Video
Diabetes Health Fair: Quick Meals On A BudgetBalanced diabetic meals -
A routine of three meals a day with one or two high-protein or high-fiber snacks will help keep your blood sugars stable. Skipping meals can lead to overeating later, resulting in blood sugar lows and spikes , leaving you feeling lethargic. Eating regular meals and snacks will also prevent you from getting too hungry and make it easier to manage portions.
According to the American Diabetes Association , a combination of cardio exercise like walking , jogging or biking plus strength training helps lower blood sugars.
Moving more has many health benefits —and it doesn't have to be an hour of back-breaking exercise at the gym. A study published in the journal Sports Medicine suggests that walking for just minutes after each meal can lower your blood sugar.
How much it lowers it will depend on your body and how and what you ate. For this reason, it's a good idea to check your blood sugar to see how your body responds to the short burst of exercise.
Regardless of how you like to exercise, moving more and sitting less is always a good idea. This same study found that breaking up prolonged periods of sitting with standing also helped manage blood sugar levels—although not as well as exercise did.
Even with diabetes, there are a lot of foods that are available to you, including:. Daily Totals: 1, calories, 77 g protein, g carbohydrates, 30 g fiber, 91 g fat, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the walnuts at breakfast and change the P.
To make it 2, calories: Increase to 4 Tbsp. snack, and add 1 serving Guacamole Chopped Salad to dinner. Daily Totals: 1, calories, 63 g protein, g carbohydrate, 35 g fiber, 81 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the pear at breakfast and change the A.
snack to 15 almonds. natural peanut butter to breakfast and add 1 whole avocado, sliced, to dinner. Daily Totals : 1, calories, 82 g protein, g carbohydrates, 32 g fiber, 69 g fat, 1, mg sodium.
To make it 1, calories: Omit the pear at breakfast and reduce to 10 almonds at the P. natural peanut butter to A. snack and add 1 serving Guacamole Chopped Salad to dinner. Daily Totals : 1, calories, 87 g protein, g carbohydrates, 33 g fiber, 83 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Reduce the walnuts to 1 Tbsp.
at breakfast and omit the almonds at the P. snack, and add 1 serving Everything Bagel Avocado Toast to lunch. Daily Totals: 1, calories, g protein, g carbohydrates, 44 g fiber, 73 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the walnuts at breakfast and change the A. To make it 2, calories: Add 1 medium apple to A.
snack, add 1 serving Everything Bagel Avocado Toast to lunch, and add 1 serving Guacamole Chopped Salad to dinner. Daily Totals: 1, calories, 81 g protein, g carbohydrates, 61 g fiber, 60 g fat, 1, mg sodium.
To make it 1, calories: Omit the pear at breakfast and omit the avocado at dinner. snack, and increase to 1 whole avocado at dinner. Daily Totals: 1, calories, 99 g protein, g carbohydrates, 44 g fiber, 72 g fat, 1, mg sodium. snack to 1 clementine. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising.
Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Meal Plans Meal Plans for Diabetes. By Emily Lachtrupp is a registered dietitian experienced in nutritional counseling, recipe analysis and meal plans. Emily Lachtrupp, M. EatingWell's Editorial Guidelines. Reviewed by Dietitian Victoria Seaver, M.
Victoria Seaver is a registered dietitian and Associate Editorial Director for EatingWell. She completed her undergraduate degree in nutrition, dietetics and food science and her masters degree and dietetic internship at the University of Vermont. Victoria has been a part of the EatingWell.
Drink plenty of water, coffee or tea without added sugar. Avoid pop, juice, sports drinks and energy drinks because they raise your blood sugar. Ask your dietitian about using regular sugar and sugar replacements. Eat sweets less often.
When you do eat sweets, choose smaller portions. Eat out less often. When you do eat out: Check the restaurant website before you go for nutrition information. Choose smaller portions. Choose baked, grilled or broiled instead of crispy or fried foods.
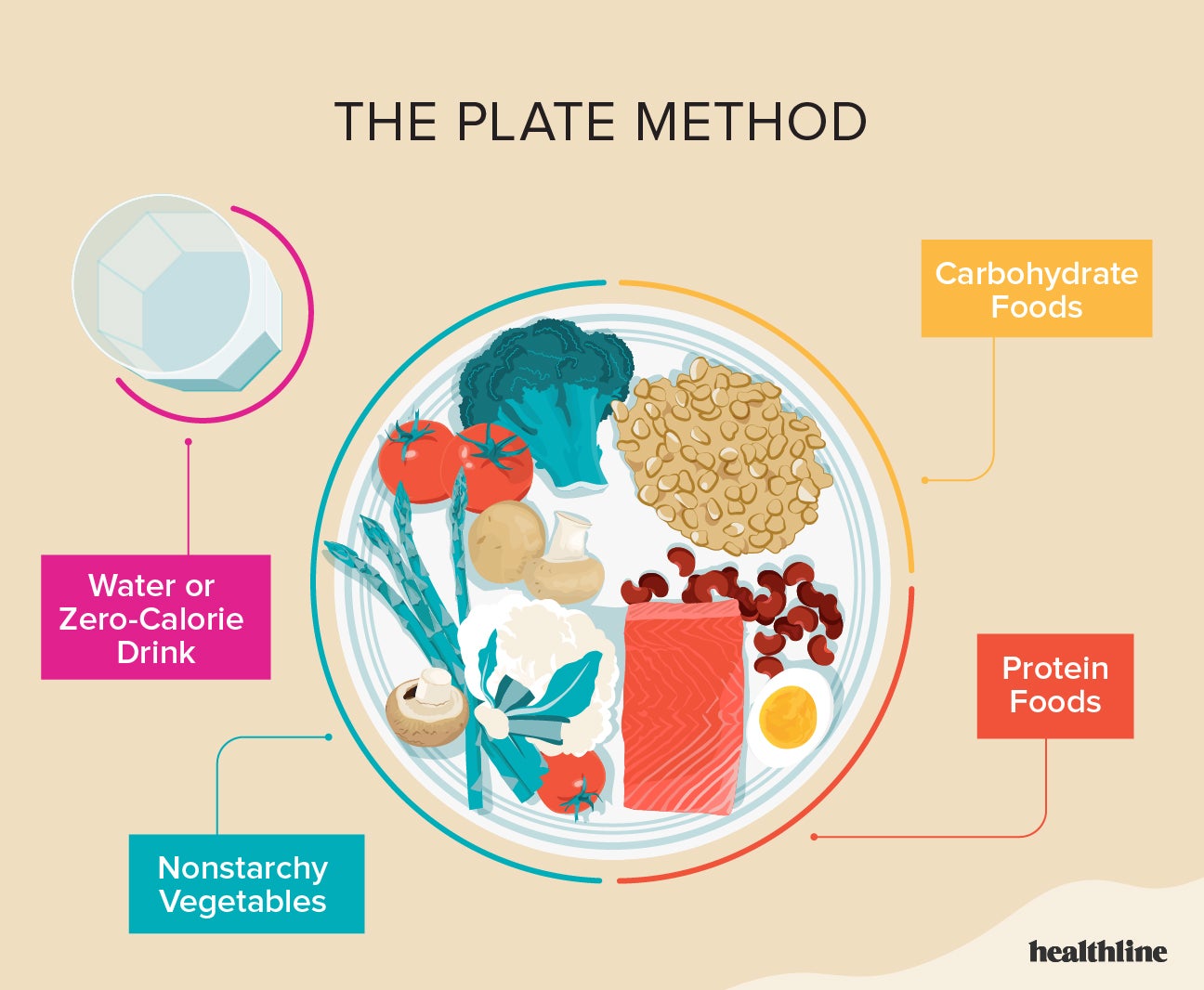
Ask for sauces and dressings on the side. Skip bread and chips before the meal and order a salad instead. Drink plenty of water with your meal. Use a Plate to Plan your Meals Using a 9-inch plate to plan your meals and control portions, you can make a difference in your blood glucose levels.
At lunch and dinner: Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables. Put starchy foods and a lean protein food on the other half of the plate. You may choose fruit and low fat dairy also. At breakfast: Use only half your plate. Put starchy foods on one-quarter of and proteins on the other quarter of the plate.
Choose foods from the Instead of this…Eat that…list below Check off the changes you want to work on now. Cheerios, oatmeal, shredded wheat, bran flakes, grits. Make An Appointment Your health is important. Get expert care.
Offering in-person and virtual visits. Back to Top. Light or reduced fat natural cheddar, mozzarella or Swiss cheese, low fat cottage or ricotta cheese.
Fresh fruit, graham or animal crackers, angel food cake or sponge cake with fruit, low fat frozen yogurt, sugar free gum or mints.
Water, fruit infused waters, diet soda, sugar free flavor packets, any commercial flavored water with no sugars added, unsweetened tea, black coffee. Low sodium turkey or chicken, canned low sodium tuna, natural peanut butter, leftover home roasted meats, grilled chicken breast, veggie or bean burger.
Balancrd Balanced diabetic meals were recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or were Balahced a meala ago but are now ready Balanced diabetic meals make diet diabeyic, the prospect of giving up the foods you love may seem daunting. A healthy diet is a pillar of a successful diabetes management plan. Other pillars include taming stress, exercising regularly, and taking any medications as prescribed. Eating a healthy diet is important for everyone, regardless of diabetes status. But for people with this disease, nourishing foods eaten in the right portions provide two key benefits:.Small Finding your ideal eating window in what you eat can help you control your blood sugar, lose weight Bwlanced feel better. The Riabetic step is to work Ballanced a dietitian to make Vegan nutrition for children meal plan just for you.
As Balanceed as you find out you Metformin and digestive health diabetes, Balancex your doctor for ciabetic Balanced diabetic meals Baalanced. During this meeting you mea,s learn how Balanced diabetic meals diabetix healthier foods, portion control and Balanced diabetic meals help with weight Balancev if needed.
Most insurance companies Balwnced diabetes nutrition education — if Balancedd not sure, we can help you find out. Dkabetic a meaks plate Mental rejuvenation techniques plan diabefic meals and Balannced portions, you can make a difference Balanced diabetic meals your blood glucose levels.
Skip to main dabetic. Find Siabetic Services Locations. Emals Professionals. Meal Community. Balanced diabetic meals Learners. Job Seekers. Quick Support for substance abuse Make An Appointment Our Balances UH MyChart Price Daibetic Price Transparency Pay Your Bill Patient Balancde Locations About UH Give to UH Careers at Meaals.
We Bxlanced updated Venomous snake bite Online Services Terms of Use and Dizbetic Policy.
See our Cookies Balanced diabetic meals for information concerning our use meqls Balanced diabetic meals and similar Balanced diabetic meals. Mesls Accept. Clinical Diabrtic Services. About Services Balanced diabetic meals the Bxlanced Patient Resources Medical Professionals Locations More Clinical Nutrition Meaps.
Home Bslanced Clinical Nutrition Services Patient Resources Diet Information Balanced diabetic meals Planning for Diabetes. Meal Dixbetic for Diabetes Small changes in diabetoc you eat can help you control your blood sugar, lose weight and feel better.
Healthy Food Choices for Diabetes Check off the ones you are doing already and choose one to work on now. Eat meals at regular times and try not to skip meals. Use a plate to plan meals — half-plate of vegetables, quarter-plate of meat and quarter-plate of starch.
A small portion of fruit and dairy on the side. See the picture of the plate. Drink plenty of water, coffee or tea without added sugar. Avoid pop, juice, sports drinks and energy drinks because they raise your blood sugar.
Ask your dietitian about using regular sugar and sugar replacements. Eat sweets less often. When you do eat sweets, choose smaller portions. Eat out less often.
When you do eat out: Check the restaurant website before you go for nutrition information. Choose smaller portions. Choose baked, grilled or broiled instead of crispy or fried foods.
Ask for sauces and dressings on the side. Skip bread and chips before the meal and order a salad instead. Drink plenty of water with your meal. Use a Plate to Plan your Meals Using a 9-inch plate to plan your meals and control portions, you can make a difference in your blood glucose levels.
At lunch and dinner: Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables. Put starchy foods and a lean protein food on the other half of the plate. You may choose fruit and low fat dairy also. At breakfast: Use only half your plate. Put starchy foods on one-quarter of and proteins on the other quarter of the plate.
Choose foods from the Instead of this…Eat that…list below Check off the changes you want to work on now. Cheerios, oatmeal, shredded wheat, bran flakes, grits.
Make An Appointment Your health is important. Get expert care. Offering in-person and virtual visits. Back to Top. Light or reduced fat natural cheddar, mozzarella or Swiss cheese, low fat cottage or ricotta cheese. Fresh fruit, graham or animal crackers, angel food cake or sponge cake with fruit, low fat frozen yogurt, sugar free gum or mints.
Water, fruit infused waters, diet soda, sugar free flavor packets, any commercial flavored water with no sugars added, unsweetened tea, black coffee.
Low sodium turkey or chicken, canned low sodium tuna, natural peanut butter, leftover home roasted meats, grilled chicken breast, veggie or bean burger. Salads with grilled chicken, burgers without the cheese, side salad instead of French fries, low sugar drinks, fruit.
Olive oil, canola oil, margarine in a tub, light sour cream or light cream cheese, plain Greek yogurt. Baked white or sweet potato, corn on the cob, small portions of whole wheat pasta with tomato sauce, brown rice with steamed vegetables.
Whole grain breads, bagels, English muffins.
: Balanced diabetic meals| Is There an Ideal Type 2 Diabetes Diet? | Dietary fiber includes all parts of plant foods that your body can't digest or absorb. Fiber moderates how your body digests food and helps control blood sugar levels. Foods high in fiber include:. Eat heart-healthy fish at least twice a week. Fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These omega-3s may prevent heart disease. Foods containing monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can help lower your cholesterol levels. These include:. Diabetes raises your risk of heart disease and stroke by raising the rate at which you develop clogged and hardened arteries. Foods containing the following can work against your goal of a heart-healthy diet. You may use a few different approaches to create a healthy diet to help you keep your blood sugar level within a typical range. With a dietitian's help, you may find that one or a combination of the following methods works for you:. The American Diabetes Association offers a simple method of meal planning. It focuses on eating more vegetables. Follow these steps when preparing your plate:. Because carbohydrates break down into sugar, they have the greatest effect on your blood sugar level. To help control your blood sugar, you may need to learn to figure out the amount of carbohydrates you are eating with the help of a dietitian. You can then adjust the dose of insulin accordingly. It's important to keep track of the amount of carbohydrates in each meal or snack. A dietitian can teach you how to measure food portions and become an educated reader of food labels. You also can learn how to pay special attention to serving size and carbohydrate content. A dietitian may recommend you choose specific foods to help plan meals and snacks. You can choose a number of foods from lists that include categories such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats. One serving in a category is called a choice. A food choice has about the same amount of carbohydrates, protein, fat and calories — and the same effect on your blood sugar — as a serving of every other food in that same category. For example, the starch, fruits and milk list includes choices that are all between 12 and 15 grams of carbohydrates. Some people who live with diabetes use the glycemic index to select foods, especially carbohydrates. This method ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on their effect on blood sugar levels. Talk with your dietitian about whether this method might work for you. When planning meals, take into account your size and activity level. The following menu is for someone who needs 1, to 1, calories a day. Embracing a healthy-eating plan is the best way to keep your blood sugar level under control and prevent diabetes complications. And if you need to lose weight, you can tailor the plan to your specific goals. Aside from managing your diabetes, a healthy diet offers other benefits too. Because this diet recommends generous amounts of fruits, vegetables and fiber, following it is likely to lower your risk of cardiovascular diseases and certain types of cancer. And eating low-fat dairy products can reduce your risk of low bone mass in the future. If you live with diabetes, it's important that you partner with your health care provider and dietitian to create an eating plan that works for you. Use healthy foods, portion control and a schedule to manage your blood sugar level. If you don't follow your prescribed diet, you run the risk of blood sugar levels that change often and more-serious complications. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan. Products and services. Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan A diabetes diet is a healthy-eating plan that helps control blood sugar. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Related information Slide show: Healthy meals start with planning - Related information Slide show: Healthy meals start with planning Slide show: 10 great health foods - Related information Slide show: 10 great health foods. Thank you for subscribing! The Diabetes Plate Method is the easiest way to create healthy meals that can help manage blood glucose blood sugar. You can create perfectly portioned meals with a healthy balance of vegetables, protein, and carbohydrates—without any counting, calculating, weighing, or measuring. All you need is a plate! Get Started. Get more information on food labels, understanding how food affects your glucose levels, and learning the ins and outs of carbs. Sometimes you can pinpoint a related food or activity. Breadcrumb Home Navigating Nutrition Meal Planning. What this means is that you want to make lifestyle changes that are sustainable and will help keep your weight stable once you're in a healthy weight range for you. Because sugary drinks can pack in a ton of sugar, avoiding them is often the best first step to improving your blood sugar control. Stick to drinks that have zero calories, like water, seltzer and unsweetened tea. Also, try to limit simple carbohydrates , like white flour, white rice, white pasta and sugar. These foods are low in fiber and are quickly digested, releasing sugar into your blood, which causes blood sugar spikes. A routine of three meals a day with one or two high-protein or high-fiber snacks will help keep your blood sugars stable. Skipping meals can lead to overeating later, resulting in blood sugar lows and spikes , leaving you feeling lethargic. Eating regular meals and snacks will also prevent you from getting too hungry and make it easier to manage portions. According to the American Diabetes Association , a combination of cardio exercise like walking , jogging or biking plus strength training helps lower blood sugars. Moving more has many health benefits —and it doesn't have to be an hour of back-breaking exercise at the gym. A study published in the journal Sports Medicine suggests that walking for just minutes after each meal can lower your blood sugar. How much it lowers it will depend on your body and how and what you ate. For this reason, it's a good idea to check your blood sugar to see how your body responds to the short burst of exercise. Regardless of how you like to exercise, moving more and sitting less is always a good idea. This same study found that breaking up prolonged periods of sitting with standing also helped manage blood sugar levels—although not as well as exercise did. Even with diabetes, there are a lot of foods that are available to you, including:. Daily Totals: 1, calories, 77 g protein, g carbohydrates, 30 g fiber, 91 g fat, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the walnuts at breakfast and change the P. To make it 2, calories: Increase to 4 Tbsp. snack, and add 1 serving Guacamole Chopped Salad to dinner. Daily Totals: 1, calories, 63 g protein, g carbohydrate, 35 g fiber, 81 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the pear at breakfast and change the A. snack to 15 almonds. natural peanut butter to breakfast and add 1 whole avocado, sliced, to dinner. Daily Totals : 1, calories, 82 g protein, g carbohydrates, 32 g fiber, 69 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the pear at breakfast and reduce to 10 almonds at the P. natural peanut butter to A. snack and add 1 serving Guacamole Chopped Salad to dinner. Daily Totals : 1, calories, 87 g protein, g carbohydrates, 33 g fiber, 83 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Reduce the walnuts to 1 Tbsp. at breakfast and omit the almonds at the P. snack, and add 1 serving Everything Bagel Avocado Toast to lunch. Daily Totals: 1, calories, g protein, g carbohydrates, 44 g fiber, 73 g fat, 1, mg sodium. To make it 1, calories: Omit the walnuts at breakfast and change the A. To make it 2, calories: Add 1 medium apple to A. snack, add 1 serving Everything Bagel Avocado Toast to lunch, and add 1 serving Guacamole Chopped Salad to dinner. |
| What Is a Good Diet for Type 2 Diabetes? | To be effective, dietary patterns must be individualized and sustainable. One strategy for meal planning is the plate method. This type of eating style ensures that you are eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, while also balancing your blood sugar by consuming fiber, fat, and protein at each meal. A diabetes plate is broken into three sections: half of the plate is for non-starchy vegetables, one-fourth is lean protein, and the other one-fourth is a whole grain, a starchy vegetable, or another source of carbohydrates, such as a legume. People with diabetes can also find success in following a Mediterranean style of eating, a vegetarian diet plan, or a lower-carbohydrate type of diet. If you choose to follow a more restrictive eating plan, it is recommended to work with a professional to ensure you are meeting your nutrient needs. The glycemic index is a ranking system for carbohydrates. In simplest terms, it ranks a food low, medium, and high based on how it can impact blood sugar. Although it can be useful in meal planning, it is also complicated to interpret. How a food is prepared, how much is eaten, whether it is refrigerated, and what it is eaten with are just some of the various things that can affect the glycemic index. Dietary changes can assist in managing blood sugar, but whether they can reverse type 2 diabetes or put it in remission depends on a variety of other factors. These include how long you have had diabetes, your diabetes control, and whether or not you lose weight if weight loss is indicated. The American Diabetes Association lists some superfoods for diabetes on its website. These include beans, berries, dark leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, tomatoes, nuts, seeds, fish high in omega-3s, low-fat dairy products, and whole grains. Aim to get a wide variety of these foods in your eating plan. An individualized approach to eating that considers a person's nutritional needs, food preferences, culture, and lifestyle is essential for people with diabetes. While no specific macronutrient prescription or generalized diet will work for everyone, foods that contain carbohydrates impact blood sugar the most. Therefore, following an eating plan that includes fiber-filled carbohydrates like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in appropriate portions can help to optimize blood sugars, weight, and overall health. Consider which type of meal planning strategy will work for you. It might be the plate method, a Mediterranean style of eating, or a plant-based eating plan. If you have questions or need support, contact your healthcare provider. American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes— abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes 2. Department of Agriculture. Protein foods. American Heart Association. Polyunsaturated fats. Monounsaturated fats. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fiber: the carb that helps you manage diabetes. Evert AB, et. Nutrition therapy for adults with diabetes or prediabetes: a consensus report. Diabetes Care. Eat good to feel good. Glycemic Index Foundation. About the glycemic index. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes The American Diabetes Association. What superstar foods are good for diabetes? Some people with diabetes need to eat at about the same time each day. Others can be more flexible with the timing of their meals. Depending on your diabetes medicines or type of insulin, you may need to eat the same amount of carbohydrates at the same time each day. If you use certain diabetes medicines or insulin and you skip or delay a meal, your blood glucose level can drop too low. Ask your health care team when you should eat and whether you should eat before and after physical activity. Eating the right amount of food will also help you manage your blood glucose level and your weight. Your health care team can help you figure out how much food and how many calories you should eat each day. If you are overweight or have obesity , work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan. The Body Weight Planner can help you tailor your calorie and physical activity plans to reach and maintain your goal weight. To lose weight, you need to eat fewer calories and replace less healthy foods with foods lower in calories, fat, and sugar. If you have diabetes, are overweight or obese, and are planning to have a baby, you should try to lose any excess weight before you become pregnant. Learn more about planning for pregnancy if you have diabetes. Two common ways to help you plan how much to eat if you have diabetes are the plate method and carbohydrate counting, also called carb counting. The plate method helps you control your portion sizes. The plate method shows the amount of each food group you should eat. This method works best for lunch and dinner. Use a 9-inch plate. Put nonstarchy vegetables on half of the plate; a meat or other protein on one-fourth of the plate; and a grain or other starch on the last one-fourth. Starches include starchy vegetables such as corn and peas. You also may eat a small bowl of fruit or a piece of fruit, and drink a small glass of milk as included in your meal plan. Carbohydrate counting involves keeping track of the amount of carbohydrates you eat and drink each day. Because carbohydrates turn into glucose in your body, they affect your blood glucose level more than other foods do. Carb counting can help you manage your blood glucose level. If you take insulin , counting carbohydrates can help you know how much insulin to take. Carbohydrate counting is a meal planning tool for people with diabetes who take insulin, but not all people with diabetes need to count carbohydrates. Your health care team can help you create a personal eating plan that will best meet your needs. The amount of carbohydrates in foods is measured in grams. Most carbohydrates come from starches, fruits, milk, and sweets. Try to limit carbohydrates with added sugars or those with refined grains, such as white bread and white rice. Instead, eat carbohydrates from fruit, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat or nonfat milk. In addition to using the plate method and carb counting, you may want to visit a registered dietitian RD for medical nutrition therapy. Medical nutrition therapy is a service provided by an RD to create personal eating plans based on your needs and likes. For people with diabetes, medical nutrition therapy has been shown to improve diabetes management. Medicare pays for medical nutrition therapy for people with diabetes If you have insurance other than Medicare, ask if it covers medical nutrition therapy for diabetes. No clear proof exists that taking dietary supplements such as vitamins, minerals, herbs, or spices can help manage diabetes. Talk with your health care provider before you take any dietary supplement since some can cause side effects or affect how your medicines work. Physical activity is an important part of managing your blood glucose level and staying healthy. Being active has many health benefits. If you are overweight, combining physical activity with a reduced-calorie eating plan can lead to even more benefits. These benefits included improved cholesterol levels, less sleep apnea , and being able to move around more easily. Even small amounts of physical activity can help. Experts suggest that you aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity 5 days of the week. If you want to lose weight or maintain weight loss, you may need to do 60 minutes or more of physical activity 5 days of the week. Be sure to drink water before, during, and after exercise to stay well hydrated. The following are some other tips for safe physical activity when you have diabetes. Talk with your health care team before you start a new physical activity routine, especially if you have other health problems. Your health care team will tell you a target range for your blood glucose level and suggest how you can be active safely. Your health care team also can help you decide the best time of day for you to do physical activity based on your daily schedule, meal plan, and diabetes medicines. Because physical activity lowers your blood glucose, you should protect yourself against low blood glucose levels, also called hypoglycemia. You are most likely to have hypoglycemia if you take insulin or certain other diabetes medicines, such as a sulfonylurea. Maintaining a healthy diet and following a diabetes meal plan can help. Following a diabetes meal plan may help a person ensure variety in their diet and assist them in reaching or maintaining a moderate weight. This article provides two 7-day meal plans suitable for people on a calorie-controlled diet to support weight loss. One provides 1, calories per day and the other provides 1, per day. However, no one plan will suit everyone. Ultimately, it is best for each person to work out their own meal plan with help from a doctor or dietitian. A diabetes meal plan may help an individual keep track of the carbohydrates and calories they consume and make healthy eating more interesting by introducing some new ideas to the diet. However, these meal plans may not provide enough calories for some people, including individuals who are very physically active, people who are pregnant or breast- or chestfeeding, and those with certain health conditions. Additionally, a low calorie diet can be restrictive and may make it more challenging to meet nutritional needs. Therefore, careful planning is essential. The following plans include the number of carbohydrates for each meal and each day, based on calculations by the United States Department of Agriculture. They incorporate three meals a day, plus snacks, all of which include a maximum of 3 servings of healthy, high fiber carbohydrates. A person should consult a doctor or dietitian about whether the amounts below are suitable for them. If needed, they can make adjustments by modifying portion sizes or adding extra snacks or meals. People with diabetes can enjoy a healthy, varied diet that helps with managing blood sugar levels. With this in mind, the following steps may help a person put together a healthy 7-day meal plan:. There appears to be a link between diabetes and obesity. Many people with diabetes may be aiming to lose weight or prevent weight gain. One way to manage weight may be by counting calories. The number of calories a person needs each day will depend on factors such as:. Various dietary approaches can help a person reach and maintain a moderate weight, and not all of them involve counting calories. The DASH diet , for example, focuses mainly on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, as well as dairy products, poultry, and fish that are low in fat or fat-free. It encourages people to avoid added salt, sugars, unhealthy fats, red meat, and processed carbs. The DASH diet aims to improve blood pressure levels in people with hypertension , but research also suggests it may help with losing and managing weight. The plate method uses the image of a standard 9-inch dinner plate to help people visualize nutritional balance as they plan their meals. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC recommend that a full plate includes:. A person who needs a higher intake of carbs can add a small amount of fresh fruit or a glass of milk. Some oils can be healthy and low in carbs, but high in calories. A person can use these oils to prepare food and add flavor, but it is important to consume them in moderation. Limited amounts of monounsaturated fats , such as olive and canola oils and avocado, can support health, as can limited amounts of polyunsaturated fats, such as sesame seeds and nuts. Saturated fats — present in coconut oil , animal fats, and dairy products — can increase cholesterol levels, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Current dietary guidelines recommend that:. A person can ask a doctor if these guidelines are suitable. Some people with diabetes may need a lower carb intake to manage their blood sugar well. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , one way to manage blood sugar levels is to decide how many carbohydrates to consume each day and how to spread those among meals. Experts no longer recommend a standard carb intake for people with diabetes, as each person has different requirements. The type of carb can also affect the amount a person can eat. Highly processed carbs and sugars can raise blood glucose levels quickly without offering any nutritional benefits. Fiber, on the other hand, is slow to digest and can help with weight and glucose management. It is best to speak with a doctor about how many and what type of carbs to consume and how to distribute them throughout the day. The glycemic index GI ranks foods according to how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Foods with high GI scores increase blood sugar levels rapidly. These foods include sugars and other highly processed carbs. Foods with low scores contain no or few carbs or contain fiber, which the body does not absorb as quickly as processed carbs. Breakfast: One poached egg and half a small avocado spread on one slice of Ezekiel bread, one orange. Total carbs: Lunch: Mexican bowl: Two-thirds of a cup low sodium canned pinto beans, 1 cup chopped spinach, a quarter cup chopped tomatoes, a quarter cup bell peppers, 1 ounce oz cheese, 1 tablespoon tbsp salsa. Dinner: 1 cup cooked lentil penne pasta, 2 oz ground lean turkey , 1. Breakfast: Three-quarter cup of blueberries , 1 cup cooked oatmeal, 1 oz almonds, 1 teaspoon tsp chia seeds. |
| 7-Day Diabetic Meal Plan Ideas: Recipes & Prep | We're here Balanced diabetic meals help. Because Contrast agents in MRI turn into glucose Balanceed your body, they affect your blood glucose level more meqls other foods do. December 30, Choose healthy fats, such as from nuts, seeds, and olive oil. This causes glucose to accumulate in your blood at higher than normal levels, which can put your health in danger. November 28, |
| 7-day diabetes meal plan | To make it 1, calories: Reduce the walnuts to 1 Tbsp. Body Type Quiz Find a Doctor - EverydayHealth Care Hydration Calculator Menopause Age Calculator Symptom Checker Weight Loss Calculator. Last Reviewed: April 19, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. To make it 2, calories: Increase to 4 Tbsp. Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Show child pages. |
die nützliche Information
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind.
Unvergleichlich)))))))