Diet.
According to a study published in in the Journal of Food Science and Technology , eating chickpeas at meals may help to reduce post-meal blood glucose levels and improve appetite regulation, adds Palinski-Wade.
It's not just chickpeas that are great for managing blood sugar— other beans, from black to pinto and kidney, have a similar effect. To maximize the resistant starch content of beans, let them cool after cooking, or purchase canned varieties , research suggests.
Beans are also high in soluble fiber, which can help slow digestion and potentially lower LDL cholesterol. According to a meta analysis in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition , consuming oat beta glucans decreases blood sugar and insulin responses to a carbohydrate-containing meal in people with or without diabetes.
Sprinkle on some seeds! If you're not sure how to use chia seeds, start by stirring them into your morning oatmeal or yogurt, or toss a tablespoonful into your salad. Dietitians recommend eating nonstarchy vegetables to boost the nutrient and fiber content of your meals. All nonstarchy vegetables are a fantastic choice, but Sheth thinks broccoli deserves a special shoutout.
Sulforaphane is a compound found in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli that has potential cancer-protecting properties. You can't go wrong with a broccoli-and-chicken stir-fry, steamed broccoli next to salmon or a few broccoli florets dipped in hummus. Use limited data to select advertising.
Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content.
Use profiles to select personalised content. With diabetes, it's important to be prepared for times of illness. When you're sick, your body makes stress-related hormones that help fight the illness. But those hormones also can raise your blood sugar.
Changes in your appetite and usual activity also may affect your blood sugar level. Plan ahead. Work with your healthcare team to make a plan for sick days. Include instructions on what medicines to take and how to adjust your medicines if needed.
Also note how often to measure your blood sugar. Ask your healthcare professional if you need to measure levels of acids in the urine called ketones. Your plan also should include what foods and drinks to have, and what cold or flu medicines you can take.
Know when to call your healthcare professional too. For example, it's important to call if you run a fever over degrees Fahrenheit Keep taking your diabetes medicine. But call your healthcare professional if you can't eat because of an upset stomach or vomiting.
In these situations, you may need to change your insulin dose. If you take rapid-acting or short-acting insulin or other diabetes medicine, you may need to lower the dose or stop taking it for a time.
These medicines need to be carefully balanced with food to prevent low blood sugar. But if you use long-acting insulin, do not stop taking it. During times of illness, it's also important to check your blood sugar often. Stick to your diabetes meal plan if you can.
Eating as usual helps you control your blood sugar. Keep a supply of foods that are easy on your stomach. These include gelatin, crackers, soups, instant pudding and applesauce. Drink lots of water or other fluids that don't add calories, such as tea, to make sure you stay hydrated.
If you take insulin, you may need to sip sugary drinks such as juice or sports drinks. These drinks can help keep your blood sugar from dropping too low.
It's risky for some people with diabetes to drink alcohol. Alcohol can lead to low blood sugar shortly after you drink it and for hours afterward. The liver usually releases stored sugar to offset falling blood sugar levels.
But if your liver is processing alcohol, it may not give your blood sugar the needed boost. Get your healthcare professional's OK to drink alcohol. With diabetes, drinking too much alcohol sometimes can lead to health conditions such as nerve damage.
But if your diabetes is under control and your healthcare professional agrees, an occasional alcoholic drink is fine. Women should have no more than one drink a day. Men should have no more than two drinks a day. One drink equals a ounce beer, 5 ounces of wine or 1. Don't drink alcohol on an empty stomach.
If you take insulin or other diabetes medicines, eat before you drink alcohol. This helps prevent low blood sugar.
Or drink alcohol with a meal. Choose your drinks carefully. Light beer and dry wines have fewer calories and carbohydrates than do other alcoholic drinks.
If you prefer mixed drinks, sugar-free mixers won't raise your blood sugar. Some examples of sugar-free mixers are diet soda, diet tonic, club soda and seltzer.
Add up calories from alcohol. If you count calories, include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily count. Ask your healthcare professional or a registered dietitian how to make calories and carbohydrates from alcoholic drinks part of your diet plan.
Check your blood sugar level before bed. Alcohol can lower blood sugar levels long after you've had your last drink. So check your blood sugar level before you go to sleep.
The snack can counter a drop in your blood sugar. Changes in hormone levels the week before and during periods can lead to swings in blood sugar levels. Look for patterns. Keep careful track of your blood sugar readings from month to month. You may be able to predict blood sugar changes related to your menstrual cycle.
Your healthcare professional may recommend changes in your meal plan, activity level or diabetes medicines. These changes can make up for blood sugar swings.
Check blood sugar more often. If you're likely nearing menopause or if you're in menopause, talk with your healthcare professional. Ask whether you need to check your blood sugar more often.
Also, be aware that menopause and low blood sugar have some symptoms in common, such as sweating and mood changes. So whenever you can, check your blood sugar before you treat your symptoms.
That way you can confirm whether your blood sugar is low. Most types of birth control are safe to use when you have diabetes.
But combination birth control pills may raise blood sugar levels in some people. It's very important to take charge of stress when you have diabetes. The hormones your body makes in response to prolonged stress may cause your blood sugar to rise.
It also may be harder to closely follow your usual routine to manage diabetes if you're under a lot of extra pressure. Take control. Once you know how stress affects your blood sugar level, make healthy changes.
Learn relaxation techniques, rank tasks in order of importance and set limits. Whenever you can, stay away from things that cause stress for you. Exercise often to help relieve stress and lower your blood sugar. Get help. Learn new ways to manage stress.
You may find that working with a psychologist or clinical social worker can help. These professionals can help you notice stressors, solve stressful problems and learn coping skills.
The more you know about factors that have an effect on your blood sugar level, the better you can prepare to manage diabetes. If you have trouble keeping your blood sugar in your target range, ask your diabetes healthcare team for help.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar. Products and services. Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes management takes awareness.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care.
Nutrition overview. American Diabetes Association. Accessed Dec. Diabetes and mental health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Insulin storage and syringe safety. Diabetes diet, eating, and physical activity. Type 2 diabetes mellitus adult. Mayo Clinic; Wexler DJ. Initial management of hyperglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes and women. Planning for sick days.
Diabetes: Managing sick days. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Hypoglycemia low blood glucose. Blood glucose and exercise.
Riddell MC. Exercise guidance in adults with diabetes mellitus. Colberg SR, et al. Palermi S, et al. The complex relationship between physical activity and diabetes: An overview. Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology.
Take charge of your diabetes: Your medicines. Sick day management for adults with type 1 diabetes. Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists. Alcohol and diabetes. Diabetes and nerve damage. Roe AH, et al. Combined estrogen-progestin contraception: Side effects and health concerns.
Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?
Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides?
Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate?
Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe?
High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern? Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure?
Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection?
Our Post-workout recovery smoothies advice is expert-vetted. If you buy through our links, we may Stabilify a blopd. Reviews ethics statement. Keeping your blood sugar levels balanced can make you feel less hangry and more satisfied. Having balanced blood sugar levels is important in the context of diseases like diabetes. Your blood sugar target is the range eugar try to blood sugar stability as much as possible. Read sttability Monitoring Stabillity Blood Sugar and All About Your A1C. Staying in your target range can also help improve your energy and mood. Find answers below to common questions about blood sugar for people with diabetes. Use a blood sugar meter also called a glucometer or a continuous glucose monitor CGM to check your blood sugar.
Es gibt die Webseite, mit der riesigen Zahl der Informationen nach dem Sie interessierenden Thema.