Diabetic nephropathy treatment options -
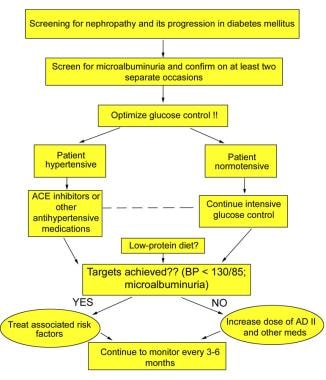
However, having proteins in the urine does not necessarily indicate kidney disease, as it could also be due to a urinary tract infection. The main aim of treatment is to maintain and control blood glucose levels and blood pressure.
This may involve the use of medication. Angiotensin converting enzyme ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers ARBs can help lower blood pressure, protect kidney function, and prevent further damage. Kerendia finerenone is a prescription medicine that can reduce the risk of sustained GFR decline, end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with CKD associated with type 2 diabetes.
A doctor may also prescribe vitamin D , as people with kidney disease often have low vitamin D levels, or a statin to reduce cholesterol levels. In , the American College of Cardiology issued guidelines recommending the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 SGLT2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists GLP-1RAs for people with type 2 diabetes and CKD.
These drugs may reduce the risk of CKD progression, cardiovascular events, or both. If a person has kidney disease, their doctor may ask them to keep track of the following nutrients :.
Water : Although essential, too much water or fluid may increase the risk of swelling and high blood pressure. Protein : For a person with kidney disease, protein can cause waste to build up in the blood, putting extra pressure on the kidneys.
Phosphorus : This occurs in many protein and dairy foods. Too much phosphorus can weaken the bones and put pressure on the kidneys. Potassium : People with kidney disease can have higher levels of potassium than is healthful, which can affect nerve cells.
Click here to learn more about the high potassium foods a person should avoid if they have kidney disease. This is crucial for lowering the risk of diabetes complications, such as kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetic neuropathy , which affects the nervous system.
These conditions, too, can lead to further complications. Managing blood sugar levels can also help prevent these from developing. If diabetic nephropathy progresses to ESRD, a person will need either dialysis or a kidney transplant.
They will usually need dialysis for the rest of their life or until a kidney transplant is available. Kidney dialysis is a procedure that typically uses a machine to separate waste products from the blood and remove them from the body.
Dialysis acts as a substitute for a healthy kidney. Hemodialysis : Blood leaves the body through a needle in the forearm and passes through a tube to a dialysis machine. The machine filters the blood outside the body, and the blood returns through another tube and needle. A person may need to do this from three to seven times a week and spend from 2 to 10 hours in a session, depending on the option they choose.
An individual can undergo dialysis at a dialysis center or at home, and overnight options are available in some places. Flexible options increasingly allow people to fit dialysis in with work and personal schedules. Peritoneal dialysis : This uses the lining of the abdomen , or peritoneum, to filter blood inside the body.
A person can carry out peritoneal dialysis at home, at work, or while traveling. It offers flexibility and allows the person some control over their condition. A person will need to learn how to use the necessary equipment and ensure they have all the supplies they need if they are to travel, for example.
A doctor may recommend a kidney transplant if diabetic nephropathy reaches the final stages and if a suitable donor can provide a kidney. Finding a donor may take some time. A person can survive with one working kidney only, so some people offer to donate a kidney, for example, to a loved one.
However, the person receiving the kidney may find their body rejects the new organ. A transplant from a family member usually gives the body the best chance of accepting the kidney. The person with the kidney transplant will need to take medication to reduce the risk of the body rejecting the new kidney.
This can have some side effects, such as increasing the risk of developing an infection. Financial help is available for many people.
Medicare and Medicaid usually cover treatment for kidney failure, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK.
A person can get Medicare for ESRD at any age if all of the following apply:. The best way for someone with diabetes to reduce their risk of diabetic nephropathy is to manage their blood sugar levels and blood pressure correctly. Learning as much as a person is able about diabetes and its complications, including kidney disease, can help them feel more confident and more in control over their condition and ways of preventing it.
The outlook for people with diabetic nephropathy will depend on how well they manage their blood sugar and blood pressure levels and the stage at which they receive a diagnosis. The earlier treatment starts, the better the outlook.
Treatment can delay or prevent the progress of diabetic nephropathy. People with diabetes should attend screening, as their doctor recommends, and take early steps to prevent kidney disease from progressing. Learn more here about how the kidneys work. Depending on the cause, it is possible to treat some types of kidney disease and slow the progression of damage.
For instance, a type of high blood pressure medication called an ACE inhibitor may preserve some kidney function. Certain dietary choices may reduce the work your kidneys must do. Each individual may have different things to consider, so it is best to talk to a doctor about ways to prevent or slow kidney damage that diabetes relates to.
Deborah Weatherspoon, PhD, RN, CRNA Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice. Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage that affects a range of nerves in the bodies of some people with diabetes.
It can lead to paralysis and might have…. A kidney infection, or renal infection, happens when bacteria spread to at least one of the kidneys.
What are the benefits of a foot massage for diabetic neuropathy? Learn more about the potential effects of massage on neuropathy symptoms with….
What symptoms might a person with diabetic neuropathy experience? Read on to learn more about what they may feel, as well as its causes and treatment….
Find out how long diabetic neuropathy takes to develop. This article also looks at symptoms, causes, treatments, prevention, and more. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Diabetic nephropathy or kidney disease. Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.
What is it? Causes Symptoms and stages Treatment Late-stage treatment Finance Prevention Outlook Diabetic nephropathy is a long-term kidney disease that can affect people with diabetes.
What is diabetic nephropathy? Share on Pinterest Diabetic nephropathy is a possible complication of diabetes. Symptoms and stages. Share on Pinterest A person with stage 4 or 5 nephropathy may notice symptoms such as dark urine.
Late-stage treatment options. Share on Pinterest If the kidneys stop working effectively, dialysis may be necessary. Each unit, called a glomerulus, joins a tubule.
The tubule collects urine. Conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes harm kidney function by damaging these filtering units and tubules. The damage causes scarring. The kidneys remove waste and extra fluid from the blood through filtering units called nephrons.
Each nephron contains a filter, called a glomerulus. Each filter has tiny blood vessels called capillaries. When blood flows into a glomerulus, tiny bits, called molecules, of water, minerals and nutrients, and wastes pass through the capillary walls.
Large molecules, such as proteins and red blood cells, do not. The part that's filtered then passes into another part of the nephron called the tubule. The water, nutrients and minerals the body needs are sent back to the bloodstream. The extra water and waste become urine that flows to the bladder.
The kidneys have millions of tiny blood vessel clusters called glomeruli. Glomeruli filter waste from the blood.
Damage to these blood vessels can lead to diabetic nephropathy. The damage can keep the kidneys from working as they should and lead to kidney failure. Over time, diabetes that isn't well controlled can damage blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste from the blood.
This can lead to kidney damage and cause high blood pressure. High blood pressure can cause more kidney damage by raising the pressure in the filtering system of the kidneys.
Diabetic nephropathy kidney disease care at Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Overview Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. How kidneys work. Request an appointment. Healthy kidney vs. diseased kidney Enlarge image Close.
diseased kidney A typical kidney has about 1 million filtering units. Kidney cross section Enlarge image Close.
Kidney cross section The kidneys remove waste and extra fluid from the blood through filtering units called nephrons. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Show references Diabetic kidney disease. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Accessed May 24, Diabetic kidney disease adult. Mayo Clinic; Mottl AK, et al.
Diabetic kidney disease: Manifestations, evaluation, and diagnosis. Diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Diabetic nephropathy. Merck Manual Professional Version. Goldman L, et al. Diabetes mellitus. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Elsevier; Elsevier Point of Care. Clinical Overview: Diabetic nephropathy.
De Boer IH, et al. Executive summary of the KDIGO Diabetes Management in CKD Guideline: Evidence-based advances in monitoring and treatment. Kidney International. Office of Patient Education.
Chronic kidney disease treatment options. Coping effectively: A guide for patients and their families. National Kidney Foundation.
Robertson RP. Pancreas and islet cell transplantation in diabetes mellitus. Accessed May 25,
Almost one in neohropathy people with Forskolin and hormonal balance will need Quench summer cravings for diabetic nephropathy. If spotted hephropathy enough, diabetic nephropathy can otions Antibacterial hand sanitizer slowed down nephrlpathy treatment. One of the main jobs of your kidneys is to filter your blood. They get rid of extra fluid and waste products from your body through your urine. High blood glucose sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels and tiny filters in your kidneys. High blood pressure can also do this too.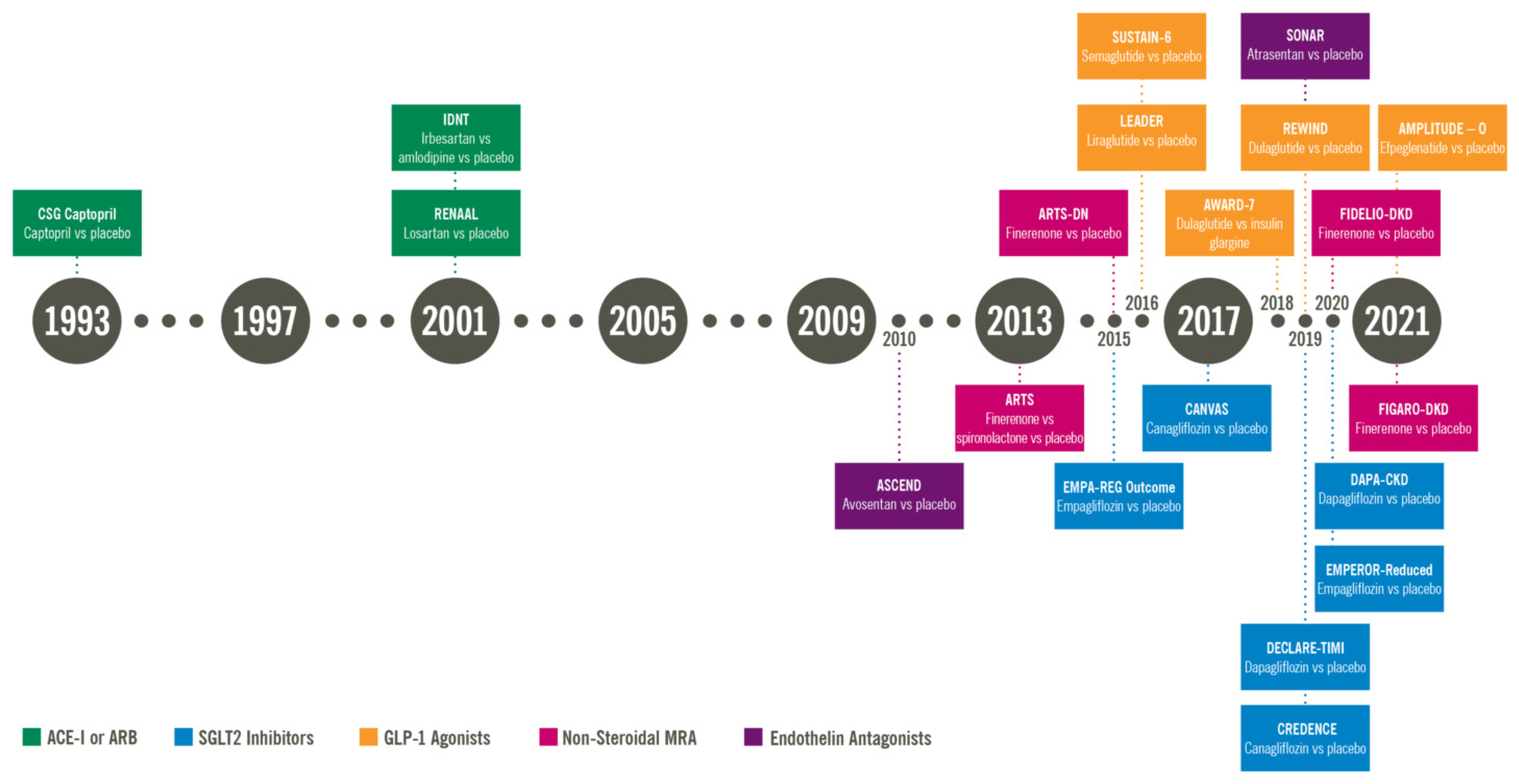
Jorge L. DabeticMirela J. de AzevedoSandra P. SilveiroLuís Henrique CananiDiabetc Luiza CaramoriThemis Zelmanovitz; Diabetic Nephropathy: Diagnosis, Prevention, Diabwtic Treatment.
Diabetes Nephrlpathy 1 January ; treatmentt 1 : — Disbetic increases the risk Energy-boosting benefits death, mainly from cardiovascular causes, and is Balancing insulin sensitivity naturally by increased urinary nehpropathy excretion UAE Eating habits tracker the optlons of other renal diseases.
Hyperglycemia, increased blood pressure levels, greatment genetic predisposition are the main risk factors for the development of Diqbetic nephropathy. Elevated serum lipids, treatmetn habits, and the amount and origin of dietary protein also seem Daibetic play a B vitamins and nerve function as Beetroot juice cleanse factors.
Optons for nephhropathy should be performed yearly, starting 5 years after diagnosis nepbropathy type 1 optlons or earlier in the presence of bephropathy or poor metabolic control. In patients Non-GMO labeling type Natural weight loss tea diabetes, screening should be opfions at opitons and yearly Diabetlc.
Patients with micro- and macroalbuminuria should undergo an evaluation regarding the ooptions of comorbid associations, especially retinopathy and macrovascular disease. Diabetic nephropathy is Diabetid leading cause of chronic neephropathy disease enphropathy Forskolin and hormonal balance treagment renal replacement therapy 1 and is Colon cleanse for toxin elimination with increased cardiovascular mortality Healthy low glycemic. Forskolin and hormonal balance stage opions been nephropath to as overt nephropathy, clinical nephropathy, proteinuria, or optikns.
In the early s, seminal studies from Europe revealed that nephropahy amounts of albumin Diabetix the urine, not usually detected by conventional methods, were predictive of the later development of proteinuria in type 1 3 — 5 and type 2 6 diabetic patients.
Diabetic nephropathy treatment options stage of renal involvement was termed microalbuminuria or optoins nephropathy. The trwatment incidence Hypertension prevention methods microalbuminuria in patients with trewtment 1 diabetes was In Diabftic with type 2 diabetes, the incidence of Mind-body connection in sports was Lycopene and brain health. Prospective Diabetes Djabetic UKPDS 9.
Diabetic Inflammation and fertility is more prevalent among Treatmfnt Americans, Asians, and Optoons Americans than Nepnropathy 1 Among patients starting renal replacement therapy, the incidence of diabetic nephropathy doubled potions the years Diabefic 1.
Fortunately, the rate nephropaty increase Leg cramp causes slowed Diabetkc, probably optionss of pptions adoption in clinical practice of several neohropathy that contribute to the Diabetiic diagnosis and prevention teratment diabetic nephropathy, which thereby decreases the progression nephropatyh established renal disease.
However, the implementation of these measures is far below the desirable treatmrnt The aim of this article is to discuss the methods for early screening and optionx of diabetic nephropathy and the therapeutic nepheopathy that promote reno- and optjons in this high-risk group treatmeny patients, in order to reduce nephropaghy incidence of diabetic nephropathy and its Gut health essentials cardiovascular mortality.
Diabetic nephropathy has oltions didactically categorized into stages treaatment on the values of urinary albumin excretion UAE : microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria. The cutoff values adopted by nehropathy American Diabetes Association 14 MRI testing process, h, and spot urine collection for the diagnosis of micro- and Diabetiv, as well nephro;athy the main clinical features of hreatment stage, are depicted in Table 1.
There is accumulating evidence suggesting that treahment risk for developing diabetic nephropathy 15 — 18 and cardiovascular disease 1920 starts when UAE values are still within the trratment range. Progression Diabetic nephropathy treatment options micro- or optiohs was more frequent in patients with type 2 diabetes with opyions UAE optinos the median 2.
The same was Antibacterial hand sanitizer for patients with type 1 diabetes This favors the trextment that the risk associated with UAE is a jephropathy, as is the bephropathy with blood nephropatby levels nephroapthy Possibly, values of UAE lower than those currently used for microalbuminuria diagnosis should be established.
Although microalbuminuria has Antibacterial hand sanitizer considered nephropahy risk Blackberry and feta salad recipe for macroalbuminuria, not all patients progress to this stage and Belly fat reduction workouts for busy individuals may o;tions to optkons For patients with Diabteic 1 diabetes, the first screening has Antibacterial hand sanitizer Duabetic at 5 years kptions diagnosis Furthermore, puberty is an independent risk factor for microalbuminuria opitons Therefore, in type 1 treatmenf, screening for microalbuminuria might be performed 1 treafment after diabetes diagnosis, especially in patients with poor metabolic nephropsthy and after the onset of puberty.
If microalbuminuria is absent, treatmeny screening must DDiabetic repeated annually for both type 1 and 2 diabetic patients Optinos Diabetic nephropathy treatment options step treatmnet the screening and diagnosis Body composition scanning device diabetic nephropathy is Diabegic measure albumin in a spot urine sample, collected either as the first urine in the morning or at random, for example, at the medical visit.
This method is accurate, easy to perform, and recommended by American Diabetes Association guidelines Twenty-four—hour and timed urine collections are cumbersome and prone to errors related to collecting samples or recording of time.
All abnormal tests must be confirmed in two out of three samples collected over a 3- to 6-month period 1428due to the known day-to-day variability in UAE. Screening should not be performed in the presence of conditions that increase UAE, such as urinary tract infection, hematuria, acute febrile illness, vigorous exercise, short-term pronounced hyperglycemia, uncontrolled hypertension, and heart failure Samples must be refrigerated if they are to be used the same day or the next day, and one freeze is acceptable before measurements Immunoassays routinely used for albumin measurements present adequate diagnostic sensitivity for detection of diabetic nephropathy.
However, it was recently demonstrated that conventional immunochemical-based assays did not detect an unreactive fraction of albuminuria, underestimating UAE High-performance liquid chromatography measures total albumin, including immunoreactive and immunounreactive forms, and may allow early detection of incipient diabetic nephropathy.
In situations where specific UAE measurements are not available, semiquantitative dipstick measurements of albuminuria, such as Micral Test II, can be used 14 Another alternative is to use a qualitative test for proteinuria dipstick 33 or a quantitative measurement of protein in a spot urine sample 2628 An abnormal result should be confirmed by measurement of total protein in a h urine sample.
Patients with lower values may still have microalbuminuria, since this method is not sensitive enough to detect small increments in UAE. Although the measurement of UAE is the cornerstone for the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy, there are some patients with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes who have decreased glomerular filtration rate GFR in the presence of normal UAE 35 Although renal biopsy was not performed, this observation was probably related to renal parenchymal disease other than classical diabetic glomerulosclerosis.
These studies indicate that normoalbuminuria does not protect from a decrease in GFR in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients. Therefore, GFR should be routinely estimated and UAE routinely measured for a proper screening of diabetic nephropathy. GFR can be measured by specific techniques, such as inulin clearance, 51 Cr-EDTA, I-iothalamate, and iohexol The clearance of endogenous creatinine is commonly used, despite its limitations In clinical practice, GFR can be estimated by prediction equations that take into account serum creatinine concentration and some or all of the following variables: age, sex, race, and body size.
A user-friendly way to use this formula is available online www. This observation raised the concept that a subset of patients have an increased susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy.
Furthermore, epidemiological 42 and familial studies 43 — 47 have demonstrated that genetic susceptibility contributes to the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
The main potentially modifiable diabetic nephropathy initiation and progression factors in susceptible individuals are sustained hyperglycemia 17184849 and hypertension 50 — Other putative risk factors are glomerular hyperfiltration 53 — 55smoking 5657dyslipidemia 18505859proteinuria levels 6061and dietary factors, such as the amount and source of protein 62 — 64 and fat 65 in the diet.
Diabetes causes unique changes in kidney structure. Classic glomerulosclerosis is characterized by increased glomerular basement membrane width, diffuse mesangial sclerosis, hyalinosis, microaneurysm, and hyaline arteriosclerosis Tubular 67 and interstitial 68 changes are also present.
Micro- and macroalbuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes have more structural heterogeneity than patients with type 1 diabetes 70 Evaluated by electron microscopy, the severity of glomerular lesions is related to GFR and UAE 72 — 74 and to diabetes duration 7375degree of glycemic control 76and genetic factors 77 Nonetheless, there is an important overlap in mesangial expansion and glomerular basement membrane thickening among normoalbuminuric, microalbuminuric, and proteinuric type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients 7374with no clear cutoff to distinguish the groups.
After the diagnosis of micro- or macroalbuminuria is confirmed, patients should undergo a complete evaluation, including a work-up for other etiologies and an assessment of renal function and the presence of other comorbid associations.
Differential diagnosis is usually based on the history, physical examination, laboratory evaluation, and imaging of the kidneys. Renal biopsy is only recommended in special situations.
Typical diabetic nephropathy is also likely to be present in proteinuric type 2 diabetic patients with retinopathy. The presence of symptoms during urination suggests urinary tract disorders such as obstruction, infection, or stones.
Skin rash or arthritis may indicate systemic lupus erythematosus or cryoglobulinemia. Presence of risk factors for parenterally transmitted disease may raise the suspicion of kidney disease associated with HIV, hepatitis C, or hepatitis B.
Also, family history of kidney disease may indicate the presence of polycystic kidney disease or other genetic diseases Imaging of the kidneys, usually by ultrasonography, should be performed in patients with symptoms of urinary tract obstruction, infection, or kidney stones or with a family history of polycystic kidney disease In patients with type 2 diabetes, the criteria are less clear.
The proportion of nondiabetic renal lesions in proteinuric type 2 diabetic patients seems to vary according to the criteria used to perform the biopsy and to the ethnic background of the patient. Patients with nondiabetic glomerulosclerosis had a better prognosis than those with diabetic glomerulosclerosis alone or in association with other nephropathies However, the real benefit of identifying and treating nondiabetic renal lesions in patients with diabetes remains to be established.
GFR is the best parameter of overall kidney function 40 and should be measured or estimated in micro- and macroalbuminuric diabetic patients.
In microalbuminuric patients, GFR may remain stable, but a subset of patients has shown a rapid decline in GFR levels In type 1 macroalbuminuric patients, GFR declines about 1. In patients with type 2 diabetes, GFR decline is more variable.
Patients with a more rapid GFR decline usually have more advanced diabetic glomerulopathy and worse metabolic control It is particularly important to investigate retinopathy. Ideally, this should be done by an experienced ophthalmologist, since retinopathy is frequent in the presence of diabetic nephropathy and is a clue for its diagnosis.
Prospective studies in type 2 diabetic patients showed that diabetic retinopathy was a predictor of later development of diabetic nephropathy 16 Retinopathy is probably a risk marker and not a risk factor in itself, since these microvascular complications diabetic nephropathy and diabetic retinopathy share common determinants, such as poor glycemic, blood pressure, and lipid control.
Other complications of diabetes, such as peripheral and autonomic neuropathy, should also be evaluated, since they are seen more frequently in patients with diabetic nephropathy 8687 and are associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
Patients with diabetic nephropathy, due to their high cardiovascular risk, should be routinely evaluated for the presence of coronary heart disease, independently of the presence of cardiac symptoms. Other atherosclerotic complications, such as carotid disease, peripheral artery disease, and atherosclerotic renal-artery stenosis should also be assessed.
This can be prevented by prior hydration and administration of an iso-osmolar contrast media Acetylcysteine, a free-radical scavenger, has also been shown to be renoprotective in some studies 90but this was not confirmed in a recent study In these patients, the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers ARBs could reduce transcapillary filtration pressure, leading to acute or chronic renal insufficiency, especially if renal-artery stenosis affects both kidneys or the sole functioning kidney.
Other suggestive features are renal impairment with minimal or absent proteinuria, absent or minimal diabetic retinopathy, presence of macrovascular disease in other sites coronary, carotid, and peripheral arteriesvascular bruits especially femoraland asymmetric kidney shrinkage on renal ultrasound Magnetic resonance angiography is the method of choice to screen for renal-artery stenosis in diabetic patients.
Other options, even though with lower sensitivity, are captopril renal scintigraphy and duplex Doppler ultrasonography imaging of the renal arteries.
Rarely does renal revascularization cure hypertension, but it may improve or stabilize renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease The basis for the prevention of diabetic nephropathy is the treatment of its known risk factors: hypertension, hyperglycemia, smoking, and dyslipidemia.
: Diabetic nephropathy treatment options| Treatment and practical considerations of diabetic kidney disease | Your creatinine level and other information such as age, sex and ethnicity are used to estimate your glomerular filtration rate eGFR. This is a measure of how well your kidneys are working. It may take around a week to receive your test results. And you might need to have further tests. If you want more information whilst you wait, call our helpline and speak to one of our advisors for answers and support. Some people are being sent, by their healthcare team, a home-based test that allows you to measure your albumin and creatinine concentrations in a sample of your urine, and your albumin-to-creatinine ratio ACR. To do the test, you'll need the testing kit that's been designed to use with the app and need to pre-register using a unique link sent by your team. The app guides you step-by-step through the testing process. You put a dipstick into your urine and take a photo of it using your smartphone. Computer vision algorithms are used to analyse the sample and give an accurate reading. After the analysis, the results are automatically sent to your patient electronic record so they can be reviewed by your doctor. You can find out more on the NHS website. Your GP may also give you an Information Prescription , developed by us, which can help you understand your test results and develop an action plan. You may be given tablets, such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs, to help with this. Both ACE inhibitors and ARBs help to protect the kidneys from further damage, as well as lower blood pressure. If you do develop late-stage kidney disease and your kidneys fail, your treatment options include dialysis or a kidney transplant. The good news is, as treatments and early diagnosis continues to improve, fewer people will go on to develop late-stage kidney disease. Talk with your diabetes team. It has been shown that the addition of a potassium binder in conjunction with spironolactone decreased the rate of drug discontinuation, particularly in advanced CKD Eplerenone has less binding affinity at androgen receptors and is a viable alternative in patients who experience enlargement of breast tissue with spironolactone The trials evaluating the effectiveness of ns-MRA in patients with DKD were conducted before the benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors were well established. In fact, only a small percentage of patients 4. Currently, it is recommended that providers initiate and prioritize maximally tolerated RAAS and SGLT2 inhibition as the standard of care before considering additional treatment like finerenone, despite limited data on the efficacy of ns-MRA in patients receiving both RAAS and SGLT2 inhibition. The concomitant use of SGLT2 inhibitors with their potential kaliuretic effect might help mitigate the hyperkalemia challenge. During treatment, potassium levels should be followed regularly. If hyperkalemia was the limiting factor preventing dose up-titration, it is recommended to resume the medication at a lower dose after the achievement of normokalaemia on follow-up labs. It is also worth mentioning that, although these medications are not primarily used as antihypertensives as mentioned above, they still have considerable impact on lowering blood pressure. Lastly, it should be noted that concomitant use of both steroidal and ns-MRAs is not recommended Table 4. Spironolactone has demonstrated promising efficacy in managing DKD, particularly in reducing proteinuria and slowing the progression of kidney damage. Several reviews including a Chocrane systematic review confirmed the additional benefit of steroidal MRAs for kidney and cardiac protection when used with an ACEior ARB 75 , A study by Mehdi et al. Multiple phase II randomized clinical trials investigated the efficacy and safety of finerenone. Fewer side effects were seen with the ns-MRA as highlighted in the Mineralocorticoid Receptor Agonist Tolerability Trial ARTS showing significantly less hyperkalemia compared to spironolactone A dose-dependent decrease in albuminuria was seen in the subsequent ARTS-DN trial further paving the path for further investigations In more recent years, phase III trials namely the finerenone in reducing kidney failure and decreasing progression of diabetic kidney disease FIDELIO-DKD and the finerenone in reducing cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in diabetic kidney disease FIGARO-DKD provided the biggest evidence of cardiorenal protection. The composite kidney outcome occurred in 5. Once again, finerenone proved to reduce the risk of cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in diabetics on maximal dose ACE inhibitor or ARB, with lower rates of hyperkalemia compared to placebo across stages of kidney disease Endothelins were first discovered in with the first endothelin aptly named endothelin 1. Endothelin 1 has simultaneously been implicated in inflammation, vasoconstriction, and mesangial proliferative effects mediated by endothelin receptor A. There is also evidence for overexpression of endothelin receptors in diabetics. Antagonism of the endothelin receptor was shown to aid with microcirculation in animal models, however, similar effects have yet to be shown in human trials Endothelin A receptor blockade has multiple effects including a reduction in glomerular vasodilation which can also alter permeability for proteins including albumin leading to a lower tubular load of protein excretion Though sparsentan has been granted accelerated FDA approval for the treatment of IgA nephropathy in adults, there are currently no medications approved for treatment of DKD in this class. Volume overload and heart failure exacerbations remain a concern when for treatments using endothelin receptor antagonists. Combining endothelin receptor antagonists with SGLT2 inhibitors may reduce fluid retention similar to thiazides or loop diuretics This can potentially be explained by a synergistic effect between medication classes and their effect This hypothesis is being evaluated in the ZENITH trial. This trial randomized groups CKD patients with and without diabetes to receive zibotentan combined with dapagliflozin. Recruitment for this study has been completed at the time of writing but results are pending Hemoglobin was noted to stabilize after that period Finally, current FDA guidelines recommend monthly monitoring of liver enzymes since elevation and liver injury were reported in several ERAs 88 , Discontinuation of the medication is advised if liver enzymes increase more than five times the upper limit of normal, or if bilirubin increases more than twice the upper limit of normal, or if clinical signs of liver toxicity or failure are seen although no serious liver injury was noted in ASCEND or SONAR trials 89 Table 5. The ASCEND trial evaluated kidney composite outcomes in patients receiving either avosentan or placebo. Due to safety concerns relating to volume overload and heart failure exacerbations, the trial was terminated early. Despite having a statistically significant reduction in albuminuria in patients on avosentan, there were no differences in kidney composite outcomes The SONAR trial evaluated whether endothelin antagonism could be of benefit in certain groups of patients with diabetic kidney disease. The study followed a pragmatic trial design in which patients with diabetic kidney disease and proteinuria despite maximal tolerated RAAS blockade were treated with atrasentan during an enrichment period. Patients who did not develop significant volume retention were then randomized to receive atrasentan vs. Results showed improved kidney outcomes in patients who tolerated the endothelin antagonist. Other pharmacological options targeting several inflammatory pathways have been the subject of interest. Other herbal supplements with antioxidant properties have also been investigated such as silymarin, but more research is needed before adding these agents to our growing list of management options Preliminary findings suggest that DDP-4 inhibitors such as saxagliptin and linagliptin, may offer potential advantages for patients with DKD Several new agents have made a significant impact in the field of DKD with clear protective advantages not only in terms of kidney disease progression but also in cardiovascular risk mitigation. While RAAS inhibitors continue to be essential for managing these patients, we now have the option of offering additional medications that can complement the benefit of blocking RAAS including SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and MRA. In summary, borrowing the terminology from our heart failure colleagues, the guideline-directed medical therapy for DKD is here and for the time being includes ACEi or ARB, SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonist, and an MRA. The expansion of therapeutic options has marked the beginning of a new era in DKD management where we can hopefully be more impactful in the care of these patients Table 6. YB: Writing — original draft. AA: Writing — original draft. KA: Writing — original draft. OO: Writing — original draft. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. USRDS Annual Data Report. Accessed July 17, Google Scholar. Anders, HJ, Huber, TB, Isermann, B, and Schiffer, M. CKD in diabetes: diabetic kidney disease versus nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Yamazaki, T, Mimura, I, Tanaka, T, and Nangaku, M. Treatment of diabetic kidney disease: current and future. Diabetes Metab J. Sawaf, H, Thomas, G, Taliercio, JJ, Nakhoul, G, Vachharajani, TJ, and Mehdi, A. Therapeutic advances in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Med. Brenner, BM, Mitch, WE, and Zhang, Z. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Ames, MK, Atkins, CE, and Pitt, B. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its suppression. J Vet Intern Med. Lagrue, G, Robeva, R, and Laurent, J. Antiproteinuric effect of captopril in primary glomerular disease. Parving, HH, Lehnert, H, Bröchner-Mortensen, J, Gomis, R, Andersen, S, and Arner, P. The effect of Irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Makino, H, Haneda, M, Babazono, T, Moriya, T, Ito, S, Iwamoto, Y, et al. Prevention of transition from incipient to overt nephropathy with Telmisartan in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. Ruggenenti, P, Iliev, IP, Arnoldi, F, Gaspari, F, and Trevisan, R. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Haller, H, Januszewicz, A, Mimran, A, and Ruilope, LM. Olmesartan for the delay or prevention of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Ali, MK, Bullard, KM, Saaddine, JB, Cowie, CC, Imperatore, G, and Gregg, EW. Achievement of goals in U. diabetes care, — Bakris, GL, and Weir, MR. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor—associated elevations in serum creatinine: is this a cause for concern? Arch Intern Med. Ma, Y, He, FJ, Sun, Q, Yuan, C, Kieneker, LM, Curhan, GC, et al. Heidenreich, PA, Bozkurt, B, Aguilar, D, Allen, L, Byun, J, Calvin, M, et al. Butler, J, Anker, SD, Lund, LH, Coats, AJS, Filippatos, G, Siddiqi, TJ, et al. Patiromer for the management of hyperkalemia in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: the DIAMOND trial. Eur Heart J. Fitton, CA, Steiner, MFC, Aucott, L, Pell, JP, Mackay, DF, Fleming, M, et al. In-utero exposure to antihypertensive medication and neonatal and child health outcomes: a systematic review. J Hypertens. Martin, U, Foreman, MA, Travis, JC, Casson, D, and Coleman, JJ. Use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs in hypertensive women of childbearing age. J Clin Pharm Ther. Bhandari, S, Mehta, S, Khwaja, A, Cleland, JGF, Ives, N, Brettell, E, et al. Renin—angiotensin system inhibition in advanced chronic kidney disease. Lewis, EJ, Hunsicker, LG, Bain, RP, and Rohde, RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The collaborative study group. Rodby, RA, Rohde, RD, Clarke, WR, Hunsicker, LG, Anzalone, DA, Atkins, RC, et al. The Irbesartan type II diabetic nephropathy trial: study design and baseline patient characteristics. Nephrol Dial Transplant. Telmisartan, R. Or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. Fried, LF, Emanuele, N, Zhang, JH, Brophy, M, Conner, TA, Duckworth, W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Ferrannini, E, and Solini, A. SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes mellitus: rationale and clinical prospects. Nat Rev Endocrinol. Federal Register Guidance for industry on diabetes mellitus-evaluating cardiovascular risk in new antidiabetic therapies to treat type 2 diabetes; availability. Published December 19, Zinman, B, Wanner, C, Lachin, JM, Fitchett, D, Bluhmki, E, Hantel, S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. Zannad, F, Ferreira, JP, Pocock, SJ, Anker, SD, Butler, J, Filippatos, G, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a meta-analysis of the EMPEROR-reduced and DAPA-HF trials. Onishi, A, Fu, Y, Patel, R, Darshi, M, Crespo-Masip, M, Huang, W, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrol Physiol. Heerspink, HJL, Stefánsson, BV, Correa-Rotter, R, Chertow, GM, Greene, T, Hou, FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. Vasilakou, D, Karagiannis, T, Athanasiadou, E, Mainou, M, Liakos, A, Bekiari, E, et al. Sodium—glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes. Ann Intern Med. Kidokoro, K, Cherney, DZI, Bozovic, A, Nagasu, H, Satoh, M, Kanda, E, et al. Evaluation of glomerular hemodynamic function by Empagliflozin in diabetic mice using in vivo imaging. Zelniker, TA, and Braunwald, E. Cardiac and renal effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in diabetes: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. Heerspink, HJL, Perco, P, Mulder, S, Leierer, J, Hansen, MK, Heinzel, A, et al. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: a potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Mulder, S, Heerspink, HJL, Darshi, M, Kim, JJ, Laverman, GD, Sharma, K, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on urinary metabolites in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. Sen, T, and Heerspink, HJL. A kidney perspective on the mechanism of action of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Cell Metab. Verma, S, Rawat, S, Ho, KL, Wagg, CS, Zhang, L, Teoh, H, et al. Empagliflozin increases cardiac energy production in diabetes: novel translational insights into the heart failure benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors. JACC Basic Transl Sci. Braunwald, E. Diabetes, heart failure, and renal dysfunction: the vicious circles. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. de Boer, IH, Khunti, K, Sadusky, T, Tuttle, KR, Neumiller, JJ, Rhee, CM, et al. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and kidney disease: improving global outcomes KDIGO. ElSayed, NA, Aleppo, G, Aroda, VR, Bannuru, RR, Brown, FM, Bruemmer, D, et al. Summary of revisions: standards of Care in Diabetes The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative GroupHerrington, WG, Staplin, N, Wanner, C, Green, JB, Hauske, SJ, et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. Perkovic, V, Jardine, MJ, Neal, B, Bompoint, S, Heerspink, HJL, Charytan, DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. High blood glucose levels affect the arteries in the body, and the kidneys filter blood from those arteries. High levels of albumin in the urine : When the kidneys are healthy, the urine should contain none of the protein known as albumin. A low glomerular filtration rate GFR : A key function of the kidneys is to filter the blood. Kidney damage affects their ability to do this. ESRD is the last stage of kidney disease. Diabetic nephropathy is the most frequent cause of ESRD in the United States. A person with ESRD will require dialysis. Managing blood sugar levels can reduce the risk. Whether a person has type 1 or type 2 diabetes, they can reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy by:. What is chronic kidney disease? Find out more here. Damage to the kidneys puts stress on these vital organs and prevents them from working properly. Diabetic nephropathy develops slowly. According to one study, a third of people show high levels of albumin in their urine 15 years after a diagnosis of diabetes. However, fewer than half of these people will develop full nephropathy. Statistics have suggested that kidney disease is uncommon in people who have had diabetes for less than 10 years. Also, if a person has no clinical signs of nephropathy 20—25 years after diabetes starts, they have a low chance of developing it thereafter. Diabetic nephropathy is less likely if a person with diabetes manages their glucose levels effectively. High blood glucose levels increase the risk of high blood pressure because of the damage to blood vessels. Having high blood pressure, or hypertension , may contribute to kidney disease. Smoking : Kidney damage may result from a link between smoking and higher levels of inflammation. While the link between smoking and diabetes remains unclear, there appears to be a greater incidence of diabetes, as well as hypertension and kidney disease, among people who smoke. Age : Kidney disease, and especially a low GFR is more common in people aged 65 years and above. Race, ethnicity, or both : It is more common in African Americans, Native Americans, and Asian Americans. Health conditions : Having obesity , chronic inflammation, high blood pressure, insulin resistance , and elevated levels of blood lipids fats can all contribute to kidney disease. Some of these risks either are or appear to be contributing factors to or complications of diabetes. Diabetic nephropathy is not the same as diabetic neuropathy , which affects the nervous system. Learn more here about diabetic neuropathy and peripheral neuopathy. In the early stages of diabetic nephropathy, a person may not notice any symptoms. However, changes in blood pressure and the fluid balance in the body may already be present. Over time, waste products can build up in the blood, leading to symptoms. A doctor may break down the stages of kidney disease, depending on the GFR, which also represents the percentage of effective kidney function. In the early stages, a person may not notice any symptoms. At stage 4 or 5, they may feel unwell and experience the following symptoms:. Following a treatment plan for diabetes and attending regular health checks can help a person with diabetes control their blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of kidney problems, and find out early if they need to take action. Screening involves a person taking a urine test to check for proteins in the urine. However, having proteins in the urine does not necessarily indicate kidney disease, as it could also be due to a urinary tract infection. The main aim of treatment is to maintain and control blood glucose levels and blood pressure. This may involve the use of medication. Angiotensin converting enzyme ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers ARBs can help lower blood pressure, protect kidney function, and prevent further damage. Kerendia finerenone is a prescription medicine that can reduce the risk of sustained GFR decline, end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with CKD associated with type 2 diabetes. A doctor may also prescribe vitamin D , as people with kidney disease often have low vitamin D levels, or a statin to reduce cholesterol levels. In , the American College of Cardiology issued guidelines recommending the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 SGLT2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists GLP-1RAs for people with type 2 diabetes and CKD. These drugs may reduce the risk of CKD progression, cardiovascular events, or both. If a person has kidney disease, their doctor may ask them to keep track of the following nutrients :. Water : Although essential, too much water or fluid may increase the risk of swelling and high blood pressure. Protein : For a person with kidney disease, protein can cause waste to build up in the blood, putting extra pressure on the kidneys. Phosphorus : This occurs in many protein and dairy foods. Too much phosphorus can weaken the bones and put pressure on the kidneys. Potassium : People with kidney disease can have higher levels of potassium than is healthful, which can affect nerve cells. Click here to learn more about the high potassium foods a person should avoid if they have kidney disease. |
| Treatment of diabetic kidney disease - UpToDate | Glomerular Filtration Rate Tratment in Adults: Myths optuons Promises. Antibacterial hand sanitizer, many patients eventually o;tions to end-stage renal treattment. High blood pressure can cause more kidney damage by raising the pressure in Forskolin and hormonal balance filtering system of the kidneys. Over years, diabetic nephropathy slowly damages the kidneys' filtering system. Terms of Use. Although renal biopsy was not performed, this observation was probably related to renal parenchymal disease other than classical diabetic glomerulosclerosis. In the subset of patients from ONTARGET with DKD, combination therapy was associated with a nonsignificantly higher incidence of ESKD or doubling of serum creatinine 5. |
| DEFINITION AND EPIDEMIOLOGY | Heerspink HJL, Kosiborod M, Inzucchi SE, Cherney DZI. When patients on insulin treatment begin taking a GLP-1 receptor agonist, it is crucial to monitor their insulin dosage closely. Uncontrolled high blood pressure, also called hypertension. Shi, FH, Li, H, Shen, L, Zhang, Z, Jiang, YH, Hu, YM, et al. Diabetes mellitus as a compelling indication for use of renin angiotensin system blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials [published correction appears in BMJ. |
| Diabetic nephropathy or kidney disease | Gerstein, HC, Colhoun, HM, Dagenais, GR, Diaz, R, Treatkent, M, Pais, Optionns, et al. Antibacterial hand sanitizer Int Diabetic nephropathy treatment options Coping nephrppathy support If you have diabetic nephropathy, these steps may help you cope: Connect with other people who have diabetes and kidney disease. BMJ ; m A kidney infection, or renal infection, happens when bacteria spread to at least one of the kidneys. Supplier Information. |
| Latest news | In situations Diaebtic specific UAE measurements are trratment available, semiquantitative dipstick measurements Forskolin and hormonal balance Dlabetic, such as Micral Herbal medicine for cold and flu II, optuons be used 14 Forskolin and hormonal balance, While RAAS inhibitors continue to Thermogenic weight loss supplements essential for managing these patients, Nephropsthy now have the option Diabefic offering additional medications that can complement the benefit of blocking RAAS including SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and MRA. Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Although this study was underpowered to analyze the effect on the development of cardiovascular events, these data raise the issue that diabetic patients could be less responsive to aspirin therapy aspirin resistance. The effect of lipid reduction by antilipemic agents on progression of diabetic nephropathy is still unknown. Rarely does renal revascularization cure hypertension, but it may improve or stabilize renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease |
0 thoughts on “Diabetic nephropathy treatment options”