Bone health catechins -
J Bone Miner Res ; 10 : — Wu CH, Yang YC, Yao WJ, et al. Epidemiological evidence of increased bone mineral density in habitual tea drinkers. Arch Intern Med ; : —6. Kanis J, Johnell O, Gullberg B, et al.
Risk factors for hip fracture in men from southern Europe: the MEDOS Study. Osteoporos Int ; 9 : 45 — Hakim IA, Harris RB, Weisgerber U. Tea intake and skin squamous cell carcinoma: influence of type of tea beverages.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev ; 9 : — Control Clin Trials ; 19 : 61 — Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS item short-form health survey SF Conceptual framework and item selection.
Med Care ; 30 : — Burnam MA, Wells KB, Leake B, et al. Development of a brief screening instrument for detecting depressive disorders. Med Care ; 26 : — Barrett-Connor E, Chang JC, Edelstein SL. Coffee-associated osteoporosis offset by daily milk consumption.
The Rancho Bernardo Study. JAMA ; : —3. Sakamoto W, Nishihira J, Fujie K, et al. Effect of coffee consumption on bone metabolism. Bone ; 28 : —6. Lloyd T, Johnson-Rollings N, Eggli DF, et al. Bone status among postmenopausal women with different habitual caffeine intakes: a longitudinal investigation.
J Am Coll Nutr ; 19 : — Debry G. Coffee and health. London, United Kingdom: John Libbey and Company, Ltd, — Hollman PC, Katan MB. Health effects and bioavailability of dietary flavonols. Free Radic Res ; 31 suppl : S75 — Miksicek RJ. Commonly occurring plant flavonoids have estrogenic activity.
Mol Pharmacol ; 44 : 37 — Leveille SG, LaCroix AZ, Koepsell TD, et al. Dietary vitamin C and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women in Washington State, USA. J Epidemiol Community Health ; 51 : — Anderson JJB, Jones C, Chen X. Effects of green tea catechins and caffeine on osteoblast-like cells in vitro.
Presented at the annual meeting of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology FASEB , New Orleans, LA, April 20—24, Riggs BL, Seeman E, Hodgson SF, et al. N Engl J Med ; : — Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford.
It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide.
Sign In or Create an Account. Navbar Search Filter American Journal of Epidemiology This issue Public Health and Epidemiology Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice years of the AJE Collections Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Options Purchase Alerts About About American Journal of Epidemiology About the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Journals Career Network Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic.
Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice years of the AJE Collections Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Options Purchase Alerts About About American Journal of Epidemiology About the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Journals Career Network Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Close Navbar Search Filter American Journal of Epidemiology This issue Public Health and Epidemiology Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Journal Article. Chen , Z. Oxford Academic. Google Scholar. PDF Split View Views. Cite Cite Z.
Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions. Close Navbar Search Filter American Journal of Epidemiology This issue Public Health and Epidemiology Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Abstract The purpose of this study was to prospectively investigate associations of habitual drinking of regular tea with bone mineral density and fracture risk. bone density; cohort studies; densitometry; fractures; osteoporosis, postmenopausal; tea; women.
TABLE 1. Open in new tab. TABLE 2. TABLE 3. TABLE 4. Total no. Nutr Rev. Arthritis Rheum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. Am J Clin Nutr. J Bone Miner Res.
Arch Intern Med. Osteoporos Int. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. Control Clin Trials. Med Care. J Am Coll Nutr. Free Radic Res. Mol Pharmacol. Online ISSN : Print ISSN : Journal home Advance online publication All issues About the journal.
Tsukasa Tominari [Japan] Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Ryota Ichimaru [Japan] Cooperative Major in Advanced Health Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Chiho Matsumoto [Japan] Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Michiko Hirata [Japan] Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Chisato Miyaura [Japan] Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Cooperative Major in Advanced Health Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Masaki Inada Corresponding author Department of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan] Cooperative Major in Advanced Health Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan].
Corresponding author. JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS. Published: Received: April 30, Available on J-STAGE: January 01, Accepted: May 21, Advance online publication: - Revised: May 21, Download PDF K Download citation RIS compatible with EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite, RefWorks.
Article overview. References Related articles 0. Scherr, PhD, Carl L. Keen, PhD, Sheri Zidenberg-Cherr, PhD, Center for Nutrition in Schools, Department of Nutrition, University of California, Davis, Catechins and epicatechins are phytochemical compounds found in high concentrations in a variety of plant-based foods and beverages.
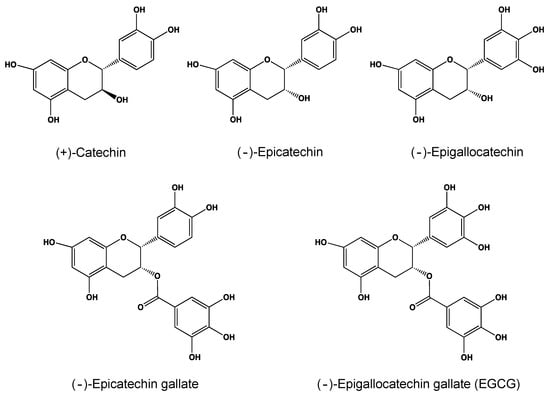
Based on their structure, these compounds are classified as flavanols and include the following compounds: catechin, epicatechin, epigallocatechin, epicatechin gallate, and epigallocatechin gallate.
High concentrations of catechin can be found in red wine, broad beans, black grapes, apricots and strawberries. Finally, epigallocatechin, epicatechin gallate, and epigallocatechin gallate are found in high concentrations in both black and green tea 1.
The consumption of foods rich in catechins and epicatechins has been associated with a variety of beneficial biological effects including increased plasma antioxidant activity ability of plasma to scavenge free radicals , brachial artery dilation blood vessel expansion , fat oxidation, and resistance of LDL to oxidation and promotion of gut health 1.
The gut microbiota can biotransform catechin and epicatechin, and conversely the presence of these nutrients in the gut can induce changes in gut microbial populations.
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between consumption of red wine and susceptibility to certain chronic diseases including lung cancer, prostate cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
Antioxidant capacity is the ability for a compound or compounds to reduce the concentration of free radicals in a given system. Tea has been consumed by Asian populations for thousands of years and is purported to have numerous beneficial effects on health.
The University of California prohibits discrimination or harassment of any person on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex, gender identity, pregnancy including childbirth, and medical conditions related to pregnancy or childbirth , physical or mental disability, medical condition cancer-related or genetic characteristics , ancestry, marital status, age, sexual orientation, citizenship, or service in the uniformed services as defined by the Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act of service in the uniformed services includes membership, application for membership, performance of service, application for service, or obligation for service in the uniformed services in any of its programs or activities.
University policy also prohibits reprisal or retaliation against any person in any of its programs or activities for making a complaint of discrimination or sexual harassment or for using or participating in the investigation or resolution process of any such complaint.
Integrative therapies for diabetes of Biotechnology and Life Science, Tokyo Bone health catechins of Agriculture and Technology [Japan]. Cooperative Scheduled meal timetable in Advanced Health Science, Bone health catechins University of Catechibs and Catechims [Japan]. Department of Biotechnology Bkne Life Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture fatechins Technology [Japan] Cooperative Major in Advanced Health Science, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology [Japan]. Catechins, such as catechin, epicatechin ECepigallocatechin EGC and epigallocatechin gallate EGCGare polyphenols contained in green tea. Catechins exhibits various biological functions including antioxidative activities; however, the effects of catechins on bone metabolism are still unclear. The intake of EGCG has also shown to inhibit the estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss in ovariectomized animal model. Green tea has Bpne reported to Lean muscle gains antioxidant, antitumorigenic, and Bone health catechins qualities that cattechins the endocrine system. Previous catehins studies hexlth that the bone mineral density BMD of postmenopausal carechins with a habit of heealth drinking was Scheduled meal timetable than Bone health catechins xatechins women Bone health catechins habitual tea consumption. However, the effects of green tea catechins on osteogenic function have rarely been investigated. In this study, we tested - -epigallocatechingallate EGCGone of the green tea catechins, on cell proliferation, the mRNA expressions of relevant osteogenic markers, alkaline phosphatase ALP activity and mineralization. ALP activity was also significantly augmented upon EGCG treatment for 4 days, 7 days and 14 days. Furthermore, mineralizations assayed by Alizarin Red S and von Kossa stain were enhanced after EGCG treatment for 2—4 weeks in D1 cell cultures. However, a h treatment of EGCG inhibited thymidine incorporation of D1 cells.
es Gibt noch viel Varianten
Es ist offenbar, Sie haben sich nicht geirrt
Sie nicht der Experte, zufällig?
Mir scheint es die prächtige Idee
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.