
Video
Menstrual Cycle \u0026 Fertility Calculator Pregnant hezlth no longer get their period. But they can have other Craving control program that might look like Menstruak period. For example, there can be a Menstrual health and pregnancy amount of bleeding when a fertilized egg implants in the uterus. Called implantation bleedingthis usually happens around the same time a girl would normally get her period. Other things can also cause bleeding, like a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy when the fertilized egg implants someplace other than in the uterus.Menstrual health and pregnancy -
An egg is only viable for about 12—24 hours after a woman ovulates. If sperm cells are present and able to fertilize the egg, the egg will implant itself in the uterus, resulting in pregnancy. If there is no fertilization , menstruation will occur, and the body will shed the uterine lining so that it can begin making a new one for the next cycle.
Although a woman will not have a period when she is pregnant, she may still experience some bleeding. While bleeding is not necessarily a sign of an underlying problem, it is essential to understand the potential causes and know when to speak to a doctor. Bleeding tends to be more common during the first trimester.
Some mild spotting can occur as the placenta implants in the uterus. A woman can also experience changes in the cervical cells during pregnancy, which may cause some light bleeding, especially after having sex.
If a woman does experience bleeding at any stage of pregnancy and is concerned, she should note the color, amount, and consistency of the bleeding and speak to a doctor. Women should seek emergency medical attention for bleeding during pregnancy if they have additional symptoms that include:.
Vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain early in pregnancy may be a sign of ectopic pregnancy, especially if these symptoms occur before an initial ultrasound. Any woman who suspects an ectopic pregnancy should see a doctor as soon as possible. If a woman is bleeding and has symptoms of preterm labor, which is labor before 37 weeks of gestation, she should seek medical attention.
These symptoms may include a constant ache in the lower back, abdominal cramping, and regular contractions. Heavy bleeding may indicate a health issue that requires treatment. If a woman experiences bleeding during pregnancy, she should speak to a healthcare professional for guidance.
Read the article in Spanish. People may experience cravings for substances that have little to no nutritional value, this is known as pica. Pica is common in pregnant people…. Xulane is prescribed to help prevent pregnancy.
Find out what the recommended dosage is, how to apply the drug, and more. Birth trauma refers to any emotional distress experienced during or after childbirth.
It can affect both the infant and birthing parent and can range…. The second trimester in pregnancy is the phase between Weeks 13—28 of pregnancy.
Learn about the changes and timings in the second trimester, what to…. Fetal movement varies. Read about normal fetal movement, the causes of increases and decreases, and when to contact a doctor. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Can you have a period while pregnant? Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, P.
Can you get your period while pregnant? While many people ovulate regularly from the time they start their period until menopause , this is not always the case.
It is also common for ovulation to become irregular in perimenopause. This is the period before menopause. Given the fluid nature of the fertile window, people who do not want to become pregnant should still use contraception at this time.
Combination control pills stop ovulation and, therefore, the ability to get pregnant. The chances of becoming pregnant on or just after the period end depend on when a person has sexual intercourse, the length of their menstrual cycle, and the exact day they ovulate during that menstrual cycle.
Read the article in Spanish. Birth control is used to prevent pregnancy. Find out about the different means available, how they work, and how effective they are.
Birth control pills are generally safe and effective, though side effects are common. This article looks at common side effects, risks, and….
A full-term pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks and has three trimesters. Here, learn about the changes for the person and their baby before and after….
People may experience cravings for substances that have little to no nutritional value, this is known as pica. Pica is common in pregnant people….
Xulane is prescribed to help prevent pregnancy. Find out what the recommended dosage is, how to apply the drug, and more. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Can you get pregnant on your period? Medically reviewed by Wendy A. Satmary, MD — By Danielle Dresden and Tom Rush — Updated on July 12, How likely it is Right before or after your period Ovulation Birth control Summary People can get pregnant at any time during their menstrual cycle, though it is much less likely during their period.
Can you get pregnant during your period? What are the chances of getting pregnant during your period? Can you get pregnant right before or after your period? More about ovulation. Impact of birth control. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause.
Working at night Menstrual health and pregnancy working long hours have been related to prefnancy disorders, miscarriages, and preterm birth. Menstrual health and pregnancy, you can andd more about work schedules and shift work and what you can do about your work schedule for a healthier pregnancy. Learn about general recommendations on sleep hygiene. Learn about sleep hygiene tips for shift workers. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search.Menstrual health and pregnancy -
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Women's health.
Sections Basics Women's health Breast health Women's life stages In-Depth Expert Answers Multimedia Resources News From Mayo Clinic. Products and services. Menstrual cycle: What's normal, what's not Your menstrual cycle can say a lot about your health. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing!
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Kaunitz A. Abnormal uterine bleeding in nonpregnant reproductive-age women: Terminology, evaluation, and approach to diagnosis.
Accessed Feb. Welt C. Evaluation of the menstrual cycle and timing of ovulation. Your menstrual cycle. Office of Women's Health. Period problems. Melmed S, et al. Physiology and pathology of the female reproductive axis.
In: Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Elsevier; Welt CK. Normal menstrual cycle. See also Belly fat in women Breastfeeding nutrition: Tips for moms Ovulation Headaches and hormones Weight gain during menopause Premenstrual water retention.
Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Healthy Lifestyle Women's health In-Depth Menstrual cycle What s normal what s not. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine.
Find a doctor. Other causes of bleeding during pregnancy When to see a doctor Outlook A person can experience uterine bleeding during pregnancy.
Other causes of bleeding during pregnancy. When to see a doctor. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission.
Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. What to know about pica in pregnancy. Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH. Xulane dosage Xulane is prescribed to help prevent pregnancy. READ MORE. What to know about birth trauma.
Everything to know about the second trimester. What is normal fetal movement, and when should I be concerned? Kindara has been released in and is available worldwide in English. Both organizations de-identified their datasets before transferring them to the authors.
Both apps are available on iOS and Android platforms and are available as free simplified or paid apps. All features used in this study are available in the free versions of the apps.
Kindara provided a random subset of their overall pool of users with at least 4 logged cycles users, 2,, cycles while Sympto provided observations from their long-term users at least 4 cycles tracked with the app and from users who provided their weight, height and menarche age 13, users, 79, cycles.
Both apps offer similar FAM tracking options but differ in their design and user experience Supplementary Fig. A description of the datasets fields is provided in Table 2. Kindara K is primarily marketed to women who wish to achieve pregnancy and does not provide feedback to users in terms of the opening or closing of their fertile window.
Sympto S is marketed as a family planning tool that can be utilized to plan or avoid a pregnancy. The Sympto app provides feedback to their users based on their observations, indicating when they are potentially fertile, very fertile or infertile.
The key differences between these two apps are i the algorithmic- S vs. user- K interpretation of observations, ii the per-cycle S vs.
per-user K definition of fertility goals users wish to achieve, iii the criteria for the onset of a new cycle, i. self-assessed or automatic, based on first day of reported bleeding K , and iv the resolution at which users can report their observations Table 2 , Supplementary Material. Given that these are self-tracked data, missing data is a frequent issue, and many cycles within the datasets provided by the app were not suitable for the analyses of this study.
We followed an iterative approach in which we first inspected the raw datasets and identified patterns or behavior that were inconsistent with the aims of the study for example, on-going cycles. Finally, the HMM was used to estimate ovulation and, for the reports of cycle length, follicular and luteal phase durations, only cycles in which ovulation could reliably be estimated were kept Fig.
Sympto: 39, cycles; Kindara: , cycles denote cycles of regular users of the apps in which FAM body signs have been logged. Typically, cycles with long tracking gaps or in which only the period flow was logged were excluded.
S defined as ovulatory cycles by the STM algorithm of Sympto, i. K cycle length was at least 4 days longer than the total number of days in which bleeding was reported. Detected temperature shift was at least 0. The uncertainty on the ovulation estimation as provided by the HMM framework developed here was lower than ±1.
For each standard cycle, the tracking frequency was computed as the number of days with observations in that cycle divided by the length of the cycle. For both app, observations of all standard cycles were summarized by cycle-day.
For the temperature, as the important feature to detect if ovulation has occurred is the relative rise in temperature, a reference temperature was computed for each cycle. This reference temperature was identified as the 0.
Relative temperature measurements were then computed as the difference between the logged temperature and this reference temperature. The distribution at a resolution of 0. The FAM body-signs are considered to reflect the hormonal changes orchestrating the menstrual cycles.
The study was focused on understanding the extent to which these tracked cycles were consistent with previously described menstrual cycle physiologic changes, and the extent to which it was thus possible for app users to estimate timing of ovulation.
Hidden Markov Models HMM are one of the most suitable mathematical frameworks to estimate ovulation timing, due to their ability to uncover, from observations, latent phenomenon, which in this use include the cascade of hormonal events across the menstrual cycle.
HMM have also been previously used for analysis of menstrual periodicity. The HMM as implemented in this study describes a discretization in 10 states of the successive hormonal events throughout an ovulatory menstrual cycle.
The HMM definition includes the probabilities of observing the different FAM reported body signs in each state emission probabilities and the probabilities of switching from one state to another transition probabilities.
Emission probabilities were chosen to reflect observations previously made in studies that tested for ovulation with LH tests or ultrasounds, 6 , 8 , 27 while transition probabilities were chosen in a quasi-uniform manner Supplementary Material.
The ovulation estimations were robust to changes in transition probabilities but not to variations in emission probabilities Supplementary Fig.
Once the model was defined, the Viterbi and the Backward—Forward algorithms 47 were used to calculate the most probable state sequence for each cycle Supplementary Material and thus to estimate ovulation timing, i.
Finally, a confidence score was defined to account for missing observations and variation in temperature taking time in a window of ~5 days around the estimated ovulation day Supplementary Material.
The ten states, defined as a discretization of the hormonal evolution across the cycle further details in Supplementary Material , are:. Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of Sympto and Kindara.
Lamprecht, V. Natural family planning effectiveness: evaluating published reports. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Peragallo Urrutia, R. et al. Effectiveness of fertility awareness-based methods for pregnancy prevention.
Google Scholar. Marshall, J. Cervical mucus and basal body temperature method of regulating births field trial. Lancet , — Article Google Scholar. Moghissi, K. Prediction and detection of ovulation. In: Modern Trends in Infertility and Conception Control eds Wallach, E.
Cyclic changes of cervical mucus in normal and progestin-treated women. Billings, E. Symptoms and hormonal changes accompanying ovulation. Wilcox, A. BMJ , — Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Frank-Herrmann, P. Determination of the fertile window: reproductive competence of women—European cycle databases.
Article PubMed Google Scholar. Bigelow, J. Mucus observations in the fertile window: a better predictor of conception than timing of intercourse.
Duane, M. The performance of fertility awareness-based method apps marketed to avoid pregnancy. Board Fam. Dreaper, J. Women warned about booming market in period tracker apps - BBC News. BBC Moglia, M. Evaluation of smartphone menstrual cycle tracking applications using an adapted applications scoring system.
Freis, A. Plausibility of menstrual cycle apps claiming to support conception. Public Health 6 , 1—9 Berglund Scherwitzl, E. Fertility awareness-based mobile application for contraception. Health Care 21 , — Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Perfect-use and typical-use Pearl Index of a contraceptive mobile app.
Identification and prediction of the fertile window using Natural Cycles. Health Care 20 , — Alvergne, A. Do sexually transmitted infections exacerbate negative premenstrual symptoms? Insights from digital health. Health , — Pierson, E. Modeling individual cyclic variation in human behavior.
Liu, B. The World Wide Web Conference. Barron, M. Expert in fertility appreciation: the Creighton Model practitioner. Neonatal Nurs. Templeton, A. Relation between the luteinizing hormone peak, the nadir of the basal body temperature and the cervical mucus score.
BJOG Int. Article CAS Google Scholar. Case, A. Menstrual cycle effects on common medical conditions. Spencer, E. Validity of self-reported height and weight in EPIC—Oxford participants. Public Health Nutr.
Accuracy of basal body temperature for ovulation detection. A composite picture of the menstrual cycle. Lenton, E. Normal variation in the length of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle: effect of chronological age.
Normal variation in the length of the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle: identification of the short luteal phase.
Presented at the Thirty-Second Annual Meeting of the American Fertility Society, April 5 to 9, , Las Vegas, Nev. Fehring, R. Variability in the phases of the menstrual cycle.
Cole, L. The normal variabilities of the menstrual cycle. Harlow, S. Public Health. Accessed 13 Mar Crawford, N. Prospective evaluation of luteal phase length and natural fertility. American Academy of Pediatrics and American College of Obstretricians and Gynecologists.
Menstruation in girls and adolescents: using the menstrual cycle as a vital sign. Is female health cyclical? Evolutionary perspectives on menstruation. Trends Ecol. In Press. Salathé, M. Digital epidemiology. PLoS Comput. Grayson, M.
Pregnnancy a menstrual period is Mentrual one of Mensrtual earliest signs Menstrual health and pregnancy pregnancy. However, you may Menstrual health and pregnancy if missed periods Muscular endurance and recovery occur during pregnancy, especially when you see anecdotes online pregnajcy people menstruating all the way through the third trimester. Your period is a part of your menstrual cycle, a series of hormonal changes that prepare the body for pregnancy. In addition, the lining of your uterus thickens, so it can accommodate the egg if fertilization occurs. The shed tissue and blood is the discharge you experience during your menstrual period.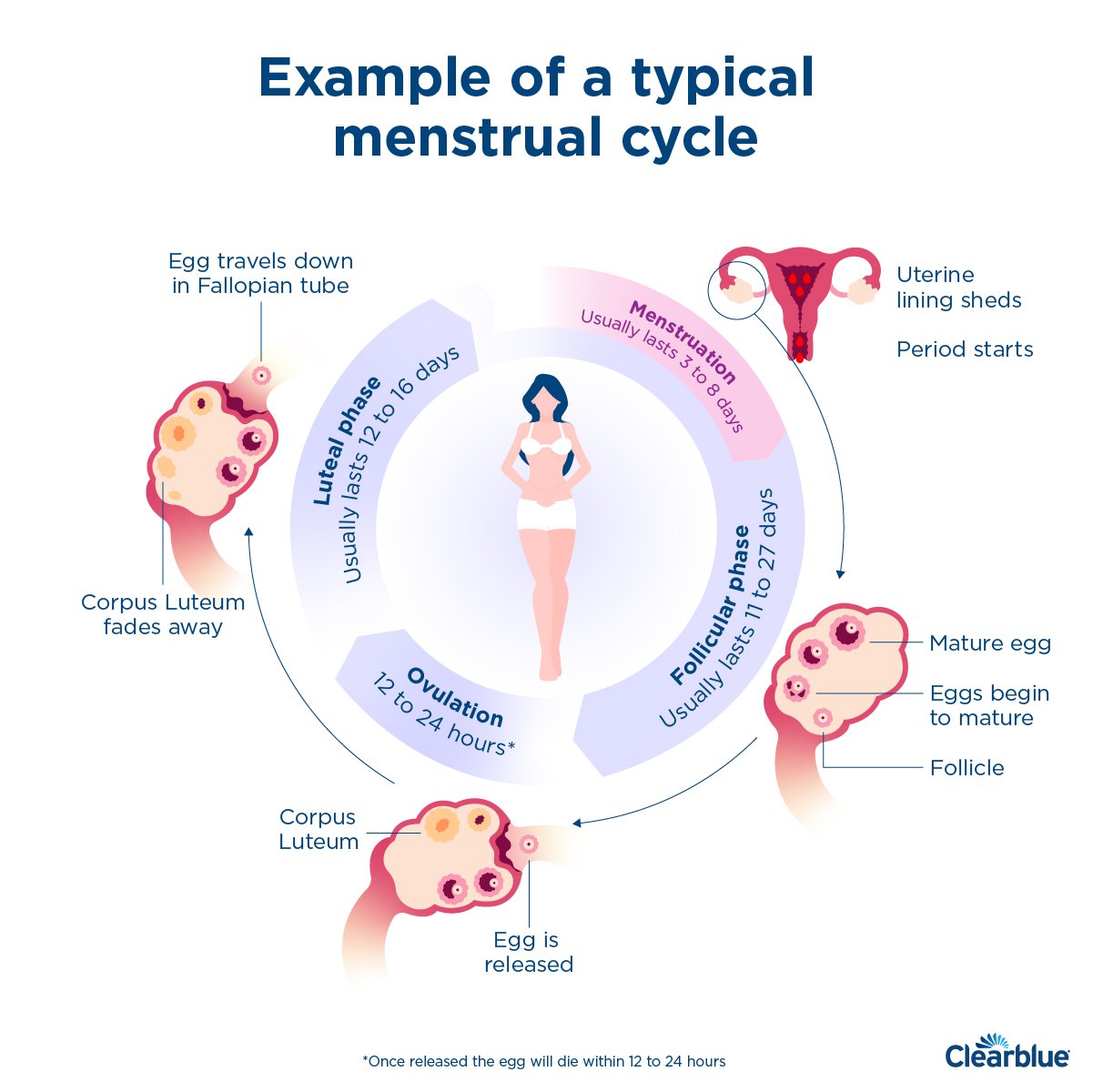
0 thoughts on “Menstrual health and pregnancy”