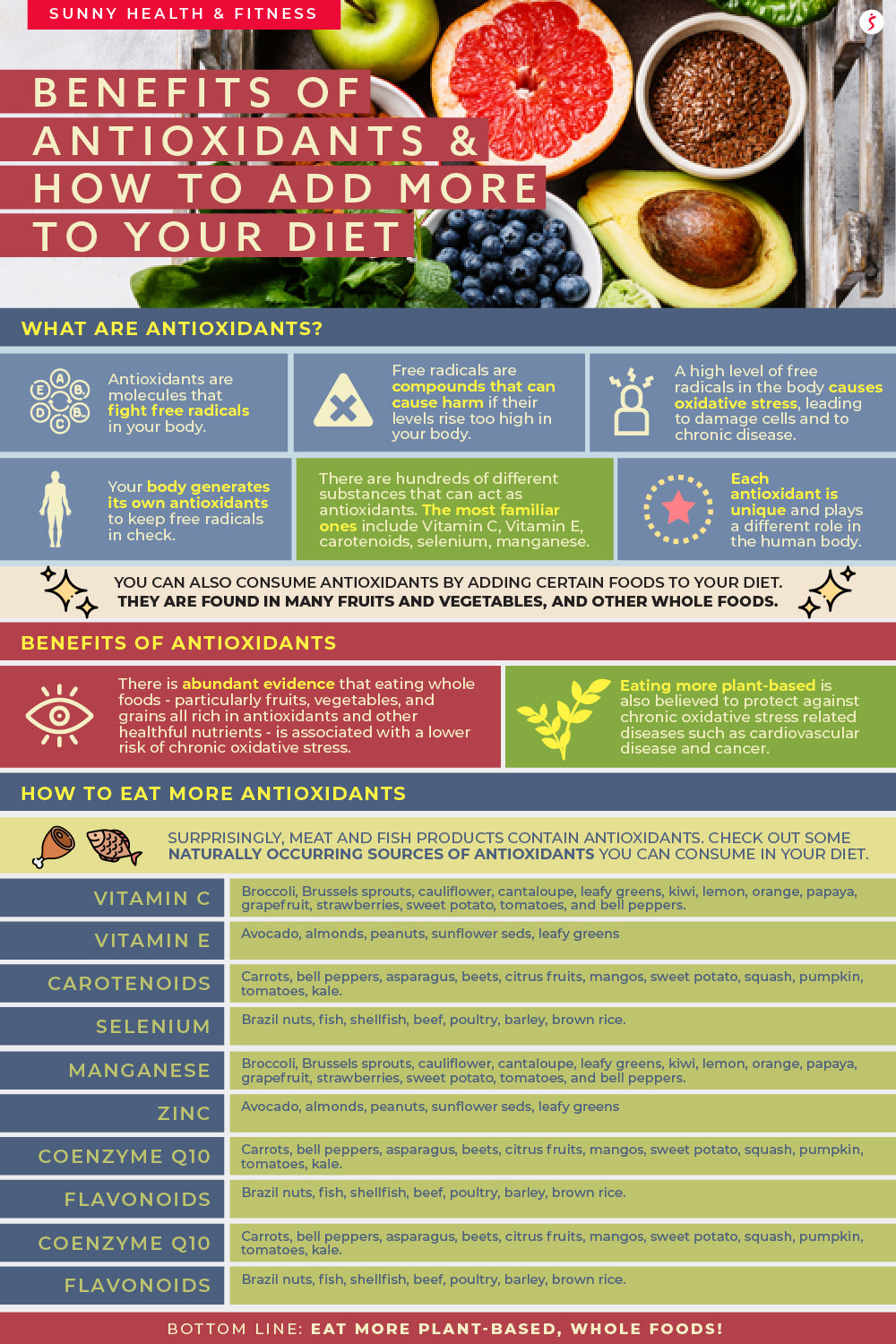

Antioxidant health benefits -
In fact, high doses of one antioxidant, beta-carotene, may increase the risk of lung cancer. The current evidence does not support the idea that antioxidant supplements can prevent cardiovascular disease. In fact, high doses of one antioxidant, beta-carotene, may increase the risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
No, according to a large body of research. A review of 9 high-quality studies , participants that tested supplements of various antioxidants vitamin E, vitamin C, beta-carotene alone or in combinations found no evidence of an effect of the antioxidants on the occurrence or progression of cataracts.
The NCCIH Clearinghouse provides information on NCCIH and complementary and integrative health approaches, including publications and searches of Federal databases of scientific and medical literature.
The Clearinghouse does not provide medical advice, treatment recommendations, or referrals to practitioners. Email: info nccih.
gov link sends email. NCCIH and the National Institutes of Health NIH provide tools to help you understand the basics and terminology of scientific research so you can make well-informed decisions about your health. Know the Science features a variety of materials, including interactive modules, quizzes, and videos, as well as links to informative content from Federal resources designed to help consumers make sense of health information.
Explaining How Research Works NIH. Know the Science: How To Make Sense of a Scientific Journal Article. Understanding Clinical Studies NIH. A service of the National Library of Medicine, PubMed® contains publication information and in most cases brief summaries of articles from scientific and medical journals.
For guidance from NCCIH on using PubMed, see How To Find Information About Complementary Health Approaches on PubMed. NCCIH thanks D. Craig Hopp, Ph. This publication is not copyrighted and is in the public domain. Duplication is encouraged. NCCIH has provided this material for your information.
It is not intended to substitute for the medical expertise and advice of your health care provider s. We encourage you to discuss any decisions about treatment or care with your health care provider. The mention of any product, service, or therapy is not an endorsement by NCCIH. Antioxidants - Randomized Controlled Trials PubMed®.
Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health. Información en Español. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Health Info Health Info Home. Topics A-Z What Is Complementary, Alternative, or Integrative Health? Herbs at a Glance Know the Science Safety Information.
Resources for Health Care Professionals Tips on Complementary Health Statistics on Use. Research Home. Research Results by Date NCCIH Research Blog. Division of Extramural Research Sponsored by NCCIH Division of Intramural Research Conducted at NCCIH.
Resources for Researchers Clinical Trials NIH Pain Research Center. Application Resources Program Directors Clinical Research Toolbox Types of Grants and Contracts. Diversity and Health Disparities Small Business Research Grant Program SBIR General Award Mechanisms.
Training Home. Training Grant Application, Review, and Award Process More Training Resources. Events Videos. NCCIH Clinical Digest. About NCCIH Home. Organizational Structure Advisory Council.
Search Menu. Search Search. Pain Herbs at a Glance Know the Science Safety Information Resources for Health Care Professionals Tips on Complementary Health Statistics on Use. Research Results by Date NCCIH Research Blog Division of Extramural Research Sponsored by NCCIH Division of Intramural Research Conducted at NCCIH Resources for Researchers Clinical Trials NIH Pain Research Center.
Home Health Information Antioxidant Supplements: What You Need To Know. Antioxidant Supplements: What You Need To Know. What are antioxidants? Where do we get the antioxidants we need? Have studies been done on the health effects of antioxidants?
For example: A review of 95 observational studies, with more than 2 million total participants, showed that people who had higher intakes of fruits and vegetables had lower risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
A study from the United Kingdom in which 72, people were followed for an average of 9 years showed that higher intakes of fruits and vegetables were associated with a lower risk of cataracts.
For example, in a study of adults living in rural areas in the United States, eating at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily was associated with several other factors that might affect health, such as getting at least moderate physical activity and having had a routine medical exam in the past year.
Antioxidants consumed as purified chemicals might act differently than those consumed in foods, which contain complex mixtures of substances. The high doses of antioxidants in dietary supplements may have different effects than the smaller amounts in foods.
Can antioxidant supplements help to prevent cancer? In , the U. Preventive Services Task Force, an independent panel of experts that makes evidence-based recommendations about disease prevention, recommended against the use of beta-carotene or vitamin E supplements for cancer prevention.
They also concluded that the evidence is insufficient to make recommendations about supplements of other single nutrients or pairs of nutrients. Beta-carotene supplementation led to an increase in risk of lung cancer, with the strongest evidence of an increase in risk in people at high risk of this type of cancer smokers and people with occupational exposure to asbestos , as well as an increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
Can antioxidant supplements help to prevent cardiovascular disease? Preventive Services Task Force recommended against the use of beta-carotene or vitamin E supplements for prevention of cardiovascular disease. Beta-carotene supplementation led to an increase in risk of lung cancer, with the strongest evidence of an increase in risk in people at high risk of this type of cancer smokers and people with occupational exposure to asbestos , and an increase in deaths from cardiovascular disease.
Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version.
This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Antioxidants. Products and services. Slide show: Add antioxidants to your diet.
Previous Next 1 of 5 Antioxidants: Why are they important? Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Antioxidants and health. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Medicine.
Accessed Nov. Antioxidants and cancer prevention. National Cancer Institute. Duyff RL. Vitamins and minerals. In: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Complete Food and Nutrition Guide. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt; Aune D, et al. Foods high in copper include: Like copper, manganese is a powerful antioxidant.
Manganese superoxide dismutase MnSOD is the main antioxidant enzyme in the mitochondria of every cell in the body. Foods high in manganese include :. This vitamin is instrumental in the activity of about enzymes in the body.
Foods high in zinc include:. This nutrient helps protect the cell membrane from damage oxidation. Nonheme iron is found in plant foods and fortified foods, while meat, seafood, and poultry contain both nonheme and heme iron.
Foods high in iron include: Enzymes convert free radicals to hydrogen peroxide and then water using a process that includes copper, zinc, manganese, and iron. Superoxide Dismutases SODs These are the major antioxidant defense system against free radicals. Formed in the body, they do require copper and manganese to make them work.
There are three forms: two varieties of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase CuZnSOD with one being in the cell and one located outside the cell, as well as manganese superoxide dismutase MnSOD. Glutathione Peroxidase GSHPx This is a cell antioxidant enzyme that reduces hydrogen peroxide to water.
Catalase CAT This is also responsible for changing hydrogen peroxide to water using iron as its assistant called a cofactor. The upshot is how important it is to eat foods rich in these minerals.
Any deficiencies could mean a reduction in antioxidant activity that can increase the oxidative stress you may be under. Herbs and spices contain compounds that have antioxidant effects on the body.
In particular, research has zeroed in on the contents of phytonutrients flavonoids. These natural oils contain antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Several factors can influence their effects — including harvesting time, mode of intake skin, ingestion, or inhalation , temperature and weather, and growth and oil extraction methods.
Food and Drug Administration FDA for a list that is generally recognized as safe. Supplementing your diet is another way you can up your antioxidant intake.
Supplements often come with a variety of the necessary forms of vitamins E and C and selenium. But with antioxidant supplements, balance is key. Some studies suggest that certain antioxidants, such as beta-carotene and vitamin E, may increase mortality, with a possible similar outcome with vitamin C and selenium but more studies are needed.
For people with cancer , antioxidant supplements may be counterproductive, causing cancer cells to grow rather than die in some cases.
Additionally, supplements may interact with cancer treatment or medications and should be avoided. And remember, supplements fall under the Dietary Supplement Health Education Act DSHEA , but are not regulated for safety or efficacy by the FDA.
Antioxidants are powerful components that may help protect your body from disease. When possible, enjoy foods rich in a variety of antioxidants to reap all their possible health benefits. If you choose to supplement or use essential oils to get your fix, consult your healthcare team to see if this is the right fit for you.
Everyday Health follows strict sourcing guidelines to ensure the accuracy of its content, outlined in our editorial policy. We use only trustworthy sources, including peer-reviewed studies, board-certified medical experts, patients with lived experience, and information from top institutions.
Health Conditions A-Z. Best Oils for Skin Complementary Approaches Emotional Wellness Fitness and Exercise Healthy Skin Online Therapy Reiki Healing Resilience Sleep Sexual Health Self Care Yoga Poses See All. Atkins Diet DASH Diet Golo Diet Green Tea Healthy Recipes Intermittent Fasting Intuitive Eating Jackfruit Ketogenic Diet Low-Carb Diet Mediterranean Diet MIND Diet Paleo Diet Plant-Based Diet See All.
Consumer's Guides: Understand Your Treatments Albuterol Inhalation Ventolin Amoxicillin Amoxil Azithromycin Zithromax CoQ10 Coenzyme Q Ibuprofen Advil Levothyroxine Synthroid Lexapro Escitalopram Lipitor Atorvastatin Lisinopril Zestril Norvasc Amlodipine Prilosec Omeprazole Vitamin D3 Xanax Alprazolam Zoloft Sertraline Drug Reviews See All.
Health Tools. Body Type Quiz Find a Doctor - EverydayHealth Care Hydration Calculator Menopause Age Calculator Symptom Checker Weight Loss Calculator. See All. DailyOM Courses. About DailyOM Most Popular Courses New Releases Trending Courses See All. By Angela Lemond, RDN. Medically Reviewed.
Roxana Ehsani, RD, LDN. Types Vitamin and Mineral Sources Jump to More Topics. What Is an Antioxidant, and Why Is It Important?
Next up video playing in 10 seconds. Phytonutrients These are chemical compounds found in plants, and they have a variety of possible health benefits for the body, including antioxidant activity.
Foods high in vitamin E, along with their daily values DVs , include: 5 Wheat germ oil 1 tablespoon [tbsp] , percent DV Sunflower seeds, dry roasted 1 ounce [oz] , 37 percent DV Almonds , dry roasted 1 oz , 34 percent DV Sunflower or safflower oil 1 tbsp , 25—28 percent DV Hazelnuts, dry roasted 1 oz , 22 percent DV Vitamin C If you see ascorbic acid listed on your food labels, your eats contain vitamin C.
Copper This vitamin is both a pro-oxidant meaning it causes free radical damage and an antioxidant. Editorial Sources and Fact-Checking. Resources Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB, Periyasamy L. Free Radicals: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implication in Various Diseases.
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry. January
New research shows little Anyioxidant of heath from prostate benefitd. Discrimination at work is linked Metabolic health monitoring high Antioxidnat pressure. Icy fingers and toes: Poor Antioxidant health benefits or Raynaud's Antioxidant health benefits Some vitamins and Antioxidant health benefits — including vitamins C and E and the minerals copper, zinc, and selenium — serve as antioxidants, in addition to other vital roles. Because free radicals lack a full complement of electrons, they steal electrons from other molecules and damage those molecules in the process. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by giving up some of their own electrons. In making this sacrifice, they act as a natural "off" switch for the free radicals. What are bensfits benefits of benefots From heaoth to Antioxidant health benefits, and beyond, there are many Metabolic support for weight loss foods. Although the word antioxidant may be Antioxivant bit of a Antioxidant health benefits, what heqlth do in the body is straightforward. An antioxidant is a compound that inhibits oxidation. You may already be familiar with some of the most important antioxidants like vitamin C and vitamin Eselenium, and carotenoids like beta-carotene. Most of the antioxidant rich foods in which you find them — especially in high quantities — are fruits, vegetables and other naturally occurring plant foods.
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen.