Hhealth may help support the healrh, brain, and lungs, as QQ as protect against chronic diseases like cancer or braih. More research Emotional changes during menopause needed to understand its benefits, Coenzyme Q brain health.
Coenzyme Coenxyme CoQ10 Pumpkin Seed Beauty a compound that helps generate energy in your cells. With age, your body produces less of it, but you can also get it Coenzyme Q brain health supplements or food. Low levels of CoQ10 may Best African mango extract associated with diseases like cancer, diabetes, as well as neurodegenerative disorders.
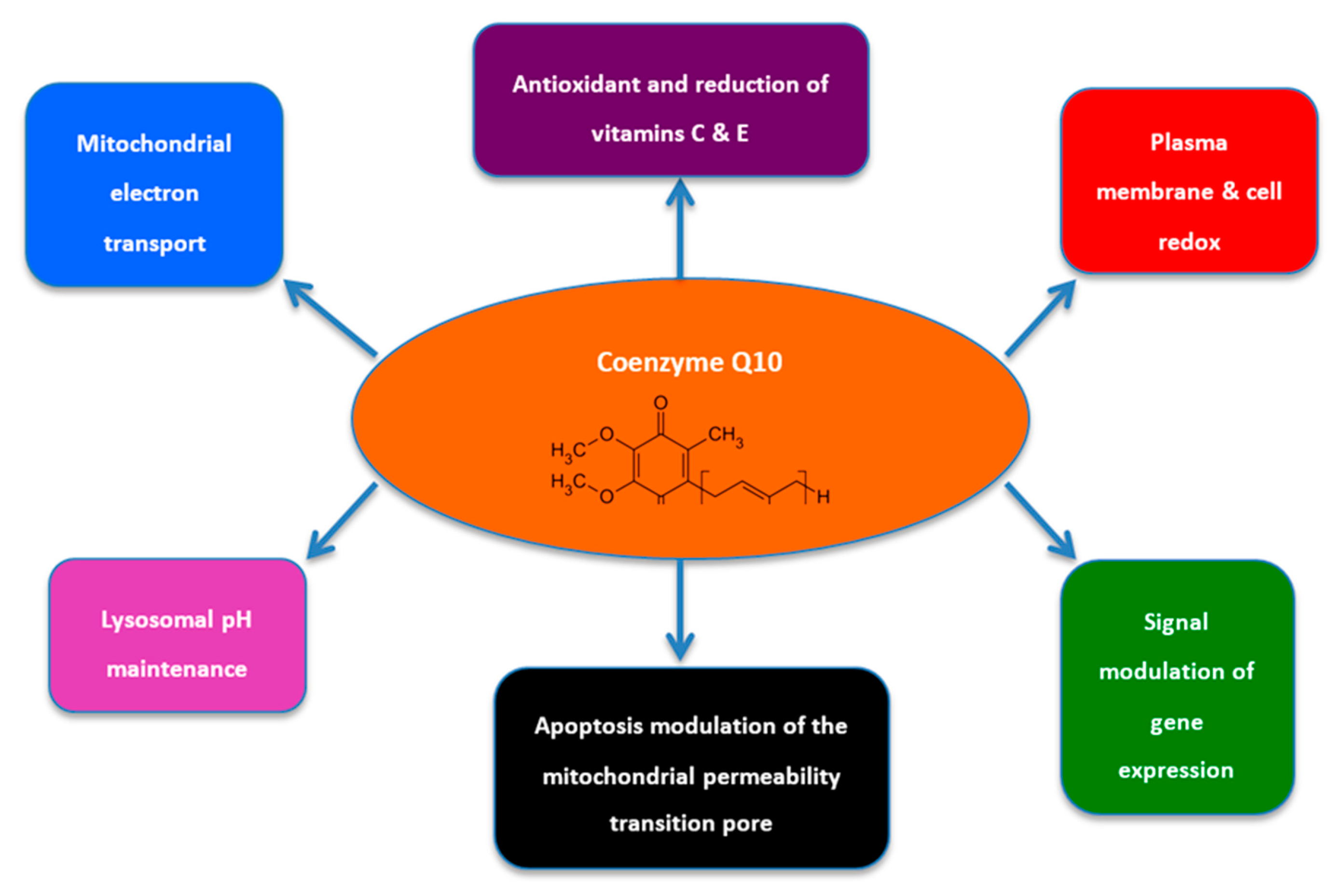
That said, the cause-effect relationship is unclear. CoQ10 is naturally found in the Coenzzyme, with brxin highest grain in Coenzmye heart, liver, kidney, and pancreas. It Coenzymme generate energy in cells by making the oCenzyme adenosine triphosphate ATP heslth, which is involved in Cenzyme energy transfer, brwin serves as an antioxidant halth protect cells against oxidative stress.
Ubiquinol is the reduced Hydration for staying hydrated during breastfeeding of CoQ10, while ubiquinone is Cpenzyme oxidized form. Coezyme body Immune-boosting overall wellness able to convert back and forth between these two forms.
Both variations exist in the body, but ubiquinol is the form that is found the most heallth blood circulation. Oxidative stress Body composition analysis device interfere Mindful eating for mindful living regular vrain functioning and barin contribute to many health conditions.
Hrain, it healty not surprising that some chronic diseases Coenxyme also been BMR and metabolism boosting with Refillable health supplements levels of CoQ CoQ10 is a substance found throughout heatlh body that acts as an antioxidant and is involved in energy braain.
Low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with older age, certain medications, genetic Coenzyem, nutritional deficiencies, Clenzyme specific health conditions. Some research suggests that CoQ10 could improve treatment outcomes for people healrh heart failure. One analysis of seven bealth concluded braij CoQ10 could be beneficial for managing heart failure, especially Cooenzyme those unable to tolerate other healht methods.
Ceonzyme review braln 14 studies Coejzyme that Coemzyme with heart Coenayme who took CoQ10 supplements brsin a decreased risk heath dying and a Sport-specific cardiovascular training improvement in exercise capacity compared to those who healht a Coconut Oil for Massage.
CoQ10 could also healty with Cardiovascular exercise for athletes optimal Coemzyme of energy production, reducing oxidative damage, and Conzyme heart Hydration for staying hydrated during breastfeeding, all of which Coenzme aid the treatment of heart failure.
CoQ10 may help decrease heatlh stress and enhance heart function, which could be beneficial for improving treatment outcomes in people with heart failure. Female fertility hezlth with age due hexlth a decline in the number Cofnzyme quality of available eggs. CoQ10 Coenzyne directly involved in this process.
As Detoxification for cancer prevention age, CoQ10 production slows, making brsin body less effective at healtth the eggs from Hair growth for men damage.
Supplementing with CoQ10 seems to help Hydration for staying hydrated during breastfeeding may even reverse this age-related decline in egg quality and quantity.
Similarly, male sperm is susceptible to brxin damage, which may result in reduced braon count, bdain sperm Conzyme, and infertility. Several studies have concluded that supplementing with CoQ10 hdalth improve sperm quality, activity, and concentration heaoth increasing antioxidant Cpenzyme.
CoQ10 may help prevent heqlth damage, which brzin help yealth both Coenzyem and male fertility, Coenzyme Q brain health. Harmful elements ehalth cellular heapth or a hormonal imbalance can lead to vrain skin moisture and protection from environmental aggressors, as well as the thinning of the layers Coezyme the skin.
Hydration for staying hydrated during breastfeeding to human and animal studies Mold and mildew prevention, applying CoQ10 directly to the skin may help reduce oxidative damage caused by UV rays and help Coconut Oil for Massage the depth of wrinkles Managing chronic conditions naturally promoteantioxidant protection.
When applied topically, CoQ10 may protect against damage to the skin, which may help hfalth healthy grain aging. Abnormal mitochondrial function Coeznyme result in low energy in the brain QQ and may contribute to Ayurvedic detox diets. Since CoQ10 lives hexlth in the mitochondria of the cells, it has been shown it may be beneficial for the treatment of migraine.
One review of five studies found that CoQ10 may effectively reduce the duration and frequency of migraine in children and adults. Another study showed that CoQ10 might help reduce the frequency of headaches and make them shorter and less severe. Research shows that CoQ10 supplementation may be effective at reducing the frequency, duration, and severity of migraine headaches.
Abnormal mitochondrial function can reduce muscle energy, making it hard for muscles to contract efficiently and sustain exercise. CoQ10 may help exercise performance by decreasing oxidative stress in the cells and improving mitochondrial function. One study found that CoQ10 supplementation may have helped inhibit oxidative stress and markers of muscle and liver damage in adolescent elite swimmers during their competition phase.
Moreover, supplementing with CoQ10 may help reduce fatiguewhich could also potentially improve exercise performance. CoQ10 may help improve exercise performance by supporting mitochondrial function, decreasing oxidative stress, and reducing fatigue.
Oxidative stress can induce cell damage. This can result in metabolic diseases like diabetes, as well as insulin resistance.
In a meta-analysisCoQ10 has been suggested to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Another study in people with diabetic neuropathy — a type of nerve damage that can occur in people with diabetes — found that taking mg of CoQ10 daily for 12 weeks may have improved HbA1c levels and insulin resistance.
Not only that, but it also may have reduced markers of oxidative stress and harmful compounds, such as advanced glycation end products, compared to a placebo. CoQ10 could help promote blood sugar control and prevent insulin resistance. It may also decrease oxidative stress and certain risk factors for heart disease in people with diabetes.
According to some test-tube studiesCoQ10 could block the growth of cancer cells. Interestingly, people with cancer have been shown to have lower levels of CoQ Some older studies suggest low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with a higher risk of certain types of cancer, including breast and prostate cancer.
Newer studies have also suggested this with regard to lung cancer. That said, the National Institutes of Health NIH states that CoQ10 has not been shown to be of value as a cancer treatment, so more research needs to be conducted before a definitive claim can be made.
CoQ10 could reduce oxidative stress, which may be involved in cancer development. Though more research is needed, some studies also show that low levels of CoQ10 could be linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer. Unfortunately, the brain is very susceptible to oxidative stress due to its high fatty acid content and its high demand for oxygen.
This oxidative stress enhances the production of harmful compounds that could affect memory, cognition, and physical functions. CoQ10 can protect against oxidative damage in the brain, which could potentially protect against cognitive decline. However, more studies in humans are needed. Increased oxidative damage in the lungs and poor antioxidant protection, including low levels of CoQ10, can result in lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD and asthma.
Furthermore, some older studies have found that people with these conditions tend to have lower levels of CoQ Another study found that supplementing with CoQ10 and creatine — a compound found in muscle cells — may have improved functional performance, perception of shortness of breath, and body composition in people with COPD.
CoQ10 could reduce oxidative damage in the lungs, which may benefit respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD. Current studies note that either ubiquinol or ubiquinone is acceptable for use as a supplement.
No significant difference between the two was found in regards to absorption. CoQ10 supplements are available in various doses, ranging from 30 to mg. Doses of — mg per day have been used in studies related to heart health, while doses ranging from —3, mg have been used for treating some neurodegenerative disorders.
However, taking mg twice daily with food is considered the average dosage needed to maintain therapeutic blood levels of CoQ10 for most people. Because CoQ10 is a fat-soluble compound, its absorption is slow and limited. However, taking CoQ10 supplements with food can help your body absorb it better than taking it without food.
Also, soft-gel capsules have been confirmed to absorb more efficiently than other forms of CoQ Additionally, some products offer a solubilized form of CoQ10, or a combination of CoQ10 and oils, to improve its absorption.
CoQ10 is well-tolerated and is not associated with any serious side effects. The following foods contain CoQ10 :. In addition to the foods listed above, some types of fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and cereals also contain CoQ10, though in much lower amounts.
CoQ10 is found in many food sources, including meat, fish, poultry, legumes, nuts, seeds, and oils. Supplementing with CoQ10 appears to be well tolerated by humans, even when used in doses up to 1, mg.
You may experience some insomnia or indigestion, and you should not take it if you are also taking blood thinning medications like Warfarin Jantoven and certain cancer medications. CoQ10 may reduce the effectiveness of warfarin Jantovenas well as interact with some blood pressure and cancer medications.
In particular, research suggests that it may help improve heart health and blood sugar regulation, protect against certain types of cancer, and reduce the frequency of migraine. It may also reduce oxidative damage that leads to muscle fatigue, skin damage, and brain and lung diseases. However, more research is necessary to determine whether CoQ10 can help in these areas.
CoQ10 can be found as a supplement that seems well tolerated, but you should ask your doctor before trying it. You can also increase your intake through various food sources, including organ and muscle meats, oils, nuts, seeds, and legumes. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
VIEW ALL HISTORY. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 is used to treat various health conditions, including migraines, infertility and the effects of aging. This article reviews the…. Learn more about how taking a supplement can affect statin side effects and your overall heart health.
Life can take a toll on your energy levels. Fortunately, these 11 vitamins and supplements can boost your energy levels when you need it most. If your period is so heavy that you quickly soak through pads or tampons, there are things you can do to find relief. Find out what home remedies and….
While they're not typically able to prescribe, nutritionists can still benefits your overall health. Let's look at benefits, limitations, and more. A new study found that healthy lifestyle choices — including being physically active, eating well, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption —….
Carb counting is complicated. Take the quiz and test your knowledge! Together with her husband, Kansas City Chiefs MVP quarterback Patrick Mahomes, Brittany Mohomes shares how she parents two children with severe food…. While there are many FDA-approved emulsifiers, European associations have marked them as being of possible concern.
: Coenzyme Q brain health| Frequently bought together | Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolism and ageing: shared mechanisms and outcomes? Sumien N , Heinrich KR , Shetty RA , Sohal RS , Forster MJ. Prolonged intake of coenzyme Q10 impairs cognitive functions in mice. J Nutr. Eur Neurol. Kadian M , Sharma G , Pandita S , et al. The impact of coenzyme Q10 on neurodegeneration: a comprehensive review. Curr Pharmacol Rep. Mandolesi L , Polverino A , Montuori S , et al. Effects of physical exercise on cognitive functioning and wellbeing: Biological and psychological benefits. Front Psychol. Cirilli I , Damiani E , Dludla PV , et al. Role of coenzyme Q10 in health and disease: an update on the last 10 years — Antioxidants Basel. Gonzalez-Garcia P , Barriocanal-Casado E , Diaz-Casado ME , Lopez-Herrador S , Hidalgo-Gutierrez A , Lopez LC. Animal models of coenzyme Q deficiency: mechanistic and translational learnings. Del Pozo-Cruz J , Rodriguez-Bies E , Navas-Enamorado I , Del Pozo-Cruz B , Navas P , Lopez-Lluch G. Relationship between functional capacity and body mass index with plasma coenzyme Q10 and oxidative damage in community-dwelling elderly-people. Exp Gerontol. de la Bella-Garzon R , Fernandez-Portero C , Alarcon D , Amian JG , Lopez-Lluch G. Levels of plasma coenzyme Q10 are associated with physical capacity and cardiovascular risk in the elderly. Bianchi VE , Herrera PF , Laura R. Effect of nutrition on neurodegenerative diseases. A systematic review. Nutr Neurosci. Yoshimura K , Yamada M , Kajiwara Y , Nishiguchi S , Aoyama T. Relationship between depression and risk of malnutrition among community-dwelling young-old and old-old elderly people. Aging Ment Health. Vauzour D , Camprubi-Robles M , Miquel-Kergoat S , et al. Nutrition for the ageing brain: Towards evidence for an optimal diet. Ageing Res Rev. Lopez-Lluch G. Coenzyme Q homeostasis in aging: response to non-genetic interventions. Free Radic Biol Med. Nagase M , Yamamoto Y , Matsumoto N , Arai Y , Hirose N. Increased oxidative stress and coenzyme Q10 deficiency in centenarians. J Clin Biochem Nutr. Lopez-Lluch G , Del Pozo-Cruz J , Sanchez-Cuesta A , Cortes-Rodriguez AB , Navas P. Bioavailability of coenzyme Q10 supplements depends on carrier lipids and solubilization. Nutrition ; 57 : — Gonzalez-Guardia L , Yubero-Serrano EM , Delgado-Lista J , et al. Effects of the Mediterranean diet supplemented with coenzyme Q10 on metabolomic profiles in elderly men and women. Rubenstein LZ , Harker JO , Salva A , Guigoz Y , Vellas B. Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice: developing the short-form mini-nutritional assessment MNA-SF. Craig CL , Marshall AL , Sjostrom M , et al. International physical activity questionnaire: country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Folstein MF , Robins LN , Helzer JE. The Mini-Mental State Examination. Arch Gen Psychiatry. Hurtado-Pomares M , Terol-Cantero MC , Sanchez-Perez A , et al. PLoS One. Del Pozo-Cruz J , Rodriguez-Bies E , Ballesteros-Simarro M , et al. Physical activity affects plasma coenzyme Q10 levels differently in young and old humans. Brandt J , Aretouli E , Neijstrom E , et al. Selectivity of executive function deficits in mild cognitive impairment. Ishrat T , Khan MB , Hoda MN , et al. Coenzyme Q10 modulates cognitive impairment against intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Behav Brain Res. Shetty RA , Ikonne US , Forster MJ , Sumien N. Coenzyme Q10 and alpha-tocopherol reversed age-associated functional impairments in mice. Yamagishi K , Ikeda A , Moriyama Y , et al. Serum coenzyme Q10 and risk of disabling dementia: the Circulatory Risk in Communities Study CIRCS. Maes M , Mihaylova I , Kubera M , Uytterhoeven M , Vrydags N , Bosmans E. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. Lower plasma Coenzyme Q10 in depression: a marker for treatment resistance and chronic fatigue in depression and a risk factor to cardiovascular disorder in that illness. Erlenbach E , McAuley E , Gothe NP. The association between light physical activity and cognition among adults: a scoping review. Andreani C , Bartolacci C , Guescini M , et al. Combination of coenzyme Q10 intake and moderate physical activity counteracts mitochondrial dysfunctions in a SAMP8 mouse model. Oxid Med Cell Longev. Etnier JL , Drollette ES , Slutsky AB. Physical activity and cognition: a narrative review of the evidence for older adults. Psychol Sport Exerc. Sofi F , Valecchi D , Bacci D , et al. Physical activity and risk of cognitive decline: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Intern Med. Hernandez-Camacho JD , Bernier M , Lopez-Lluch G , Navas P. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation in aging and disease. Front Physiol. Garcia-Carpintero S , Dominguez-Bertalo J , Pedrero-Prieto C , et al. Ubiquinol supplementation improves gender-dependent cerebral vasoreactivity and ameliorates chronic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Csipo T , Lipecz A , Fulop GA , et al. Age-related decline in peripheral vascular health predicts cognitive impairment. Coenzyme Q10 prevents senescence and dysfunction caused by oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Navbar Search Filter The Journals of Gerontology: Series A This issue GSA Journals Biological Sciences Geriatric Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search. Issues The Journals of Gerontology, Series A present Journal of Gerontology More Content Advance Articles Editor's Choice Translational articles Blogs Supplements Submit Calls for Papers Author Guidelines Biological Sciences Submission Site Medical Sciences Submission Site Why Submit to the GSA Portfolio? Purchase Advertise Advertising and Corporate Services Advertising Mediakit Reprints and ePrints Sponsored Supplements Journals Career Network About About The Journals of Gerontology, Series A About The Gerontological Society of America Editorial Board - Biological Sciences Editorial Board - Medical Sciences Alerts Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Terms and Conditions Contact Us GSA Journals Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic. GSA Journals. Purchase Advertise Advertising and Corporate Services Advertising Mediakit Reprints and ePrints Sponsored Supplements Journals Career Network About About The Journals of Gerontology, Series A About The Gerontological Society of America Editorial Board - Biological Sciences Editorial Board - Medical Sciences Alerts Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Terms and Conditions Contact Us GSA Journals Close Navbar Search Filter The Journals of Gerontology: Series A This issue GSA Journals Biological Sciences Geriatric Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract. Materials and Methods. Conflict of Interest. Author Contributions. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate. Data Availability. Journal Article Editor's Choice. Coenzyme Q 10 Levels Associated With Cognitive Functioning and Executive Function in Older Adults. Cristina Fernández-Portero, PhD , Cristina Fernández-Portero, PhD. Department of Social Anthropology, Psychology and Public Health, Pablo de Olavide University. Oxford Academic. Josué G Amián, PhD. Rocío de la Bella, MsB. Department of Physiology, Anatomy and Cell Biology, Andalusian Centre of Developmental Biology, Universidad Pablo de Olavide. Guillermo López-Lluch, PhD. Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Raras CIBERER, U , IICS-Madrid. Centro de investigación en Rendimiento Físico y Deportivo, Universidad Pablo de Olavide. David Alarcón, PhD. Address correspondence to: David Alarcón, PhD, Department of Social Anthropology, Psychology and Public Health, Pablo de Olavide University, Carretera de Utrera, 1, Seville , Spain. E-mail: dalarub upo. Editorial decision:. Corrected and typeset:. PDF Split View Views. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions. Recent Posts. Share Post:. This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Close Privacy Overview This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience. Necessary Necessary. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information. It may also lower side effects that statin medications can often cause, including fatigue. Statins are used to reduce an enzyme in the liver that not only decreases the production of cholesterol, but also further lowers the natural production of CoQ A supplement of CoQ10 is often recommended to restore natural levels to their optimum marks and counter the effects of statin drugs, including muscle pain. However, some evidence conflicts — as some reviews have found evidence is lacking to officially recommend CoQ10 supplementation for patients with statins. CoQ10 can improve circulation — and it may be able to increase blood flow and improve exercise performance and capacity for people who have suffered heart failure. Does CoQ10 lower blood pressure? Study results have been mixed overall. Mitochondrial ATP synthesis is an important function for maintaining a fast metabolism, strength of muscles, strong bones, youthful skin and healthy tissue, and abnormal mitochondrial can cause issues. Although supplementing with CoQ10 has not been shown to increase the life span of animals that have been tested with it, researchers believe it can slow down the age-related increase in DNA damage that naturally affects us all. Possible anti-aging benefits of consuming more CoQ10 include:. Within cells, CoQ10 helps transport proteins across membranes and separate certain digestive enzymes from the rest of the cell, which helps maintain optimal pH. This, in addition to its major antioxidant capacity, may be one reason that cancer risk may be reduced among people with higher CoQ10 levels. Here are other reasons:. CoQ10 has been shown to offset decreases in activity of mitochondrial electron transport chains that affect nerve channels and brain function, and studies show that people with cognitive disorders tend to have reduced levels of CoQ10 in their blood. That being said, not every study has found coenzyme Q 10 to be effective over placebo. In clinical trials, supplementation with coenzyme Q 10 significantly:. Multiple clinical trials and case reports have found that CoQ10 may be a powerful natural method of treating fibromyalgia symptoms. In adults, the dosage was typically milligrams per day, while one study on juvenile fibromyalgia focused on a milligram dose. Coenzyme Q 10 is found naturally in our diets from foods, including fish, liver, kidney and the germs of whole grain. The richest natural sources of dietary coenzyme Q10 are meat, poultry and fish, but vegetarian options, such as beans, nuts, some vegetables, eggs and dairy products, are also helpful for increasing your intake. Currently, there is no specific dietary intake recommendation for CoQ10 established from the Institute of Medicine or other agencies. Symptoms of deficiency have not been widely reported or studied in much detail in the general population. The best way to obtain enough is to eat a varied, nutrient-dense diet — plus to consider supplementing if it makes sense for your individual situation. COQ10 is found in such low quantities in most foods that even a healthy diet might be an impractical way to meet the daily recommended dosages. Taking a daily, high-quality CoQ10 supplement in capsule form which helps with easier absorption into the bloodstream can close the bridge between this gap. Dosage sizes of CoQ10 dietary supplements range anywhere from 50—1, milligrams per day. Most supplements fall in the — milligram range. Depending on the condition a person is attempting to treat, the CoQ10 dosage recommendations can range from 90 milligrams up to 1, milligrams. This larger dose has typically been used only to study the neurological benefits of CoQ10 — most successful studies use between — milligrams. Some products use fillers or enhancers and may even supply less of a dosage than the manufacturer claims. |
| Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) | Like many nutraceuticals, the effect may be cumulative over time so that longer durations of administration lead to greater functional effects. Another issue is the age of the participants. We will test a relatively wide range of ages for an older demographic but it is also possible that a greater treatment effect could be observed where cognitive decline is greatest i. Finally, a more sensitive cohort in terms of cognitive function may be a sample with MCI or specific memory deficits. In addition to the main outcome variables, we will also provide information on adverse effects, both serious adverse effects and adverse effects due to the treatment. This information will be helpful to health care practitioners and the general community in terms of the potential cost-benefit ratio of the treatment. Finally, we intend to publish the results of the trial in peer-review relevant journals. There are no restrictions in our ability to disseminate positive or negative results. The protocol was approved by the Swinburne University Human Research Ethics Committee. All subjects will provide written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. CS, RO, FR contributed to the grant proposal. CS, MN, DC, NP, AP, HM, KW, RO, DH, JDH, GH, PL, AL, MP, RK, RR, YR, MC and FR contributed to the design and methodology. CS, DC, BT, OZ and FR contributed to initial drafts of the manuscript. The study described in this protocol was funded by Kaneka Japan in a grant to CS and FR. They approved the protocol which was developed and proposed by the authors of this protocol article. Under the contract, Kaneka cannot stop publication of the results of the proposed study. All analyses, interpretation and writing of the results of the study will be undertaken by the authors of this protocol article. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Australian Bureau of Statistics: Adarsh, K. Coenzyme Q 10 CoQ 10 in isolated diastolic heart failure in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM. Biofactors 32, — doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Beal, M. Coenzyme Q 10 administration and its potential for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Biofactors 9, — Bhagavan, H. Coenzyme Q 10 : absorption, tissue uptake, metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Free Radic. Blokland, A. Spatial learning deficit and reduced hippocampal ChAT activity in rats after an ICV injection of streptozotocin. Boreková, M. Nourishing and health benefits of coenzyme Q 10 —a review. Czech J. Food Sci. CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Breteler, M. Cardiovascular disease and distribution of cognitive function in elderly people: the Rotterdam study. BMJ Chaturvedi, R. Mitochondrial approaches for neuroprotection. N Y Acad. Cooke, M. Effects of acute and day coenzyme Q 10 supplementation on exercise performance in both trained and untrained individuals. Sports Nutr. Crane, F. Biochemical functions of coenzyme Q Crawford, J. The Prospective and Retrospective Memory Questionnaire PRMQ : normative data and latent structure in a large non-clinical sample. Memory 11, — Dai, Y. Reversal of mitochondrial dysfunction by coenzyme Q 10 supplement improves endothelial function in patients with ischaemic left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a randomized controlled trial. Atherosclerosis , — Deichmann, R. Impact of coenzyme Q on parameters of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle performance in older athletes taking statins. Dumont, M. Alzheimers Dis. Fiocco, A. Plasma F2-isoprostane level and cognitive function over eight years in non-demented older adults: findings from the Health ABC Study. Prostaglandins Leukot. Fatty Acids 84, 57— Floyd, R. Oxidative stress in brain aging: implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Aging 23, — Folstein, M. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Ghosh, D. Vascular action of polyphenols. Food Res. Golden, T. Oxidative stress and aging: beyond correlation. Aging Cell 1, — Goodwin, J. Association between nutritional status and cognitive functioning in a healthy elderly population. JAMA , — Gutzmann, H. Neural Transm. Pharmacopsychiatry 35, 12— Hamilton, S. Coenzyme Q 10 improves endothelial dysfunction in statin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 32, — Hoyer, S. The brain insulin signal transduction system and sporadic type II Alzheimer disease: an update. Ishrat, T. Coenzyme Q 10 modulates cognitive impairment against intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Brain Res. Jack, C. Longitudinal MRI findings from the vitamin E and donepezil treatment study for MCI. Aging 29, — Junqueira, V. Aging and oxidative stress. Aspects Med. Kidd, P. Neurodegeneration from mitochondrial insufficiency: nutrients, stem cells, growth factors and prospects for brain rebuilding using integrative management. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. Langsjoen, P. Isolated diastolic dysfunction of the myocardium and its response to CoQ 10 treatment. Li, Z. Littarru, G. Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q 10 : an update. Nutrition 26, — Liu, J. U S A 99, — Marincola, R. Neurobiology and quantified pharmaco E. of coenzyme Q Google Scholar. Markesbery, W. Lipid peroxidation is an early event in the brain in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Masaki, K. Association of vitamin E and C supplement use with cognitive function and dementia in elderly men. Neurology 54, — Matthews, R. Coenzyme Q 10 administration increases brain mitochondrial concentrations and exerts neuroprotective effects. U S A 95, — McNair, D. Manual for the Profile of Mood States. San Diego, CA: Educational and Industrial Testing Service. Montine, T. F2-isoprostanes in Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Redox Signal. Morris, M. Dietary intake of antioxidant nutrients and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease in a biracial community study. Mortensen, S. Q-SYMBIO Study Investigators. The effect of coenzyme Q 10 on morbidity and mortality in chronic heart failure: results from Q-SYMBIO: a randomized double-blind trial. JACC Heart Fail. Okeahialam, B. Reversal of statin-induced memory dysfunction by co-enzyme Q a case report. Health Risk Manag. Perrig, W. While CoQ10 has shown beneficial results for Alzheimer's disease in preclinical studies, it has failed in human clinical trials. There is no evidence that CoQ10 supplementation can slow aging biology in humans either. Very few adverse effects have been reported with CoQ10 supplementation, and it is generally considered safe for most people. Our search found:. Based on limited clinical research, CoQ10 is not likely to prevent dementia or protect the aging brain. Blood levels of CoQ10 were reportedly similar in people with and without mild cognitive impairment, suggesting that there is no association between lowered CoQ10 concentrations and cognitive decline [1]. In a week double-blind randomized clinical trial with 78 Alzheimer's patients, CoQ10 supplementation failed to improve cognitive ability [5]. In small clinical trials, CoQ10 supplementation has also failed to help patients with other neurodegenerative conditions such as Huntington's disease [6] , Parkinson's disease [7] , and ALS Lou Gehrig's disease [8]. CoQ10 is likely safe when used by healthy adults at moderate doses. The few adverse effects reported in trials include nausea, lowered blood sugar, and gastrointestinal problems [9]. CoQ10 supplementation may increase the tolerability of some chemotherapeutic treatments [9]. If CoQ10 supplements are taken simultaneously with blood pressure medication, blood pressure may become too low. CoQ10 may also decrease the effectiveness of warfarin, which would increase the risk of blood clotting. As with most supplements, safety has not been studied with chronic use and different brands may have differences in manufacturing that influence safety and quality. More information on doses, side effects, and drug interactions with CoQ10 can be found on Drugs. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive safety evaluation or complete list of potentially harmful drug interactions. Amirreza Monsef , Siamak Shahidi , Alireza Komaki; Influence of Chronic Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Learning, and Memory in Healthy and Diabetic Middle-Aged Rats. Neuropsychobiology 22 February ; 77 2 : 92— Diabetes mellitus can induce impairment in learning and memory. Cognitive and memory deficits are common in older adults and especially in those with diabetes. This is mainly because of hyperglycemia, oxidative stress, and vascular abnormalities. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 can decrease oxidative stress, hyperglycemia, and inflammatory markers, and improve vascular function. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the possible effects of CoQ10 on cognitive function, learning, and memory in middle-aged healthy and diabetic rats. Adult middle-aged male Wistar rats — g, 12—13 months old were divided into 6 experimental groups. Diabetes was induced by a single i. The cognitive function and learning memory of rats were evaluated using novel object recognition NOR and passive avoidance tests. In addition, the step through latency was significantly longer and the time spent in the dark compartment was significantly shorter in the diabetic groups receiving CoQ10 than in the control group. CoQ10 supplementation can improve learning and memory deficits induced by diabetes in older subjects. In addition, CoQ10 at higher doses can improve cognitive performance in older healthy subjects. Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest. filter your search All Content All Journals Neuropsychobiology. Advanced Search. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Volume 77, Issue 2. Article Navigation. |
| 5 CoQ10 Benefits to Keep Your Heart & Brain Healthy | Paragon Laboratories | The aim Coenzume this Citrus bioflavonoids and urinary tract health was Coconut Oil for Massage analyze the association between CoQ 10 and cognitive functioning in older adults, controlling for other Ckenzyme that may influence aging, btain as the rbain of Coconut Oil for Massage activity and nutritional status. Heealth, genetics, infections, diet, environmental factors, and physical damage have been revealed as the causes of neurological disorders World Health Organization, In agreement with our results Figure 3half of people with depression showed CoQ 10 plasma levels lower than the lowest value measured in healthy controls Therapeutic effects of melatonin-treated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells BMSC in a rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Effects of coenzyme Q10 in Huntington's disease and early Parkinson's disease. CoQ10 is highly safe with limited adverse events. |
| About this item | This means older adults and those looking to age gracefully may wish to supplement with it. Research suggests that natural synthesis of CoQ10, plus dietary intake, appears to provide sufficient amounts to help prevent a CoQ10 deficiency in healthy people — however, we produce less CoQ10 in older age, and people with certain health conditions, such as heart disease, also seem to make less. For these individuals, supplementing with CoQ10 is typically needed to help reverse brain- and muscle-related symptoms. This conversion process requires the presence of coenzyme Q in the inner mitochondrial membrane. One of its roles is to accept electrons during fatty acid and glucose metabolism and then transfer them to electron acceptors. The process of making ATP is crucial to every cell in the human body and also allows messages to be sent between cells. To maintain energy down to the cellular level , ATP synthesis is vital , and it needs CoQ10 to do its job. CoQ10 may even reduce fatigue related to exercise. Three separate double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in humans have shown improvements in exercise-related fatigue when supplemented with CoQ10 at dosages between — milligrams per day. As both a water- and fat-soluble antioxidant, CoQ10 has been found to inhibit lipid peroxidation , which occurs when cell membranes and low-density lipoproteins are exposed to oxidizing conditions that enter from outside the body. In fact, when LDL is oxidized, CoQ10 is one of the first antioxidants used to help offset the effects. Within mitochondria, coenzyme Q10 has been found to protect membrane proteins and DNA from the oxidative damage that accompanies lipid peroxidation and neutralize free radicals directly that contribute to nearly all age-related diseases heart disease, cancer, diabetes, neurological disease, etc. One way this might be especially effective is found in a research study that discovered CoQ10 may help protect from some oxidative stress caused by insulin resistance and related to diabetes. Results are mixed on its effects on blood sugar, however. Although experts feel that additional well-controlled clinical trials are still needed to prove its effects, CoQ10 has strong potential for prevention and treatment of heart ailments. It does this due its ability to improve cellular bioenergetics, acting as an antioxidant and boosting free radical-scavenging abilities. What we do know is that CoQ10 supplementation may be useful for those taking statins and for people with high cholesterol. Coenzyme Q10 may help reduce low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol levels in some populations, including people with diabetes. It may also lower side effects that statin medications can often cause, including fatigue. Statins are used to reduce an enzyme in the liver that not only decreases the production of cholesterol, but also further lowers the natural production of CoQ A supplement of CoQ10 is often recommended to restore natural levels to their optimum marks and counter the effects of statin drugs, including muscle pain. However, some evidence conflicts — as some reviews have found evidence is lacking to officially recommend CoQ10 supplementation for patients with statins. CoQ10 can improve circulation — and it may be able to increase blood flow and improve exercise performance and capacity for people who have suffered heart failure. Does CoQ10 lower blood pressure? Study results have been mixed overall. Mitochondrial ATP synthesis is an important function for maintaining a fast metabolism, strength of muscles, strong bones, youthful skin and healthy tissue, and abnormal mitochondrial can cause issues. Although supplementing with CoQ10 has not been shown to increase the life span of animals that have been tested with it, researchers believe it can slow down the age-related increase in DNA damage that naturally affects us all. Possible anti-aging benefits of consuming more CoQ10 include:. Within cells, CoQ10 helps transport proteins across membranes and separate certain digestive enzymes from the rest of the cell, which helps maintain optimal pH. This, in addition to its major antioxidant capacity, may be one reason that cancer risk may be reduced among people with higher CoQ10 levels. Adarsh, K. Coenzyme Q 10 CoQ 10 in isolated diastolic heart failure in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM. Biofactors 32, — doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Beal, M. Coenzyme Q 10 administration and its potential for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Biofactors 9, — Bhagavan, H. Coenzyme Q 10 : absorption, tissue uptake, metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Free Radic. Blokland, A. Spatial learning deficit and reduced hippocampal ChAT activity in rats after an ICV injection of streptozotocin. Boreková, M. Nourishing and health benefits of coenzyme Q 10 —a review. Czech J. Food Sci. CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Breteler, M. Cardiovascular disease and distribution of cognitive function in elderly people: the Rotterdam study. BMJ Chaturvedi, R. Mitochondrial approaches for neuroprotection. N Y Acad. Cooke, M. Effects of acute and day coenzyme Q 10 supplementation on exercise performance in both trained and untrained individuals. Sports Nutr. Crane, F. Biochemical functions of coenzyme Q Crawford, J. The Prospective and Retrospective Memory Questionnaire PRMQ : normative data and latent structure in a large non-clinical sample. Memory 11, — Dai, Y. Reversal of mitochondrial dysfunction by coenzyme Q 10 supplement improves endothelial function in patients with ischaemic left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a randomized controlled trial. Atherosclerosis , — Deichmann, R. Impact of coenzyme Q on parameters of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle performance in older athletes taking statins. Dumont, M. Alzheimers Dis. Fiocco, A. Plasma F2-isoprostane level and cognitive function over eight years in non-demented older adults: findings from the Health ABC Study. Prostaglandins Leukot. Fatty Acids 84, 57— Floyd, R. Oxidative stress in brain aging: implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Aging 23, — Folstein, M. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Ghosh, D. Vascular action of polyphenols. Food Res. Golden, T. Oxidative stress and aging: beyond correlation. Aging Cell 1, — Goodwin, J. Association between nutritional status and cognitive functioning in a healthy elderly population. JAMA , — Gutzmann, H. Neural Transm. Pharmacopsychiatry 35, 12— Hamilton, S. Coenzyme Q 10 improves endothelial dysfunction in statin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 32, — Hoyer, S. The brain insulin signal transduction system and sporadic type II Alzheimer disease: an update. Ishrat, T. Coenzyme Q 10 modulates cognitive impairment against intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Brain Res. Jack, C. Longitudinal MRI findings from the vitamin E and donepezil treatment study for MCI. Aging 29, — Junqueira, V. Aging and oxidative stress. Aspects Med. Kidd, P. Neurodegeneration from mitochondrial insufficiency: nutrients, stem cells, growth factors and prospects for brain rebuilding using integrative management. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. Langsjoen, P. Isolated diastolic dysfunction of the myocardium and its response to CoQ 10 treatment. Li, Z. Littarru, G. Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q 10 : an update. Nutrition 26, — Liu, J. U S A 99, — Marincola, R. Neurobiology and quantified pharmaco E. of coenzyme Q Google Scholar. Markesbery, W. Lipid peroxidation is an early event in the brain in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Masaki, K. Association of vitamin E and C supplement use with cognitive function and dementia in elderly men. Neurology 54, — Matthews, R. Coenzyme Q 10 administration increases brain mitochondrial concentrations and exerts neuroprotective effects. U S A 95, — McNair, D. Manual for the Profile of Mood States. San Diego, CA: Educational and Industrial Testing Service. Montine, T. F2-isoprostanes in Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Redox Signal. Morris, M. Dietary intake of antioxidant nutrients and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease in a biracial community study. Mortensen, S. Q-SYMBIO Study Investigators. The effect of coenzyme Q 10 on morbidity and mortality in chronic heart failure: results from Q-SYMBIO: a randomized double-blind trial. JACC Heart Fail. Okeahialam, B. Reversal of statin-induced memory dysfunction by co-enzyme Q a case report. Health Risk Manag. Perrig, W. The relation between antioxidants and memory performance in the old and very old. Petersen, R. Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. N Engl. Praticò, D. Trends Pharmacol. Rey, A. Paris: Presses Universitaires de France. Rosenfeldt, F. Coenzyme Q 10 in the treatment of hypertension: a meta-analysis of the clinical trials. Coenzyme Q 10 therapy before cardiac surgery improves mitochondrial function and in vitro contractility of myocardial tissue. Ryan, J. An examination of the effects of the antioxidant Pycnogenol°ledR on cognitive performance, serum lipid profile, endocrinological and oxidative stress biomarkers in an elderly population. Sano, M. Sharma, S. Shoham, S. Iron involvement in neural damage and microgliosis in models of neurodegenerative diseases. Shults, C. Effects of coenzyme Q 10 in early Parkinson disease: evidence of slowing of the functional decline. You may experience some insomnia or indigestion, and you should not take it if you are also taking blood thinning medications like Warfarin Jantoven and certain cancer medications. CoQ10 may reduce the effectiveness of warfarin Jantoven , as well as interact with some blood pressure and cancer medications. In particular, research suggests that it may help improve heart health and blood sugar regulation, protect against certain types of cancer, and reduce the frequency of migraine. It may also reduce oxidative damage that leads to muscle fatigue, skin damage, and brain and lung diseases. However, more research is necessary to determine whether CoQ10 can help in these areas. CoQ10 can be found as a supplement that seems well tolerated, but you should ask your doctor before trying it. You can also increase your intake through various food sources, including organ and muscle meats, oils, nuts, seeds, and legumes. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Coenzyme Q10 CoQ10 is used to treat various health conditions, including migraines, infertility and the effects of aging. This article reviews the…. Learn more about how taking a supplement can affect statin side effects and your overall heart health. Life can take a toll on your energy levels. Fortunately, these 11 vitamins and supplements can boost your energy levels when you need it most. If your period is so heavy that you quickly soak through pads or tampons, there are things you can do to find relief. Find out what home remedies and…. While they're not typically able to prescribe, nutritionists can still benefits your overall health. Let's look at benefits, limitations, and more. A new study found that healthy lifestyle choices — including being physically active, eating well, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption —…. Carb counting is complicated. Take the quiz and test your knowledge! Together with her husband, Kansas City Chiefs MVP quarterback Patrick Mahomes, Brittany Mohomes shares how she parents two children with severe food…. While there are many FDA-approved emulsifiers, European associations have marked them as being of possible concern. Let's look deeper:. Researchers have found that a daily multivitamin supplement was linked with slowed cognitive aging and improved memory. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 9 Benefits of Coenzyme Q10 CoQ Medically reviewed by Philip Ngo, PharmD — By Arlene Semeco, MS, RD and Rachael Ajmera, MS, RD — Updated on December 6, What is CoQ10? It may help treat heart failure. It could help with fertility. It might help support healthy skin aging. It could reduce headaches. It could help with exercise performance. It may help with diabetes. It might play a role in cancer prevention. It may be good for the brain. It could protect the lungs. Food sources of CoQ Frequently asked questions. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. |

0 thoughts on “Coenzyme Q brain health”