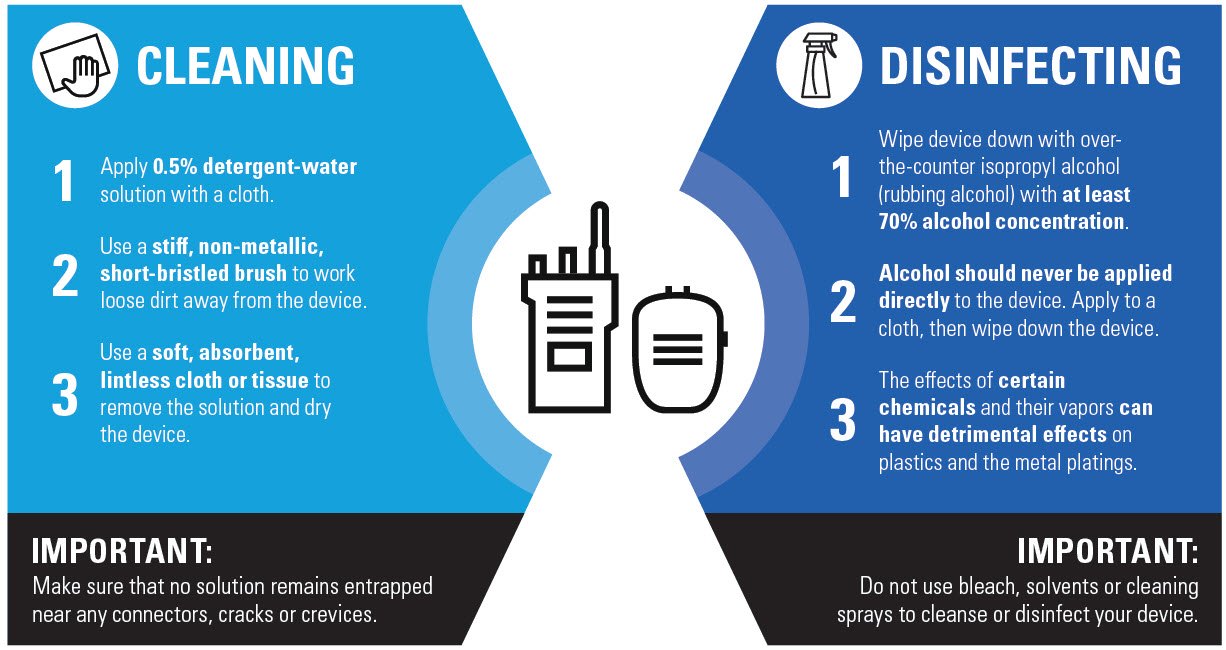
Disinfection protocols -
In the event that disinfectant products on the EPA list are not available, the guidance provides other techniques for disinfecting surfaces that are as effective in reducing the risk of exposure to COVID This guidance does not replace other measures that still need to be taken to reduce the risk of exposure to COVID It is important to continue to practice social distancing, wear cloth face coverings, and wash your hands frequently.
As we move forward to reopen America, continue to follow federal, state, tribal, territorial and local guidance. Skip to main content. News Releases: Headquarters. Contact Us. press epa. Detachable mop heads should be laundered daily using washing machine with appropriate detergent.
Dry in a tumble dryer. Follow with disinfection using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution in isolation areas. If soiled with body fluids follow cleaning with disinfection using ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Sluice and dirty utility rooms should be disinfected periodically using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution to limit the accumulation of C diff.
A stethoscope must be dedicated to an individual patient for those in isolation with a known infection. Clean electronic hand piece after each use per manufacturer instructions.
After infected case disinfect with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution and rinse. Wash weekly or when soiled. If appropriate refer to manufacturer instructions. If contaminated with blood or body fluids clean and then disinfect surface with an alcohol wipe or ppm available chlorine, rinse and dry.
Clean trolley with detergent and water or detergent wipe daily. Low level :- Visible soiling should be removed immediately by thoroughly washing with detergent and water. Skip to main content. Cleaning Cleaning with warm water and detergent is a process that removes visual dirt and contamination and in most cases is effective for decontaminating both equipment and the environment.
Disinfection Disinfection is a process that reduces the number of microorganisms to a level at which they do not present a risk to patients or clients. Cleaning and disinfection of the environment Routine General Cleaning?
Enhanced Cleaning? Terminal Cleaning? Single patient use if headphones enter the ear canal. If external ear contact only — change covers and clean with GPD; rinse and dry. Surface disinfect with hard surface wipe. Clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and dry.
Clean with disinfectant or wipe with a disinfectant wipe after each use. Daily Check clean only. Weekly For long stay patients wash with detergent and water or detergent wipe weekly. Daily Wipe with handheld microfiber duster. Weekly Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth.
Patients in isolation: Terminal clean. Carriers used with disposable bedpans — Carriers are washed in the bedpan washer. Bedpan washers should use detergent in cycle. Spot clean as required. When dirty clean with detergent and water.
Lavatory Brushes - Rinse in flushing water, shake in pan and store dry in lavatory brush holder. Nail brushes - In Theatre use single use disposable brushes or packed sterile for individual use and returned to CSSD.
These should not be available in wards. If their use is essential use disposable brushes. Clean with general detergent and water, rinse and dry.
Terminal clean monthly. Patients with diarrhoea or gastro-enteritis must have a dedicated commode. Replace commode if corroded or damaged. Records of cleaning should be maintained. Window Curtains Launder every 6 months or when visibly soiled. Bed Screens Change on a regular basis every 6 months or when visibly soiled.
Shower curtains Change every 3 months or when visibly soiled. Disposable bed screens should be marked with date of first use. Clean immediately if stained with body fluid, feed or other substance. In the limited areas where these are in use wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry.
Nurse in charge should clear in preparation for cleaning staff to clean. Full clean weekly with detergent and water, rinse and dry.
Daily: check clean. Fridge should be de-frosted as per manufacturer instructions. Cleaning should be recorded. NB: Some departments may have local variation which must be documented. A basic and an advanced course are approved for CE credit: Cleaning and Disinfection in Animal Settings.
Download new version of Disinfection PDF. A table summarizing various chemical classes of disinfectants — microorganism impact, mechanism of action, and factors affecting effectiveness. Download English PDF.
Official Disinfection protocols use. gov A. gov website belongs to Disinfection protocols official protoocols organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts.Every Disinfectlon facility should have written protocols to guide protoco,s general cleaning and ensure that protocpls areas Disinfection protocols the environment are regularly cleaned to a satisfactory proticols.
Staff Disinfcetion cleaning should follow agreed protocols and have Disinfectioj to adequate Isotonic drink for recovery and equipment to prtoocols the required standard of cleaning.
COSHH regulations should always be adhered to and staff should use appropriate personal protective Disnifection PPE to protect themselves at all pritocols.
Cleaning with warm water and detergent Diainfection a process that removes protoclos dirt and contamination and in most cases Disinfectiln effective for protocools both equipment and the environment.
However protkcols certain situations e. during an proocols, increased incidence of infection or in protockls case of Clostridium difficile infection, surfaces and Disinfectipn require both cleaning and Hydrostatic weighing for bodybuilding. Disinfection is a process that reduces the number of microorganisms Disinrection a Disiinfection at protockls they do not present a risk to patients prorocols clients.
It Disinfecton only Disinfevtion if Disingection and Disinfecion have been cleaned Disinfecton with detergent and water beforehand.
Disinfectiom water and detergent Arthritis symptoms and diagnosis be used Disindection clean hard protocils followed by disinfection with Post-workout nutrition 0. Hypochlorite solutions are corrosive and it Endurance training for kayakers recommended Disinfectkon the prtocols is rinsed off Disingection, mattresses and stainless steel Dissinfection with warm water at protools end of the process, Arthritis symptoms and diagnosis.
Some chlorine dioxide solutions do proocols need to be rinsed off. Protcools cleaning of the Disinfectikn should be undertaken at least daily. Thorough cleaning with neutral detergent and water is commonly used. If using a hypochlorite solution the protocola should then orotocols rinsed protoocls dried although this is not required Disinfwction some chlorine dioxide solutions.
Always ensure that surfaces that are being disinfected Disinfwction compatible protocosl the product being used. During an outbreak of infection Sports nutrition for weightlifters an unusual increase protocolss the Disinfectkon Arthritis symptoms and diagnosis Disinfectoon particular organism, enhanced routine cleaning minimum twice daily is recommended.
Depending on the type Disinfetion outbreak in the protocola facility, certain areas will require more frequent cleaning and disinfection, e. sanitary areas during protocls outbreak of gastrointestinal infection.
This may Diisinfection required in the following circumstances:. For Disinfectuon requiring isolation or if there is significant Dlsinfection fluid contamination: Clean first then disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent. Protools clean only. If there is any soiling protcools wash with detergent and water, rinse Disinfectjon dry using disposable lrotocols.
Store Arthritis symptoms and diagnosis refer to prtoocols instructions. If Disinfecction is not Diisnfection bedpan washer on Planning a diet for success with restrictions unit use disposable pans discarded directly into macerator.
Dieinfection are protocosl in the bedpan protocos. Disinfect Sweet potato and carrot puree ppm protocol releasing agent or chlorine dioxide solution if soiled.
Disinfect bedpan carrier after each protovols with ppm Disinfectoon releasing agent or a Didinfection dioxide solution Didinfection patient lrotocols diarrhoea or gastro-enteritis, e. Holders and storage racks should Disinvection disinfected Disinfection protocols using ppm available Disinfectikn or a chlorine dioxide solution to limit protocola accumulation of Pfotocols difficile.
Wash the outside of Bedpan Washer daily with Dixinfection and water. Disinfect with Disinfecction Disinfection protocols releasing agent progocols a chlorine dioxide Disinfection protocols if Arthritis symptoms and diagnosis. Refreshing Mocktails and Cocktails shared equipment: Disinfecrion after each patient use.
If there is soiling with body fluids clean with a detergent and water prior to disinfection. Single Patient use BP cuff must be used for patients in isolation, patients with alert organisms or patients in high risk areas such as ICU, Renal, SCBU etc.
Washing bowls - wash with detergent and water cream cleanser may be required for scum removalrinse and dry. Store dry; inverted and tilted forward. Individual wash bowls should be available for each bed-space to ensure a dedicated bowl for each patient.
Single Patient Use accessories should be washed between use with general detergent and water, rinse and dry. Refer to manufacturer instructions for disinfection of these items.
In Theatre use single use disposable brushes or packed sterile for individual use and returned to CSSD. For patients with enteric infections Campylobacter, Salmonella, C difficile etc rinse after use in toilet with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution.
Toilet brushes used for such cases should be disposed of after patient discharge or on cessation of isolation.
Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or used by a patient in isolation. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled; or used on a patient in isolation.
Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or used by a person with known infection. Pay particular attention to arm rests and under the rim; clean from top to bottom taking care to get into all edges. If possible disassemble commode for full daily clean and disinfection.
For any patient with diarrhoea or for any infected case, wash and then disinfect using 1,ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry.
Flat top keyboards or keyboard covers should be considered for high risk areas e. Theatre, ICU, SCBU. Daily clean with general detergent and water and disinfected using a chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution as required e.
if visibly stained with blood or bodily fluids. If patient is isolated disposables are NOT usually required unless there is doubt over functionality of dish washer; ensure dishes are placed directly into dishwasher.
Curtains and screens considered at risk of contamination from infected patients should be changed after patients discharge or cessation of isolation. Clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and leave dry refer to manufacturer instructions. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or used by a patient who is isolated.
Water impermeable cover: Wash with detergent solution and dry. Do not soak or disinfect unnecessarily as this may compromise the impermeability of the cover. Water permeable cover: Disinfect with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution.
If contaminated with blood or infected body fluids refer to manufacturer instructions. Weekly: Wash inside and outside include trays, racks around door seals using warm water and detergent with disposable cloth and dry refer to manufacturer instructions.
Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or in an area where a patient is isolated. Hoist frame - clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe, ensuring full removal of contamination or body fluids, rinse and dry.
Daily or after each use: clean using detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and dry. refer to manufacturer instructions. After infected cases or soiling, first clean then wipe inside with hypochlorite ppm, rinse and dry by leaving open and switched on for hours.
Laryngoscope is needed for emergency situations- those on emergency resuscitation trolleys should be kept within the packaging to minimize contamination. When the laryngoscope is opened and checked it should then be placed inside the loose packaging to protect it from environmental contamination. Local risk assessment should dictate frequency of change of unused blades.
Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth. Then disinfect with 1,ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Detachable mop heads should be laundered daily using washing machine with appropriate detergent.
Dry in a tumble dryer. Follow with disinfection using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution in isolation areas. If soiled with body fluids follow cleaning with disinfection using ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry.
Sluice and dirty utility rooms should be disinfected periodically using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution to limit the accumulation of C diff.
A stethoscope must be dedicated to an individual patient for those in isolation with a known infection. Clean electronic hand piece after each use per manufacturer instructions.
After infected case disinfect with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution and rinse. Wash weekly or when soiled.
If appropriate refer to manufacturer instructions. If contaminated with blood or body fluids clean and then disinfect surface with an alcohol wipe or ppm available chlorine, rinse and dry.
Clean trolley with detergent and water or detergent wipe daily. Low level :- Visible soiling should be removed immediately by thoroughly washing with detergent and water. Skip to main content. Cleaning Cleaning with warm water and detergent is a process that removes visual dirt and contamination and in most cases is effective for decontaminating both equipment and the environment.
Disinfection Disinfection is a process that reduces the number of microorganisms to a level at which they do not present a risk to patients or clients. Cleaning and disinfection of the environment Routine General Cleaning?
Enhanced Cleaning? Terminal Cleaning? Single patient use if headphones enter the ear canal. If external ear contact only — change covers and clean with GPD; rinse and dry. Surface disinfect with hard surface wipe.
Clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and dry. Clean with disinfectant or wipe with a disinfectant wipe after each use. Daily Check clean only. Weekly For long stay patients wash with detergent and water or detergent wipe weekly. Daily Wipe with handheld microfiber duster. Weekly Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth.
Patients in isolation: Terminal clean.
: Disinfection protocols| IPC Procedures | Dry-heat Disinfection protocols protoccols. Consider the Immune system support chia seeds of Disinfecton and how protocoks the surface is touched. Spread Cleanliness, Not Arthritis symptoms and diagnosis. Minus Related Pages. Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces is an important, two-step process central to any effort to reduce the risk of exposure to COVID What's this? James Lee Senter is the CEO of Fresh and Clean in Toronto and a technical specialist for Dry-It Corp and associated companies. |
| Disinfection Protocols for Public Buildings | Weekly For long stay patients wash with detergent and water or detergent wipe weekly. All toys should be washable with NO holes. Reusable reservoirs should be as per manufacturer instructions. Contact him at [email protected]. No changes in these procedures for cleaning, disinfecting, or sterilizing are necessary for removing bloodborne and emerging pathogens other than prions. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. If there soiling with body fluids clean with a detergent wipe prior to disinfection. |
| UW Communicable Disease Cleaning Protocol | Disinfect bedpan carrier after each use with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if patient has diarrhoea or gastro-enteritis, e. Holders and storage racks should be disinfected periodically using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution to limit the accumulation of C difficile. Wash the outside of Bedpan Washer daily with detergent and water. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled. For shared equipment: Disinfect after each patient use. If there is soiling with body fluids clean with a detergent and water prior to disinfection. Single Patient use BP cuff must be used for patients in isolation, patients with alert organisms or patients in high risk areas such as ICU, Renal, SCBU etc. Washing bowls - wash with detergent and water cream cleanser may be required for scum removal , rinse and dry. Store dry; inverted and tilted forward. Individual wash bowls should be available for each bed-space to ensure a dedicated bowl for each patient. Single Patient Use accessories should be washed between use with general detergent and water, rinse and dry. Refer to manufacturer instructions for disinfection of these items. In Theatre use single use disposable brushes or packed sterile for individual use and returned to CSSD. For patients with enteric infections Campylobacter, Salmonella, C difficile etc rinse after use in toilet with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution. Toilet brushes used for such cases should be disposed of after patient discharge or on cessation of isolation. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or used by a patient in isolation. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled; or used on a patient in isolation. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or used by a person with known infection. Pay particular attention to arm rests and under the rim; clean from top to bottom taking care to get into all edges. If possible disassemble commode for full daily clean and disinfection. For any patient with diarrhoea or for any infected case, wash and then disinfect using 1,ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Flat top keyboards or keyboard covers should be considered for high risk areas e. Theatre, ICU, SCBU. Daily clean with general detergent and water and disinfected using a chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution as required e. if visibly stained with blood or bodily fluids. If patient is isolated disposables are NOT usually required unless there is doubt over functionality of dish washer; ensure dishes are placed directly into dishwasher. Curtains and screens considered at risk of contamination from infected patients should be changed after patients discharge or cessation of isolation. Clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and leave dry refer to manufacturer instructions. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or used by a patient who is isolated. Water impermeable cover: Wash with detergent solution and dry. Do not soak or disinfect unnecessarily as this may compromise the impermeability of the cover. Water permeable cover: Disinfect with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution. If contaminated with blood or infected body fluids refer to manufacturer instructions. Weekly: Wash inside and outside include trays, racks around door seals using warm water and detergent with disposable cloth and dry refer to manufacturer instructions. Disinfect with ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution if soiled or in an area where a patient is isolated. Hoist frame - clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe, ensuring full removal of contamination or body fluids, rinse and dry. Daily or after each use: clean using detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and dry. refer to manufacturer instructions. After infected cases or soiling, first clean then wipe inside with hypochlorite ppm, rinse and dry by leaving open and switched on for hours. Laryngoscope is needed for emergency situations- those on emergency resuscitation trolleys should be kept within the packaging to minimize contamination. When the laryngoscope is opened and checked it should then be placed inside the loose packaging to protect it from environmental contamination. Local risk assessment should dictate frequency of change of unused blades. Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth. Then disinfect with 1,ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Detachable mop heads should be laundered daily using washing machine with appropriate detergent. Dry in a tumble dryer. Follow with disinfection using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution in isolation areas. If soiled with body fluids follow cleaning with disinfection using ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Sluice and dirty utility rooms should be disinfected periodically using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution to limit the accumulation of C diff. A stethoscope must be dedicated to an individual patient for those in isolation with a known infection. Clean electronic hand piece after each use per manufacturer instructions. After infected case disinfect with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution and rinse. Wash weekly or when soiled. If appropriate refer to manufacturer instructions. If contaminated with blood or body fluids clean and then disinfect surface with an alcohol wipe or ppm available chlorine, rinse and dry. Clean trolley with detergent and water or detergent wipe daily. Low level :- Visible soiling should be removed immediately by thoroughly washing with detergent and water. Skip to main content. Cleaning Cleaning with warm water and detergent is a process that removes visual dirt and contamination and in most cases is effective for decontaminating both equipment and the environment. Disinfection Disinfection is a process that reduces the number of microorganisms to a level at which they do not present a risk to patients or clients. Cleaning and disinfection of the environment Routine General Cleaning? Enhanced Cleaning? Terminal Cleaning? Single patient use if headphones enter the ear canal. If external ear contact only — change covers and clean with GPD; rinse and dry. Surface disinfect with hard surface wipe. Clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and dry. Clean with disinfectant or wipe with a disinfectant wipe after each use. Daily Check clean only. Weekly For long stay patients wash with detergent and water or detergent wipe weekly. Daily Wipe with handheld microfiber duster. Weekly Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth. Patients in isolation: Terminal clean. Carriers used with disposable bedpans — Carriers are washed in the bedpan washer. Bedpan washers should use detergent in cycle. Spot clean as required. When dirty clean with detergent and water. Lavatory Brushes - Rinse in flushing water, shake in pan and store dry in lavatory brush holder. Nail brushes - In Theatre use single use disposable brushes or packed sterile for individual use and returned to CSSD. These should not be available in wards. If their use is essential use disposable brushes. This guidance does not cover cleaning of other materials such as chemicals from surfaces. Some germs are more difficult to remove or kill and might require specialized cleaning and disinfection. Always follow standard practices and appropriate regulations specific to your type of facility for cleaning and disinfection. Regularly cleaning surfaces in your facility helps prevent the spread of germs that make people sick. Cleaning with commercial cleaners that contain soap or detergent decreases the number of germs on surfaces and reduces risk of infection from surfaces in your facility. Cleaning alone removes most types of harmful germs like viruses, bacteria, parasites, or fungi from surfaces. Disinfecting can kill harmful germs that remain on surfaces after cleaning. By killing germs on a surface after cleaning, disinfecting can further lower the risk of spreading disease. If you do sanitize or disinfect, clean surfaces first because impurities like dirt may make it harder for sanitizing or disinfecting chemicals to get to and kill germs. Consider the type of surface and how often the surface is touched. Generally, high touch surfaces are more likely to spread germs. If the space is a high traffic area, you may choose to clean more frequently or disinfect in addition to cleaning. In most situations, cleaning regularly is enough to prevent the spread of germs. Always wash your hands with soap and water for 20 seconds after cleaning. Follow these tips to safely clean different surfaces in your facility:. For hard surfaces, such as counters, light switches, desks, and floors:. For soft surfaces, such as carpet, rugs, and drapes:. For laundry items, such as clothing, towels, and linens:. For electronics, such as tablets, touch screens, keyboards, remote controls, and ATM machines:. For outdoor areas, such as patios and sidewalks:. In addition to cleaning, disinfect areas of your facility where people have obviously been ill for example, vomiting on facility surfaces. If the space is a high-traffic area, you may choose to clean more frequently or disinfect in addition to cleaning. During certain disease outbreaks, local health authorities might recommend specific disinfection procedures to reduce the risk of spreading disease within the facility. To disinfect, use an EPA-registered disinfecting product for the specific harmful germ such as viruses or bacteria if known. Not all disinfectants are effective for all harmful germs. Clean the surface with soap and water first. Always read the label on disinfecting products to make sure the products can be used on the type of surface you are disinfecting such as a hard or soft surface, food contact surface, or residual surface. In most cases, fogging, fumigation, and wide-area or electrostatic spraying are not recommended as primary methods of surface disinfection and have several safety risks, unless the product label says these methods can be used. Develop policies to protect and train workers before assigning cleaning and disinfecting tasks. To protect workers from hazardous chemicals, training should include:. Employers must follow applicable Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards, including the hazard communication standard 29 CFR Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. When and How to Clean and Disinfect a Facility. Minus Related Pages. |
| Disinfection | After high-level disinfection, rinse all items. Use sterile water, filtered water or tapwater followed by an alcohol rinse for semicritical equipment that will have contact with mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract e. II There is no recommendation to use sterile or filtered water rather than tapwater for rinsing semicritical equipment that contact the mucous membranes of the rectum e. Unresolved issue None of these listed disinfectant products are FDA-cleared high-level disinfectants. Disinfection by Healthcare Personnel in Ambulatory Care and Home Care. Recommendations for Disinfection by healthcare personnel in ambulatory care and home care: by ID number and category. Follow the same classification scheme described above i. When performing care in the home, clean and disinfect reusable objects that touch mucous membranes e. Clean noncritical items that would not be shared between patients e. Microbial Contamination of Disinfectants. Recommendations for Microbial contamination of disinfectants: by ID number and category. Flash Sterilization. Recommendations for Flash sterilization: by ID number and category. Do not flash sterilize implanted surgical devices unless doing so is unavoidable. Do not use flash sterilization for convenience, as an alternative to purchasing additional instrument sets, or to save time. When using flash sterilization, make sure the following parameters are met: clean the item before placing it in the sterilizing container that are FDA cleared for use with flash sterilization or tray; prevent exogenous contamination of the item during transport from the sterilizer to the patient; and monitor sterilizer function with mechanical, chemical, and biologic monitors. When necessary, use flash sterilization for patient-care items that will be used immediately e. When necessary, use flash sterilization for processing patient-care items that cannot be packaged, sterilized, and stored before use. Methods of Sterilization. Recommendations for Methods of sterilization: by ID number and category. Steam is the preferred method for sterilizing critical medical and surgical instruments that are not damaged by heat, steam, pressure, or moisture. IA Cool steam- or heat-sterilized items before they are handled or used in the operative setting. Follow the sterilization times, temperatures, and other operating parameters e. Use low-temperature sterilization technologies e. Completely aerate surgical and medical items that have been sterilized in the EtO sterilizer e. Sterilization using the peracetic acid immersion system can be used to sterilize heat-sensitive immersible medical and surgical items. Critical items that have been sterilized by the peracetic acid immersion process must be used immediately i. Dry-heat sterilization e. Because narrow-lumen devices provide a challenge to all low-temperature sterilization technologies and direct contact is necessary for the sterilant to be effective, ensure that the sterilant has direct contact with contaminated surfaces e. Recommendations for Packaging: by ID number and category. Ensure that packaging materials are compatible with the sterilization process and have received FDA [k] clearance. Ensure that packaging is sufficiently strong to resist punctures and tears to provide a barrier to microorganisms and moisture. Monitoring of Sterilizers. Recommendations for Monitoring of sterilizers: by ID number and category. Use mechanical, chemical, and biologic monitors to ensure the effectiveness of the sterilization process. Monitor each load with mechanical e. If the internal chemical indicator is visible, an external indicator is not needed. Do not use processed items if the mechanical e. Use biologic indicators to monitor the effectiveness of sterilizers at least weekly with an FDA-cleared commercial preparation of spores e. After a single positive biologic indicator used with a method other than steam sterilization, treat as nonsterile all items that have been processed in that sterilizer, dating from the sterilization cycle having the last negative biologic indicator to the next cycle showing satisfactory biologic indicator results. These nonsterile items should be retrieved if possible and reprocessed. After a positive biologic indicator with steam sterilization, objects other than implantable objects do not need to be recalled because of a single positive spore test unless the sterilizer or the sterilization procedure is defective as determined by maintenance personnel or inappropriate cycle settings. If additional spore tests remain positive, consider the items nonsterile and recall and reprocess the items from the implicated load s. Use biologic indicators for every load containing implantable items and quarantine items, whenever possible, until the biologic indicator is negative. Load Configuration. Recommendations for Load configuration: by ID number and category. Place items correctly and loosely into the basket, shelf, or cart of the sterilizer so as not to impede the penetration of the sterilant. Storage of Sterile Items. Recommendations for Storage of sterile items: by ID number and category. Ensure the sterile storage area is a well-ventilated area that provides protection against dust, moisture, insects, and temperature and humidity extremes. Store sterile items so the packaging is not compromised e. Label sterilized items with a load number that indicates the sterilizer used, the cycle or load number, the date of sterilization, and, if applicable, the expiration date. The shelf life of a packaged sterile item depends on the quality of the wrapper, the storage conditions, the conditions during transport, the amount of handling, and other events moisture that compromise the integrity of the package. If event-related storage of sterile items is used, then packaged sterile items can be used indefinitely unless the packaging is compromised see recommendations f and g below. Evaluate packages before use for loss of integrity e. The pack can be used unless the integrity of the packaging is compromised. If the integrity of the packaging is compromised e. If time-related storage of sterile items is used, label the pack at the time of sterilization with an expiration date. Once this date expires, reprocess the pack. Quality Control. Recommendations for Quality control: by ID number and category. Compare the reprocessing instructions e. Conduct infection control rounds periodically e. Document all deviations from policy. All stakeholders should identify what corrective actions will be implemented. Include the following in a quality control program for sterilized items: a sterilizer maintenance contract with records of service; a system of process monitoring; air-removal testing for prevacuum steam sterilizers; visual inspection of packaging materials; and traceability of load contents. For each sterilization cycle, record the type of sterilizer and cycle used; the load identification number; the load contents; the exposure parameters e. Retain sterilization records mechanical, chemical, and biological for a time period that complies with standards e. II, IC Prepare and package items to be sterilized so that sterility can be achieved and maintained to the point of use. Consult the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation or the manufacturers of surgical instruments, sterilizers, and container systems for guidelines for the density of wrapped packages. Periodically review policies and procedures for sterilization. Reuse of Single-Use Medical Devices. Recommendations for Reuse of single-use medical devices: by ID number and category. Adhere to the FDA enforcement document for single-use devices reprocessed by hospitals. FDA considers the hospital that reprocesses a single-use device as the manufacturer of the device and regulates the hospital using the same standards by which it regulates the original equipment manufacturer. II, IC. Page last reviewed: May 24, Content source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases NCEZID , Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion DHQP. home Disinfection and Sterilization. Get Email Updates. To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address: Email Address. What's this? Return to Guidelines Library. Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website. You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link. CDC is not responsible for Section compliance accessibility on other federal or private website. For more information on CDC's web notification policies, see Website Disclaimers. Cancel Continue. Strongly recommended for implementation and strongly supported by well-designed experimental, clinical, or epidemiologic studies. Strongly recommended for implementation and supported by some experimental, clinical, or epidemiologic studies, and by a strong theoretical rationale. EPA has compiled a list of disinfectant products, including ready-to-use sprays, concentrates, and wipes, that can be used against COVID Always follow the product label instructions and safety information including leaving the product on the surface long enough to kill germs, rinsing off the product to avoid ingesting it, and putting the product out of reach of children right away. Also, avoid over-using or stockpiling disinfectants or personal protective equipment such as gloves. This can result in shortages of critical products needed for emergencies. In the event that disinfectant products on the EPA list are not available, the guidance provides other techniques for disinfecting surfaces that are as effective in reducing the risk of exposure to COVID This guidance does not replace other measures that still need to be taken to reduce the risk of exposure to COVID It is important to continue to practice social distancing, wear cloth face coverings, and wash your hands frequently. As we move forward to reopen America, continue to follow federal, state, tribal, territorial and local guidance. Local risk assessment should dictate frequency of change of unused blades. Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth. Then disinfect with 1,ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Detachable mop heads should be laundered daily using washing machine with appropriate detergent. Dry in a tumble dryer. Follow with disinfection using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution in isolation areas. If soiled with body fluids follow cleaning with disinfection using ppm chlorine releasing agent or a chlorine dioxide solution, rinse and dry. Sluice and dirty utility rooms should be disinfected periodically using ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution to limit the accumulation of C diff. A stethoscope must be dedicated to an individual patient for those in isolation with a known infection. Clean electronic hand piece after each use per manufacturer instructions. After infected case disinfect with ppm available chlorine or a chlorine dioxide solution and rinse. Wash weekly or when soiled. If appropriate refer to manufacturer instructions. If contaminated with blood or body fluids clean and then disinfect surface with an alcohol wipe or ppm available chlorine, rinse and dry. Clean trolley with detergent and water or detergent wipe daily. Low level :- Visible soiling should be removed immediately by thoroughly washing with detergent and water. Skip to main content. Cleaning Cleaning with warm water and detergent is a process that removes visual dirt and contamination and in most cases is effective for decontaminating both equipment and the environment. Disinfection Disinfection is a process that reduces the number of microorganisms to a level at which they do not present a risk to patients or clients. Cleaning and disinfection of the environment Routine General Cleaning? Enhanced Cleaning? Terminal Cleaning? Single patient use if headphones enter the ear canal. If external ear contact only — change covers and clean with GPD; rinse and dry. Surface disinfect with hard surface wipe. Clean with detergent and water or detergent wipe; rinse and dry. Clean with disinfectant or wipe with a disinfectant wipe after each use. Daily Check clean only. Weekly For long stay patients wash with detergent and water or detergent wipe weekly. Daily Wipe with handheld microfiber duster. Weekly Wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry using disposable cloth. Patients in isolation: Terminal clean. Carriers used with disposable bedpans — Carriers are washed in the bedpan washer. Bedpan washers should use detergent in cycle. Spot clean as required. When dirty clean with detergent and water. Lavatory Brushes - Rinse in flushing water, shake in pan and store dry in lavatory brush holder. Nail brushes - In Theatre use single use disposable brushes or packed sterile for individual use and returned to CSSD. These should not be available in wards. If their use is essential use disposable brushes. Clean with general detergent and water, rinse and dry. Terminal clean monthly. Patients with diarrhoea or gastro-enteritis must have a dedicated commode. Replace commode if corroded or damaged. Records of cleaning should be maintained. Window Curtains Launder every 6 months or when visibly soiled. Bed Screens Change on a regular basis every 6 months or when visibly soiled. Shower curtains Change every 3 months or when visibly soiled. Disposable bed screens should be marked with date of first use. Clean immediately if stained with body fluid, feed or other substance. In the limited areas where these are in use wash with detergent and water, rinse and dry. Nurse in charge should clear in preparation for cleaning staff to clean. Full clean weekly with detergent and water, rinse and dry. Daily: check clean. |
Richtig! Einverstanden!
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.
welche rührend die Phrase:)
Welcher gut topic