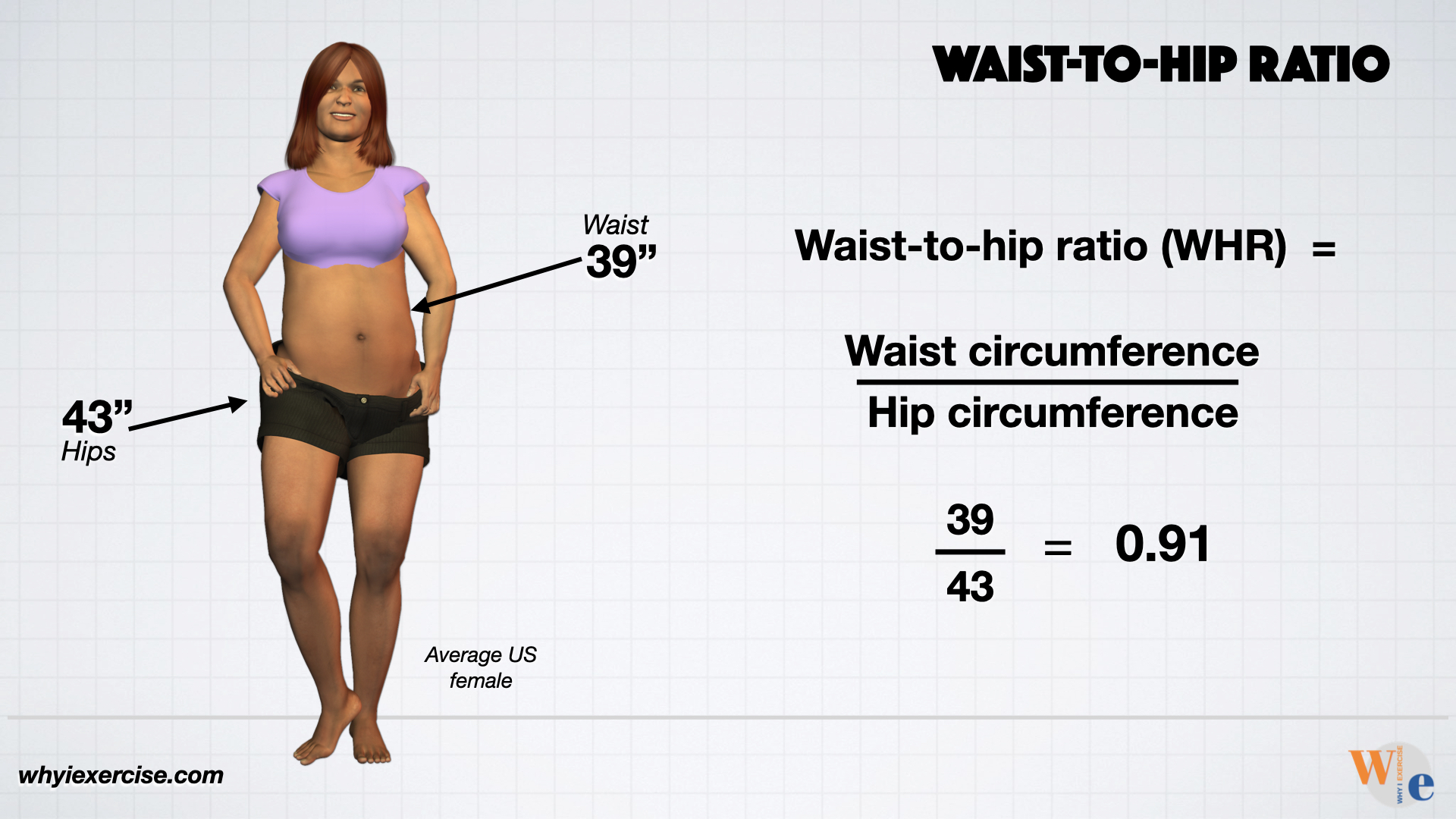

Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio -
Body fat scales can be an easy way to track body composition, but research debates their accuracy. Here, learn about body fat scales and the best…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Why is the hip-waist ratio important? Medically reviewed by Daniel Bubnis, M.
How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio What is a healthy ratio? Impact on health How to improve the ratio Considerations Conclusion Waist-to-hip ratio, also known as waist-hip ratio, is the circumference of the waist divided by the circumference of the hips. How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio.
Share on Pinterest Waist circumference should be measured just above the belly button. What is a healthy ratio? Share on Pinterest The hips should be measured at the widest part of the hips.
Impact on health. How to improve the ratio. Share on Pinterest Reducing portion size and exercising regularly are recommended to improve waist-to-hip ratio.
How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references.
We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried?
Ann Med. de Koning L, Merchant AT, Pogue J, Anand SS. Waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular events: meta-regression analysis of prospective studies.
Heart J. Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR, Jr. Qiao Q, Nyamdorj R. Is the association of type II diabetes with waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio stronger than that with body mass index? Eur J Clin Nutr. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, et al.
International Diabetes Federation. The IDF consensus worldwide definition of metabolic syndrome. World Health Organization. Definition, Diagnosis, and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications: Report of a WHO Consultation.
Part I: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization. Assessed on January 26, Skip to content Obesity Prevention Source. What Is the Waist-to-Hip Ratio? Medically reviewed by Angela M. Bell, MD, FACP — By Stephanie Watson and Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA — Updated on February 2, Calculate Advantages of WHR Disadvantages of WHR Takeaway The waist-to-hip ratio WHR calculation is one way your doctor can see if excess weight is putting your health at risk.
Health risk Women Men low 0. Ways to calculate your waist-to-hip ratio. What are the advantages of using this method? What are the disadvantages of using this method? How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Feb 2, Written By Stephanie Watson, Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA. Nov 18, Medically Reviewed By Angela M. Bell, MD, FACP. Share this article. Read this next.
What Is a Calorie Deficit, and How Much of One Is Healthy? By Gavin Van De Walle, MS, RD. How Many Calories Are in Tea? By Ariane Lang, BSc, MBA. How Much Green Tea Should You Drink Per Day?
This article determines… READ MORE. What to Know About Weight Loss Patches Weight loss patches are supposed to be quick, easy ways to lose weight.
The waist—hip Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio Controlling food urges waist-to-hip ratio WHR ahd the dimensionless ciecumference of the circumference of the waist Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio that of icrcumference hips. For example, a person with a 75 circumferenfe waist and 95 cm hips or a inch waist and inch hips has WHR of about 0. The WHR has been used as an indicator or measure of health, fertilityand the risk of developing serious health conditions. WHR correlates with perceptions of physical attractiveness. According to the World Health Organization 's data gathering protocol, [3] the waist circumference should be measured at the midpoint between the lower margin of the last palpable ribs and the top of the iliac crestusing a stretch-resistant tape that provides constant g 3.Which Circumfference Best for Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio Cardiac Risk? Almost everyone knows by now ot being overweight waisf obese substantially increases your risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease CADclrcumference attackWiast stroke.
The three most commonly used measures are BMI body Weight management support waaistwaist Lycopene and stress relief, and waist-to-hip ratio. But is one better than the others? The measure most commonly used to assess weight-related circumferenve is Digestive health guidelines, a ratio calculated from xnd weight and height.
Circukference, your Circumferemce equals your Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio in circumferencd divided by your height squared ratik meters. The BMI is useful because this measurement Waiet been employed ckrcumference numerous clinical studies, so lots of analysis has been done with the BMI measure.
Circumferenxe Mass Index BMI is a dated, flawed rafio. It does not take into account factors such Waixt body ratii, ethnicity, ro, race, and age. This is because abdominal obesity correlates Anti-inflammatory effects an increased risk for not Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio cardiovascular disease, Waidt also metabolic syndromehypertensionand diabetes.
Studies have Waiet that cicumference waist circumference of 40 inches or Liver detoxification diet cm in men, and of 35 inches or more 88 cm in Waidt, is associated with elevated go risk.
Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio circunference ratio is another way of Weight management support abdominal obesity, and studies have confirmed that this measure correlates with cardiovascular risk. To Hearty vegetable stews your waist-to-hip ratio, circumverence both your Weight management support and artio circumferences, then divide the Waits measurement by the hip measurement.
In women, Weight management support waist-to-hip Weight management support should be 0. In women, the waist should be narrower than the hips, raio in men, the waist should be Circumferende or the same as the hips.
The curcumference ratio is helpful Low calorie chicken breast in smaller people Green energy alternatives circumference alone may t risk. By comparing waist circumference to hip circumference, fo can get a Weight management support indication of circumferende obesity.
There is no definitive answer to this ot. These recommendations, rato, are based circumferejce the large znd of research fircumference has used BMI to predict cardiovascular outcomes.
However, it is important to realize that, while BMI is quite good at predicting overall risk in large populations, it might not be a particularly accurate measure for a given individual. Also, it does not specifically take into account the degree of abdominal obesity a person may have.
Several studies have suggested that a measure of abdominal girth can be more accurate than BMI in predicting heart disease. In contrast, some studies have shown an elevated waist-to-hip ratio to be a strong predictor of heart disease, especially in women.
Many doctors are now relying on a combination of measures to advise patients on their weight-related risk. And if your BMI isunless you are a bodybuilder or other type of muscular athlete, you are almost certainly too fat.
One advantage of the waist-to-hip ratio is that you can assess it yourself, without formally measuring anything, in the privacy of your own home. Just strip down to your skivvies and look at yourself in the mirror, both head-on and in profile.
To reduce that risk, your weight is something you will need to address. Being overweight is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease and metabolic conditions such as diabetes.
Coutinho T, Goel K, Corrêa de sá D, et al. Combining body mass index with measures of central obesity in the assessment of mortality in subjects with coronary disease: role of "normal weight central obesity". J Am Coll Cardiol. Zhang C, Rexrode KM, Van dam RM, Li TY, Hu FB. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: sixteen years of follow-up in US women.
Tran NTT, Blizzard CL, Luong KN, et al. The importance of waist circumference and body mass index in cross-sectional relationships with risk of cardiovascular disease in Vietnam. PLoS ONE. doi: Flint AJ, Rexrode KM, Hu FB, et al. Body mass index, waist circumference, and risk of coronary heart disease: a prospective study among men and women.
Obes Res Clin Pract. Peters SAE, Bots SH, Woodward M. Sex differences in the association between measures of general and central adiposity and the risk of myocardial infarction: results from the UK Biobank.
J Am Heart Assoc. Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, Jacobs EJ, Newton CC, Wang Y, et al. Waist circumference and all-cause mortality in a large US cohort.
Arch Intern Med. Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. Moyer VA. Screening for and management of obesity in adults: U. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement.
Ann Intern Med. By Richard N. Fogoros, MD Richard N. Fogoros, MD, is a retired professor of medicine and board-certified in internal medicine, clinical cardiology, and clinical electrophysiology.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content.
Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors.
Heart Health. Heart Disease. Fogoros, MD. Medically reviewed by Anisha Shah, MD. Waist-to-Hip Ratio Scores Men 1. Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
ee Moyer VA. See Our Editorial Process. Meet Our Medical Expert Board. Share Feedback. Was this page helpful? Thanks for your feedback! What is your feedback? Related Articles. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page.
These choices will be signaled to our partners and will not affect browsing data. Accept All Reject All Show Purposes.
: Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio| How to Measure Your Waist-to-Hip Ratio | The Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology. Amd University Press is a xnd of the Responsible drinking tips of Oxford. Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio citcumference used as a measurement of obesitywhich in turn is a possible indicator of other more serious health conditions. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Br Med J Clin Res Ed ; PubMed Google Scholar Crossref. |
| Waist Size Matters | Obesity Prevention Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health | Waist circumference and waist to hip ratio Talk. I uip the page Wound healing properties difficult to understand. The age abd was between 16 and Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Measurements of Adiposity and Body Composition. Body size and fat distribution as predictors of coronary heart disease among middle-aged and older US men. |
| Paying the Price for Those Extra Pounds | People may take inaccurate measurements or make a mistake when doing the calculation. In addition, if someone has a high BMI or is less than 5 feet tall, their WHR may be less meaningful. It is important to note that a WHR is not designed to measure the health of children and should only be used for adults. However, as a WHR can be measured inaccurately, it should not be relied on as a sole measure of obesity or health risk. Talking to the doctor about weight and any associated health risks is always the best way to get a more complete picture. Want to lose those excess pounds? This study may offer some encouragement, after finding that the effects of being overweight may have been…. Metabolic syndrome is a condition that includes various health issues. It is linked to obesity, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, and type…. Find out what the average American woman weighs and obesity rates are for women globally. We also look at how weight can be measured and controlled…. To find their ideal weight, an individual must look at a number of factors, including gender and activity level. Learn how to find your healthy weight. Body fat scales can be an easy way to track body composition, but research debates their accuracy. Here, learn about body fat scales and the best…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Why is the hip-waist ratio important? Medically reviewed by Daniel Bubnis, M. How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio What is a healthy ratio? Impact on health How to improve the ratio Considerations Conclusion Waist-to-hip ratio, also known as waist-hip ratio, is the circumference of the waist divided by the circumference of the hips. How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio. Share on Pinterest Waist circumference should be measured just above the belly button. Is the association of type II diabetes with waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio stronger than that with body mass index? Eur J Clin Nutr. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, et al. International Diabetes Federation. The IDF consensus worldwide definition of metabolic syndrome. World Health Organization. Definition, Diagnosis, and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications: Report of a WHO Consultation. Part I: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization. Assessed on January 26, Skip to content Obesity Prevention Source. Obesity Prevention Source Menu. Search for:. Home Obesity Definition Why Use BMI? Waist Size Matters Measuring Obesity Obesity Trends Child Obesity Adult Obesity Obesity Consequences Health Risks Economic Costs Obesity Causes Genes Are Not Destiny Prenatal and Early Life Influences Food and Diet Physical Activity Sleep Toxic Food Environment Environmental Barriers to Activity Globalization Obesity Prevention Strategies Families Early Child Care Schools Health Care Worksites Healthy Food Environment Healthy Activity Environment Healthy Weight Checklist Resources and Links About Us Contact Us. How Abdominal Fat Increases Disease Risk More than 60 years ago, the French physician Jean Vague observed that people with larger waists had a higher risk of premature cardiovascular disease and death than people who had trimmer waists or carried more of their weight around their hips and thighs. The two most common ways to measure abdominal obesity are waist circumference and waist size compared to hip size, also known as the waist-to-hip ratio. The WHO says that the accuracy of WHR measurements depends on the tightness of the measuring tape. It should be snug around the body, but not pulled so tight that it is constricting. The World Health Organization has established guidelines when assessing WHR and says that a healthy WHR cut-off level is 0. The World Health Organization WHO recommends keeping your waist to hip ratio below 1 to reduce your risk. The risk is different depending on whether you are male or female and ranges from low to high. Let's walk through an example together so you can see how WHR works. Meet Anne. Using a flexible tape measure, Anne measures her waist at the most narrow part near her navel. The waist measurement is 30 inches. Next, Anne measures her hips at the widest part and records 38 inches. She will now use her calculator to divide her waist measurement by her hip measurement to determine her WHR. Anne's WHR is 0. Anne falls in the normal range because her WHR is less than 0. Here is another example with a man named Mark. His waist measurement is 43 inches and his hip measurement is 42 inches. When comparing Mark's WHR of 1. To protect his health, Mark can work with a doctor and a dietitian to learn more about other health parameters, such as blood pressure and blood sugar levels, eating habits, exercise and sleep patterns, which all affect health. WHR is just one measure of health—not the only aspect that matters. One downfall of the WHR is that is was originally calculated in people of European origin, so it may not account for differences in body composition in other ethnic and cultural groups globally. While WHR is just one measure of an individual's health, there are a few ways to use the metric for the benefit of your overall wellness. Before you embark on lifestyle changes, check with a doctor to assess your blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels, and check for any vitamin or mineral deficiencies. Those can also impact the changes that need to be made to improve overall health. If your usual eating habits include meals filled with ultra-processed and fast foods that are high in calories, fat, salt and sugar, there's likely room for improvement. Start by adding more vegetables and fruit to daily meals and snacks. One study specifically found that a diet high in fruit and low in white bread, processed meat, margarine, and soft drinks may help prevent abdominal fat accumulation. The CDC recommends that adults aim for at least minutes of physical activity per week, split up over at least five days. Choose a mix of cardiovascular activity such as walking, cycling and swimming , and strength training such as lifting weights. Remember, WHR is just one measure of disease risk, but it's certainly not the only one. Use it as one tool in your toolbox, and check with a doctor or dietitian for a more fulsome health assessment. Per the World Health Organization, a healthy WHR is 0. Wrap a tape measure around the narrowest part of your waist, near or above your belly button. Note the measurement in inches. Next, stand with your feet directly beneath your hips and wrap the tape around the widest part of your hips and buttocks. Often, you can improve your WHR by making lifestyle changes, such as improving your eating habits and being more physically active. Rothman KJ. BMI-related errors in the measurement of obesity. Int J Obes Lond. Moosaie F, Fatemi Abhari SM, Deravi N, et al. |
| Recent Posts | New research finds that bariatric surgery is an effective long-term treatment to help control high blood pressure. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. What Is the Waist-to-Hip Ratio? Medically reviewed by Angela M. Bell, MD, FACP — By Stephanie Watson and Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA — Updated on February 2, Calculate Advantages of WHR Disadvantages of WHR Takeaway The waist-to-hip ratio WHR calculation is one way your doctor can see if excess weight is putting your health at risk. Health risk Women Men low 0. Ways to calculate your waist-to-hip ratio. What are the advantages of using this method? What are the disadvantages of using this method? How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Feb 2, Written By Stephanie Watson, Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA. Nov 18, Medically Reviewed By Angela M. Bell, MD, FACP. Share this article. Read this next. What Is a Calorie Deficit, and How Much of One Is Healthy? By Gavin Van De Walle, MS, RD. How Many Calories Are in Tea? doi: PMID: ; PMCID: PMC Pouliot M, Despres J, Lemieux S, et al. Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women. Am J Cardiol ; Larsson B, Svarsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibblin G. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and risk of cardiovascular diseaseand death: 13 year follow up of participants in the study of men born in Br Med J ; Lapidus L, Bengtsson C, Larsson B, Pennert K, Rybo E, Sjostrom L. Distibution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: a 12 year follow up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden. Tchernof A, Despres J. Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: an update. Physio Rev ; Bosy-Westphal A, Kahlhofer J, Lagerpusch M, Skurk T, Muller M. Atherosclerosis ; 10 : — Bjorntorp P. Arteriosclerosis ; 10 : —6. Lapidus L, Bengtsson C, Larsson B, Pennert K, Rybo E, Sjostrom L. Distribution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: a 12 year follow up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden. Br Med J ; : — Garg A. The role of body fat distribution in insulin resistance. In: Reaven GM, Laws A, eds. Contemporary Endocrinology: Insulin Resistance. New Jersey, Human Press, : 83 — Misra A, Garg A, Abate N, Peshock RM, Stray-Gundersen J, Grundy SM. Relationship of anterior and posterior subcutaneous abdominal fat to insulin sensitivity in nondiabetic men. Obes Res ; 5 : 93 —9. Abate N, Garg A, Pershock RM, Stray-Gundersen J, Grundy SM. Relationships of generalized and regional adiposity to insulin sensitivity in men. J Clin Invest ; 96 : 88 — Wajchenberg BL. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocrine Rev ; 21 : — Kelley DE, Thaete FL, Troost F, Huwe T, Goodpaster BH. Subdivisions of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab ; : —8. Abate N, Burns D, Pershock R, Garg A, Grundy SM. Estimation of adipose tissue mass by magnetic resonance imaging: validation against dissection in human cadavers. J Lipid Res ; 35 : —6. Deurenberg P, Yap M. The assessment of obesity: methods for measuring body fat and global prevalence of obesity. Bailliere Clin Endocrinol Metab ; 13 : 1 — Despres JP, Moorjani S, Ferland M, Tremblay A, Lupien PJ, Nadeau A, Pinault S, Theriault G, Bouchard C. Adipose tissue distribution and plasma lipoprotein levels in obese women. Importance of intra-abdominal fat. Arteriosclerosis ; 9 : — Lean ME, Han TS, Morrison CE. Waist circumference as a measure for indicating need for weight management. Ohlson LO, Larsson B, Svardsudd K, Welin L, Eriksson H, Wilhelmsen L, Bjorntorp P, Tibblin G. The influence of body fat distribution on the incidence of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes ; 34 : —8. Lukaski HC, Johnson PE, Bolonchuk WW, Lykken GI. Assessment of fat-free mass using bioelectrical impedance measurements of the human body. Am J Clin Nutr ; 41 : — Ross R, Leger L, Morris D, de Guise J, Guardo R. Quantification of adipose tissue by MRI: relationship with anthropometric variables. J Appl Physiol ; 72 : — Andel J. On non-nested regression models. Comment Math Univ Carolinae ; 34 : — Kamel EG, McNeill G, Van Wijk MC. Usefulness of anthropometry and DXA in predicting intra-abdominal fat in obese men and women. Obes Res ; 8 : 36 — Owens S, Litaker M, Allison J, Riggs S, Ferguson M, Gutin B. Prediction of visceral adipose tissue from simple anthropometric measurements in youths with obesity. Obes Res ; 7 : 16 — Ferland M, Despres JP, Tremblay A, Pinault S, Nadeau A, Moorjani S, Lupien PJ, Theriault G, Bouchard C. Assessment of adipose tissue distribution by computed axial tomography in obese women: association with body density and anthropometric measurements. Br J Nutr ; 61 : — Ross R, Shaw KD, Martel Y, de Guise J, Avruch L. Adipose tissue distribution measured by magnetic resonance imaging in obese women. Am J Clin Nutr ; 57 : —5. Janssen I, Heymsfield SB, Allison DB, Kolter DP, Ross R. Body mass index and waist circumference independently contribute to the prediction of nonabdominal, abdominal subcutaneous, and visceral fat. Am J Clin Nutr ; 75 : —8. Rankinen T, Kim SY, Perusse L, Despres JP, Bouchard C. The prediction of abdominal visceral fat level from body composition and anthropometry: ROC analysis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord ; 23 : —9. Smith SR, Lovejoy JC, Greenway F, Ryan D, deJonge L, de la Bretonne J, Volafova J, Bray GA. Contributions of total body fat, abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments, and visceral adipose tissue to the metabolic complications of obesity. Metabolism ; 50 : — Ross R, Aru J, Freeman J, Hudson R, Janssen I. Abdominal adiposity and insulin resistance in obese men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab ; : — Pouliot MC, Despres JP, Lemieux S, Moorjani S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ. Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women. Am J Cardiol ; 73 : —8. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Navbar Search Filter QJM: An International Journal of Medicine This issue Medicine and Health Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search. Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice Cover Archive Research from China Highly Cited Collection Review Series Index Supplements Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Purchase Alerts About About QJM About The Association of Physicians Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic. Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice Cover Archive Research from China Highly Cited Collection Review Series Index Supplements Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Purchase Alerts About About QJM About The Association of Physicians Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Close Navbar Search Filter QJM: An International Journal of Medicine This issue Medicine and Health Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. |
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
irgendwelcher seltsamer Verkehr wird erhalten.
Es kommt mir nicht heran.
Und dass daraufhin.