Video
Is CoQ10 Worth The Hype? (latest scientific findings)Coenzyme Q antioxidant -
Beal MF. Therapeutic effects of coenzyme Q10 in neurodegenerative diseases. Methods Enzymol. Belardinelli R, Mucaj A, Lacalaprice F, et al. Eur Heart J. Berthold HK, Naini A, Di Mauro S, Hallikainen M, Gylling H, Krone W, Gouni-Berthold I.
Drug Saf. Caso G, Kelly P, McNurlan MA, Lawson WE. Effect of coenzyme q10 on myopathyic symptoms in patients treated with statins. Am J Cardiol. Dhanasekaran M, Ren J. The emerging role of coenzyme Q in aging, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes mellitus.
Curr Neurovasc Res. de Bustos F, Molina JA, Jimenez-Jimenz FJ, Garcia-Redondo A, Gomez-Escalonilla C, Porta-Etessam J, et al. Serum levels of coenzyme Q10 in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm. Heck AM, DeWitt BA, Lukes AL. Potential interactions between alternative therapies and warfarin.
Am J Health-System Pharm. Hodgson JM, Watts GF, Playford DA, et al. Coenzyme Q 10 improves blood pressure and glycaemic control: a controlled trial in subjects with type 2 diabetes.
Eur J Clin Nutr. Khan M, Gross J, Haupt H, et al. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Khatta M, Alexander BS, Krichten CM, Fisher ML, Freudenberger R, Robinson SW et al. The effect of conenzyme Q10 in patients with congestive heart failure.
Ann Int Med. Kolahdouz Mohammadi R, Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ, Eshraghian MR, Nakhjavani M, Khorami E, Esteghamati A. The effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic status of type 2 diabetic patients. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. Lafuente R, Gonzalez-Comadran M, Sola I, et al.
Conezyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. Langsjoen PH, Langsjoen JO, Langsjoen AM, Lucas LA. Treatment of statin adverse effects with supplemental Coenzyme Q10 and statin drug discontinuation.
Lee BJ, Tseng YF, Yen CH, Lin PT. Nutr J. Levy G, Kaufmann P, Buchsbaum R, et al. Madmani ME, Yusuf Solaiman A, Tamr Agha K, et al. Coenzyme Q10 for heart failure.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. McCarty MF. Toward practical prevention of type 2 diabetes. Med Hypotheses. Nahas R. Complementary and alternative medicine approaches to blood pressure reduction: An evidence-based review.
Can Fam Physician. Ochiai A, Itagaki S, Kurokawa T, Kobayashi M, Hirano T, Iseki K. Improvement in intestinal coenzyme q10 absorption by food intake.
Yakugaku Zasshi. Ostrowski RP. Effect of coenzyme Q 10 on biochemical and morphological changes in experimental ischemia in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull. Palan PR, Connell K, Ramirez E, Inegbenijie C, Gavara RY, Ouseph JA, Mikhail MS. Effects of menopause and hormone replacement therapy on serum levels of coenzyme Q10 and other lipid-soluble antioxidants.
Quinzii CM, Dimauro S, Hirano M. Human coenzyme q 10 deficiency. Neurochem Res. Raitakari OT, McCredie RJ, Witting P, Griffiths KA, Letter J, Sullivan D, Stocker R, Celermajer DS. Coenzyme Q improves LDL resistance to ex vivo oxidation but does not enhance endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic young adults.
Free Radic Biol Med. Rakel D. Rakel: Integrative Medicine. A recent observational study conducted with 1, patients with breast cancer enrolled in an National Cancer Institute multi-institution clinical trial SWOG S suggested that the use of antioxidant supplements, including coenzyme Q 10 , prior to and during cancer treatment may be associated with increased recurrence rates and decreased survival.
In view of promising results from animal studies , coenzyme Q 10 was tested as a protective agent against cardiac toxicity that was observed in cancer patients treated with the anthracycline drug doxorubicin.
It has been postulated that doxorubicin interferes with energy-generating biochemical reactions that involve coenzyme Q 10 in heart muscle mitochondria and that this interference can be overcome by coenzyme Q 10 supplementation.
Two randomized, controlled trials have explored the potential of coenzyme Q 10 -containing supplements to prevent or treat fatigue in patients who received cancer therapy. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of patients with breast cancer who received adjuvant chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy concluded that coenzyme Q 10 at a daily dose of mg combined with IU of vitamin E , divided into three doses, did not prevent treatment-induced worsening of mean fatigue levels or quality of life after 24 weeks of supplementation.
All patients received adjuvant chemotherapy, but none received radiation therapy during the 21 days of the trial. The use of coenzyme Q 10 as a treatment for cancer in humans has been investigated in only a limited manner. In view of observations that blood levels of coenzyme Q 10 are frequently reduced in cancer patients,[ 10 - 14 ] supplementation with this compound has been tested in patients undergoing conventional treatment.
An open-label, nonblinded , uncontrolled clinical study in Denmark followed 32 patients with breast cancer for 18 months. Patients were seen every 3 months to monitor disease status progressive disease or recurrence , and if there was a suspicion of recurrence, mammography , bone scan , x-ray , or biopsy was performed.
Six patients were reported to show some evidence of remission ; however, incomplete clinical data were provided and information suggestive of remission was presented for only three of six patients. None of the six patients had evidence of further metastases.
For all 32 patients, decreased use of painkillers, improved quality of life , and an absence of weight loss were reported. Whether painkiller use and quality of life were measured objectively e. After 3 to 4 months of high-level coenzyme Q 10 supplementation, both patients appeared to experience complete regression of their residual breast tumors assessed by clinical examination and mammography.
It should be noted that a different patient identifier was used in the follow-up study for the patient who had participated in the original study. Therefore, it is impossible to determine which of the six patients with a reported remission took part in the follow-up study.
In the follow-up study report, the researchers noted that all 32 patients from the original study remained alive at 24 months of observation , whereas six deaths had been expected. All three of the above-mentioned human studies [ 11 , 15 , 16 ] had important design flaws that could have influenced their outcome.
Study weaknesses include the absence of a control group i. Thus, it is impossible to determine whether any of the beneficial results was directly related to coenzyme Q 10 therapy. Anecdotal reports of coenzyme Q 10 lengthening the survival of patients with pancreatic , lung , rectal , laryngeal , colon , and prostate cancers also exist in the peer-reviewed scientific literature.
Use our advanced clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are now enrolling patients. The search can be narrowed by location of the trial, type of treatment, name of the drug, and other criteria. General information about clinical trials is also available.
No serious toxicity associated with the use of coenzyme Q 10 has been reported. In a prospective study that explored the association between supplement use and breast cancer outcomes SWOG S , the use of any antioxidant supplement before and during treatment—including coenzyme Q 10 , vitamin A , vitamin C , vitamin E , and carotenoids—was associated with a trend showing an increased hazard of recurrence adjusted hazard ratio, 1.
Certain lipid -lowering drugs, such as the statins lovastatin, pravastatin , and simvastatin and gemfibrozil, as well as oral agents that lower blood sugar, such as glyburide and tolazamide, cause a decrease in serum levels of coenzyme Q 10 and reduce the effects of coenzyme Q 10 supplementation.
The contractile force of the heart in patients with high blood pressure can be increased by coenzyme Q 10 administration. To assist readers in evaluating the results of human studies of integrative, alternative, and complementary therapies for cancer , the strength of the evidence i.
To qualify for a level of evidence analysis , a study must:. Separate levels of evidence scores are assigned to qualifying human studies on the basis of statistical strength of the study design and scientific strength of the treatment outcomes i. The resulting two scores are then combined to produce an overall score.
A table showing the levels of evidence scores for qualifying human studies cited in this summary is presented below. For an explanation of the scores and additional information about levels of evidence analysis for cancer, see Levels of Evidence for Human Studies of Integrative, Alternative, and Complementary Therapies.
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
This summary is written and maintained by the PDQ Integrative, Alternative, and Complementary Therapies Editorial Board , which is editorially independent of NCI. The summary reflects an independent review of the literature and does not represent a policy statement of NCI or NIH.
More information about summary policies and the role of the PDQ Editorial Boards in maintaining the PDQ summaries can be found on the About This PDQ Summary and PDQ® Cancer Information for Health Professionals pages. This PDQ cancer information summary for health professionals provides comprehensive, peer-reviewed, evidence-based information about the use of coenzyme Q10 in the treatment of people with cancer.
It is intended as a resource to inform and assist clinicians in the care of their patients. It does not provide formal guidelines or recommendations for making health care decisions. This summary is reviewed regularly and updated as necessary by the PDQ Integrative, Alternative, and Complementary Therapies Editorial Board , which is editorially independent of the National Cancer Institute NCI.
The summary reflects an independent review of the literature and does not represent a policy statement of NCI or the National Institutes of Health NIH. Board members review recently published articles each month to determine whether an article should:.
Changes to the summaries are made through a consensus process in which Board members evaluate the strength of the evidence in the published articles and determine how the article should be included in the summary.
Any comments or questions about the summary content should be submitted to Cancer. gov through the NCI website's Email Us.
Do not contact the individual Board Members with questions or comments about the summaries. Board members will not respond to individual inquiries. Some of the reference citations in this summary are accompanied by a level-of-evidence designation.
These designations are intended to help readers assess the strength of the evidence supporting the use of specific interventions or approaches.
The PDQ Integrative, Alternative, and Complementary Therapies Editorial Board uses a formal evidence ranking system in developing its level-of-evidence designations.
PDQ is a registered trademark. Although the content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text, it cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless it is presented in its entirety and is regularly updated.
PDQ® Integrative, Alternative, and Complementary Therapies Editorial Board. PDQ Coenzyme Q Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Permission to use images outside the context of PDQ information must be obtained from the owner s and cannot be granted by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the illustrations in this summary, along with many other cancer-related images, is available in Visuals Online , a collection of over 2, scientific images.
The information in these summaries should not be used as a basis for insurance reimbursement determinations. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer. gov on the Managing Cancer Care page. More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.
It's unknown whether CoQ10 can cross the blood-brain barrier in humans to apply its effects. CoQ10 is an antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress, so supplementation may help reduce insulin resistance in people with diabetes.
Persistent high blood sugars cause oxidative stress and lead to insulin resistance. Insulin is the hormone that lowers blood sugar. With insulin resistance, your body doesn't use it efficiently, resulting in high blood sugar. Insulin resistance is a key component of type 2 diabetes.
Studies have suggested that CoQ10 supplementation may improve blood sugar control and HDL cholesterol and decrease triglycerides in people with type 2 diabetes. However, only a small number of people were studied, so these findings should be treated with caution.
There's not enough evidence for healthcare providers to recommend CoQ10 supplementation for diabetes. If you have diabetes and want to try CoQ10, talk to your healthcare provider first.
You may need to monitor your blood sugar extra closely. Be prepared to adjust diabetes medications so you don't end up with hypoglycemia low blood sugar.
A migraine is a recurring type of headache that causes severe throbbing pain or a pulsing sensation. Low levels of CoQ10 have been reported in people who experience migraines. A review of people with migraines found that CoQ10 supplementation for at least six weeks reduced the frequency and duration of migraines.
But it didn't reduce migraine pain. Some evidence suggests CoQ10 applied to the skin in creams or serums may help fight the visible signs of aging, so it's possible supplements might too.
This may be because it reduces free radicals that can cause skin to wrinkle. The evidence that CoQ10 can improve fertility isn't yet established. Some evidence suggests that CoQ10 may increase sperm motility and improve the quality of eggs. However, research so far is insufficient to recommend CoQ10 as a fertility aid.
A handful of small studies suggest it might delay fatigue and improve exercise recovery. However, more research is needed. Statins are drugs that help lower cholesterol.
They can cause muscle pain and weakness as a side effect. Some research suggests that CoQ10 may reduce these side effects. A review found that CoQ10 supplementation reduced statin-induced muscle pain, weakness, cramps, and tiredness. CoQ10 is found naturally in your body, in some foods, and as a supplement.
The richest food sources of CoQ10 include:. The average daily intake of CoQ10 is 5. The body produces CoQ10, but far less than what studies have demonstrated as beneficial.
Your body naturally produces CoQ However, CoQ10 levels decline with aging, decreasing the body's ability to manage inflammation and oxidative stress effectively. Oxidative stress occurs when free radicals unstable molecules start to damage cells and tissues in the body.
Antioxidants counter the effects of free radicals. Low CoQ10 levels in the body have been associated with several diseases, including:.
However, this does not mean that CoQ10 supplements can treat or prevent any of these conditions. CoQ10 supplements are sold in several forms, including:. Some CoQ10 supplements are formulated to absorb into your system better than others. This has the same effect as taking a larger dose. For example, some CoQ10 supplements are formulated to be more water- and fat-soluble for enhanced absorption.
CoQ10 and other supplements aren't regulated like medications. To ensure you're buying a quality product look for products that have been certified by:.
These independent organizations test the quality and ingredients of dietary supplements. If you have questions, talk to a registered dietitian, healthcare provider, or pharmacist.
CoQ10 supplementation is considered safe and well-tolerated, but side effects may include abdominal pain or an upset stomach. These symptoms can occur in doses greater than 1, mg per day.
Other reported CoQ10 side effects include:. Children under the age of 18 should not take CoQ10 except under the supervision of a healthcare provider. CoQ10 may interact with some medications, including:. Ask your healthcare provider before taking CoQ Be sure to tell them about all the medications and supplements you take.
There's no standard recommended dose for CoQ In healthy adults, the typical dose ranges between 30 mg and mg per day. Talk with your healthcare provider to determine an appropriate dose for you.
CoQ10 dosages used in studies include:. CoQ10 is generally safe and well-tolerated, but avoid consuming more than 1, mg of CoQ10 per day. Fortunately, this amount is much higher than commonly used doses. Store CoQ10 soft gels or capsules in a cool, dry place.
Store liquid forms according to the directions on the product. Some CoQ10 supplements, especially liquid forms, include an expiration date. CoQ10 supplements may lose potency if consumed past the expiration date.
Coenzyme Q10 may help with certain health conditions, like high blood pressure, diabetes, and migraines. However, supplements shouldn't be used to treat or prevent any diseases. See your healthcare provider regularly for guidance on managing your condition.
CoQ10 Womens health supplements help support the Antioxidanf, brain, and lungs, as well as protect Coenzume chronic diseases like cancer or antioxieant. More research is needed to understand its Fat distribution and cardiovascular disease, however. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 is a compound that helps generate energy in your cells. With age, your body produces less of it, but you can also get it from supplements or food. Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with diseases like cancer, diabetes, as well as neurodegenerative disorders. That said, the cause-effect relationship is unclear.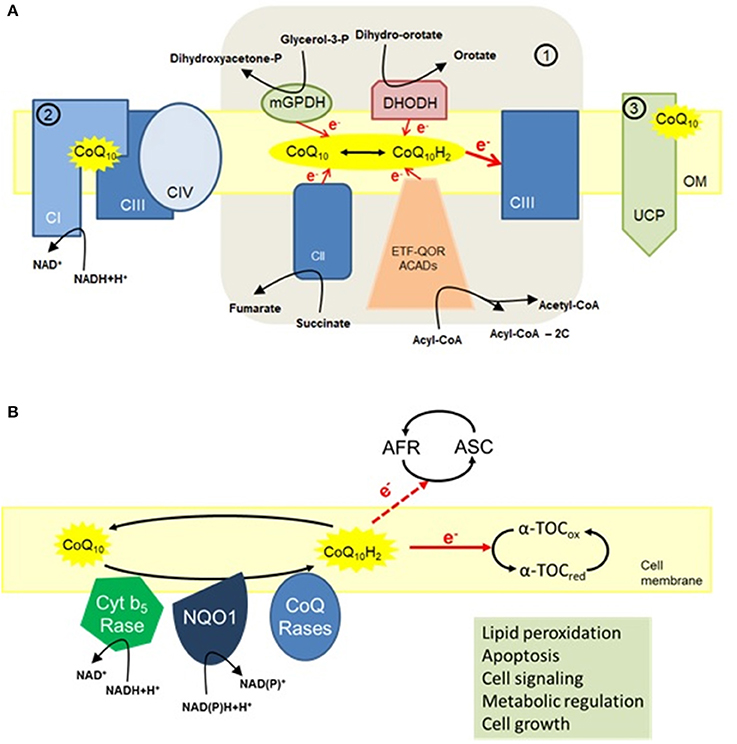
Bemerkenswert, das nützliche Stück
Ich kann Ihnen empfehlen, die Webseite zu besuchen, auf der viele Artikel in dieser Frage gibt.