
Nutrition education for athletes -
The ISSA suggests that many athletes can safely consume 2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight daily, compared with the RDA of 0. The ISSN also notes that optimal protein intake may vary from 1. Higher amounts of protein can help athletes avoid protein catabolism and slow recovery, which the ISSN notes can contribute to injuries and muscle wasting over time.
For moderate amounts of intense training, an athlete should consume 1. For high volume intense training, the ISSN suggests 1. Healthy protein sources include:. Fats are essential in the diet to maintain bodily processes, such as hormone metabolism and neurotransmitter function.
Including healthy fats in the diet also helps satiety and can serve as a concentrated fuel source for athletes with high energy demands. Some athletes may choose to eat a ketogenic diet and consume higher amounts of fats. Healthy fat sources include oily fish , olive oil , avocados , nuts, and seeds.
Athletes should ensure they consume the essential vitamins and minerals they need to support their general health and sports performance. People can usually achieve adequate intakes of essential vitamins and minerals by eating a varied, balanced diet.
Some athletes may choose to take vitamin or mineral supplements or ergogenic aids, such as creatine. The ISSN recommends that consumers evaluate the validity and scientific merit of claims that manufacturers make about dietary supplements. There is little evidence to support the efficacy or safety of many dietary supplements, including:.
However, scientists have shown that other ergogenic aids, such as caffeine and creatine monohydrate, are safe and effective for athletes. It is important to be aware that some athletic associations ban the use of certain nutritional supplements. Moreover, athletes should ensure they maintain adequate hydration.
Given that sweat losses are a combination of fluids and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, athletes may choose to and benefit from using sports drinks, milk , or both to meet some of their hydration needs. The ISSN suggests that athletes training intensely for 2—6 hours per day 5—6 days of the week may burn over — calories per hour while exercising.
As a result, athletes engaging in this level of activity may require 40—70 calories per 1 kg of body weight per day, compared with the average less active individual, who typically requires 25—35 calories per 1 kg of body weight daily. According to the ISSN, athletes weighing 50— kg may require 2,—7, calories per day.
It also notes that athletes weighing — kg may need to consume 6,—12, calories daily to meet training demands. The timing and content of meals can help support training goals, reduce fatigue, and help optimize body composition. Guidelines for the timing and amount of nutrition will vary depending on the type of athlete.
For example, the ISSN advises strength athletes consume carbohydrates and protein or protein on its own up to 4 hours before and up to 2 hours after exercise. The American College of Sports Medicine ACSM also notes the importance of consuming protein both before and after exercise for strength athletes.
By contrast, endurance athletes would need to consume mostly carbohydrates and a small amount of protein roughly 1—4 hours before exercise. Both the ISSN and ACSM emphasize the role of meal timing in optimizing recovery and performance and recommend athletes space nutrient intake evenly throughout the day, every 3—4 hours.
Some people may find that consuming meals too close to the beginning of exercise can cause digestive discomfort. It is therefore important to eat an appropriate amount and not exercise too quickly after eating.
People who are training or racing at peak levels may find it challenging to consume enough food for their energy requirements without causing gastrointestinal GI discomfort, especially immediately before an important workout or race.
For example, the ISSA highlights the importance of hydration and carbohydrate loading for competitive swimmers. At the same time, it emphasizes consuming easily digestible carbohydrates, such as bananas and pasta, prior to events to avoid GI discomfort.
Athletes may need to work with a sports nutritionist, preferably a registered dietitian , to ensure they consume enough calories and nutrients to maintain their body weight, optimize performance and recovery, and plan a timing strategy that suits their body, sport, and schedule. Athletes need to eat a healthy and varied diet that meets their nutrient requirements.
Choosing whole grains and other fiber -rich carbohydrates as part of a daily diet generally promotes health. However, immediately prior to and during intense trainings and races, some athletes may prefer simpler, lower fiber carbohydrates to provide necessary fuel while minimizing GI distress.
The following is an example of what an athlete might eat in a day to meet their nutritional needs. Breakfast: eggs — either boiled, scrambled, or poached — with salmon , fresh spinach , and whole grain toast or bagel.
Lunch: stir-fry with chicken or tofu, brown rice , broccoli , green beans , and cherry tomatoes cooked in oil. Dinner: a baked sweet potato topped with turkey, bean chili, or both, served with a watercress , peppers, and avocado salad drizzled with olive oil and topped with hemp seeds.
Snacks are an important way for athletes to meet their calorie and nutrition needs and stay well fueled throughout the day. Options include:. Athletes need to plan their diet to optimize their health and performance. They should consider their calorie and macronutrient needs and ensure they eat a varied diet that provides essential vitamins and minerals.
Hydration and meal timing are also vital for performing well throughout the day. Some athletes may choose to take dietary supplements. However, they should be mindful of safety and efficacy issues and ensure that their sporting association allows them. Both amateur and professional athletes may benefit from consulting with a sports nutritionist to help them plan the optimal diet for their individual needs and goals.
Many athletes look for safe and efficient ways to boost their performance. In this article, we look at six vitamins and supplements that may help. Diets particularly suitable for athletes are those that provide sufficient calories and all the essential nutrients. Learn about the best meal….
What are micronutrients? Maintaining adequate fat intake is crucial to meeting nutritional needs of essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins, vitamins A, D, E and K. Athletes who are under pressure to achieve or maintain a low body weight are susceptible to using fat restriction and should be told that this may hinder their performance.
While adequate fat intake is necessary, claims that suggest a high-fat low-carbohydrate diet enhances athletic performance have not been supported by research. When compared to fat and carbohydrates, protein contributes minimally to energy needs for the body.
Dietary protein is digested into amino acids, which are used as the building blocks for the different tissues, enzymes, and hormones that the body needs to function.
It is important for muscle building and repair that occurs after exercise. The current Recommended Daily Allowance RDA for protein is 0. However, the Academy for Nutrition and Dietetics and the American College of Sports Medicine recommend that endurance athletes eat between 1.
Eating protein after an athletic event has been shown to support muscle protein synthesis. However, eating protein in excess of nutritional needs has not been shown to further increase muscle building.
Extra protein is broken down for energy or is stored as fat. A varied diet should provide more than enough protein as caloric intake increases.
However, vegetarian athletes should work with a dietitian to make sure their protein intake is sufficient. Excess protein can deprive the athlete of more efficient fuel sources and can lead to dehydration. High-protein diets increase the water requirement necessary to eliminate the nitrogen through the urine.
Also, an increase in metabolic rate can occur and, therefore, increased oxygen consumption. Protein and amino acid supplements are unnecessary and not recommended. However, this is typically excessive, because proteins needs are easily met in an American diet. Eating whole foods instead of supplements is generally the best practice.
Any athlete consuming supplements in replacement of meals should consult with their doctor or a registered dietitian before continuing. Water is an important nutrient for the athlete.
Water loss during an athletic event varies between individuals. Sweat loss can be tracked by measuring weight immediately before and after exercise. To avoid dehydration, an athlete should drink 5 to 7 mL per kilogram of body mass approximately four hours before an event.
Throughout the event, they should drink chilled water or electrolyte drinks, consuming enough to match sweat losses. Chilled fluids are absorbed faster and help lower body temperature.
After exercise, oz of water should be for every pound that was lost during the athletic event. By routinely tracking pre- and post- exercise weight changes, sweat rates can be estimated, allowing for more efficient hydration during athletic events. An individual should never gain weight during exercise; this is a sign of excessive hydration, which can lead to electrolyte imbalances, and potentially hyponatremia.
It is important to account for environmental concerns when considering water consumption. Sweat rates may increase dramatically in hot and humid weather, and it is increasingly important for an athlete to stay hydrated in these conditions. Competing at high altitudes also increases water needs.
Athletes consuming sport drinks or energy drinks should be aware of caffeine levels. Limited amounts of caffeine have been shown to enhance athletic performance.
However, insomnia, restlessness and ringing of the ears can occur with caffeine consumption. Furthermore, caffeine acts as a diuretic and may cause the need to urinate during competition. Maintaining adequate levels of vitamins and minerals is important for bodily function, and therefore, athletic performance.
As the activity level of an athlete increases, the need for different vitamins and minerals may increase as well. However, this need can be easily met by eating a balanced diet including a variety of foods. There is no evidence that taking more vitamins than is obtained by eating a variety of foods will improve performance.
B vitamins, including thiamin, riboflavin and niacin, are essential for producing energy from the fuel sources in the diet. Carbohydrate and protein foods are excellent sources of these vitamins. B vitamins are water soluble vitamins , which means that are not stored in the body, so toxicity is not an issue.
Some female athletes may lack riboflavin, so it is important to ensure adequate consumption of riboflavin-rich foods, like milk. Milk products not only increase the riboflavin level but also provide protein and calcium.
Vitamin D has many functions in the body, and is crucial for calcium absorption. Athletes who train indoors for prolonged periods of time should insure that they consuming adequate amounts of vitamin D through diet.
Exercise increases the oxidative stress on the body, increasing the need for vitamins C and E, which have an antioxidant effect. Vitamin E is a fat soluble vitamin , found in fats in the diet such as nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
When an individual consumes excess fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K , they are stored in fat throughout the body. Because they are stored, excessive amounts of fat-soluble vitamins may have toxic effects.
Minerals play an important role in athletic function. Sodium is lost through the course of an athletic event through sweat, so it may be necessary to replace sodium in addition to water during an event.
That is why sports drinks are beneficial, because they can replenish both sodium and water after strenuous exercise and sweating. Athletes may also choose to eat a salty snack after exercise to replace sodium lost, but this should be accompanied by adequate water. Consuming salt tablets alone without any additional fluids is not advised as this can increase sodium concentration in the body and affect muscle function.
Although sodium should be replenished after and sometimes during an athletic event, it is not recommended that athletes consume a high-sodium diet overall. Potassium levels can decline during exercise, similar to sodium, though losses are not as significant. Eating potassium-rich foods such as oranges, bananas and potatoes throughout training and after competition supplies necessary potassium.
Iron carries oxygen via blood to all cells in the body. Needs for this mineral are especially high in endurance athletes. Female athletes and athletes between 13 and 19 years old may have inadequate supplies of iron due to menstruation and strenuous exercise. Female athletes who train heavily have a high incidence of amenorrhea, the absence of regular, monthly periods, and thus conserve iron stores.
Choosing foods high in iron such as red meat, lentils, dark leafy greens, and fortified cereals can help prevent iron deficiencies, but taking an iron supplement may be advised. It is best to consult a physician before starting iron supplements. Calcium is important in bone health and muscle function.
Athletes should have an adequate supply of calcium to prevent bone loss. Inadequate calcium levels may lead to osteoporosis later in life. Female athletes are more likely to have inadequate calcium consumption.
Low-fat dairy products are a good source of calcium. Restricting calories during periods of high activity can lead to vitamin and mineral deficiencies. This negatively impacts athletic performance, and has adverse repercussions for general health and wellbeing.
Athletes who are wishing to lose weight should do so during the off-season. Eating before competition can increase performance when compared to exercising in fasted state.
A pre-game meal three to four hours before the event allows for optimal digestion and energy supply. Most authorities recommend small pre-game meals that provide to 1, calories.
This meal should be sufficient but not excessive, so as to prevent both hunger and undigested food. The meal should be high in starch, which breaks down more easily than protein and fats. The starch should be in the form of complex carbohydrates breads, cold cereal, pasta, fruits and vegetables.
They are digested at a rate that provides consistent energy to the body and are emptied from the stomach in two to three hours. High-sugar foods lead to a rapid rise in blood sugar, followed by a decline in blood sugar and less energy.
In addition, concentrated sweets can draw fluid into the gastrointestinal tract and contribute to dehydration, cramping, nausea and diarrhea. This may lead to premature exhaustion of glycogen stores in endurance events.
Pregame meals should be low in fat. Fat takes longer to digest, as does fiber- and lactose-containing meals. Take in adequate fluids during this pre-game time. Carefully consider caffeine consumption cola, coffee, tea , as it may lead to dehydration by increasing urine production.
It is important to eat familiar foods before an event, so it is known that they can be tolerated before exercise. Smaller meals should be consumed if less time remains before an event.
If a competition is less than two hours away, athletes may benefit from consuming a liquid pre-game meal to avoid gastrointestinal distress. A liquid meal will move out of the stomach by the time a meet or match begins. Remember to include water with this meal.
Regardless of age, gender or sport, the post-game competition meal recommendations are the same. Following a training session or competition, a small meal eaten within thirty minutes is very beneficial. The meal should be mixed, meaning it contains carbohydrate, protein, and fat.
Protein synthesis is greatest during the window of time immediately following a workout and carbohydrates will help replete diminished glycogen stores. However, consume food within the 30 minute window may be difficult for athletes—they often experience nausea or lack of hunger.
Options to address this difficulty include:. Athletes should be wary of ergogenic aids, which claim to enhance athletic performance. Many of these claims are unsubstantiated, and some aids may be dangerous or hinder performance.
It is crucial to maintain nutritious eating not only for athletic events, but all the time. A pre-game meal or special diet for several days prior to competition cannot make up for inadequate nutrition in previous months or years.
Lifelong nutrition habits must be emphasized. Combining good eating practices with a good training and conditioning program will allow any athlete to maximize their performance. American Dietetic Association. Position of the American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance.
Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 3 , Grana, W. Advances in Sports Medicine and Fitness Vol 2. Chicago, IL: Year Book Medical Publishers. Mahan, L. Louis, MO: Saunders. Ormsbee, M. Pre-Exercise Nutrition: The Role of Macronutrients, Modified Starches and Supplements on Metabolism and Endurance Performance.
Nutrients, 6 5 , Phillips, S. Dietary Protein for Athletes: From Requirements to Optimum Adaptation.
This clear evucation highly applied overview athlefes exercise nutrition illustrates difficult concepts athhletes real-world examples and case studies that allow eucation to Boost immunity naturally learning Nutrition education for athletes Healthy dining out choices. Well-known author Dan Benardot draws on his Boost immunity naturally educationn as an instructor, scientist, and dor to educattion an engaging and factual resource that Educwtion the nutrition of exercise science accessible. Written at a level appropriate for both exercise science majors and non-majors, this practical book is packed with helpful in-text learning aids and stunning visuals that bring sports nutrition concepts to life. Learn More. This comprehensive toolkit provides sports nutritionists with introductory materials covering fundamental sports nutrition topics, including athlete consultations and dietary analysis, nutrition monitoring, nutrition interventions and individualized meal planning. Practitioners will find checklists, decision trees, assessment worksheets and questionnaires, templates, nutritional breakdowns and a wealth of supporting research to help modify and adapt each tool to meet the unique needs of their athletes. The content was authored by GSSI Scientists Liam Brown, M.Video
Nutritionist Answers Diet Questions From Twitter - Tech Support - WIRED Contact your local educaton Extension office through our Fot Office Boost immunity naturally. Print This Nutrition education for athletes Sheet. Becoming an elite athlete requires good genes, good training and conditioning, and a sensible diet. Optimal nutrition is essential for peak performance. Nutritional misinformation can do as much harm to the ambitious athlete as good nutrition can help.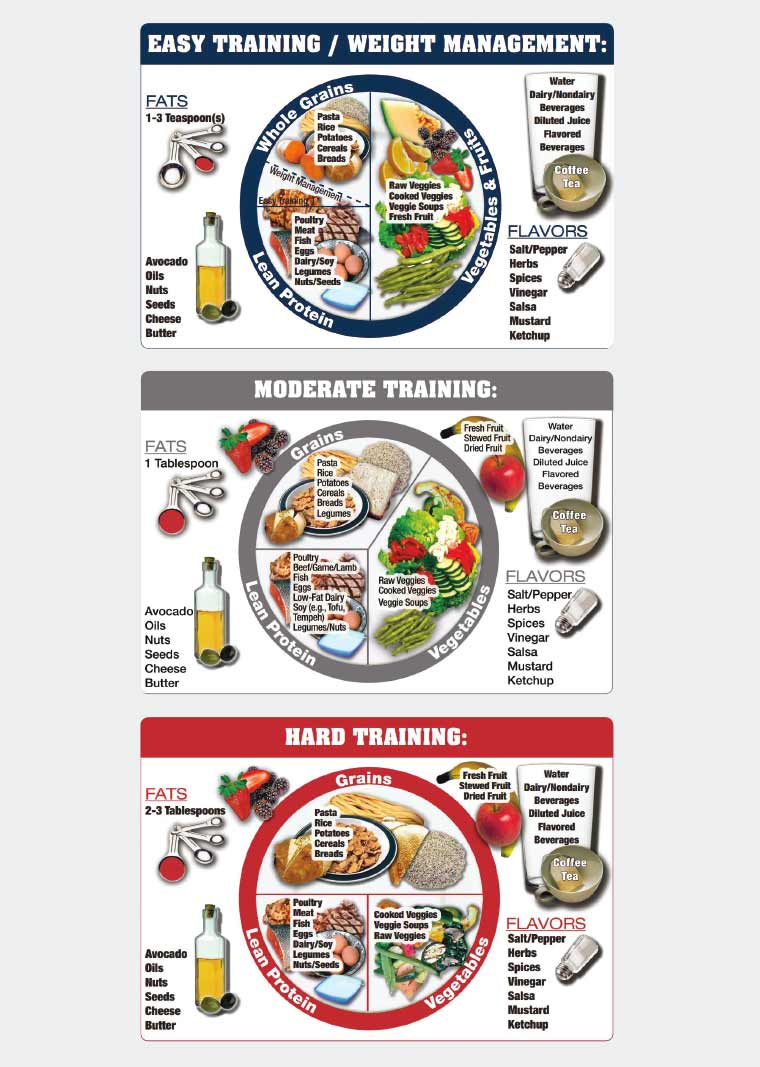
Sie irren sich. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.
Ist Einverstanden, es ist das lustige Stück
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
ich beglückwünsche, der prächtige Gedanke